BCR基因
| Bcr-Abl肿瘤蛋白齐聚反应结构域 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Bcr-Abl肿瘤蛋白齐聚反应结构域机制 | |||||||||
| 鑑定 | |||||||||
| 標誌 | Bcr-Abl_Oligo | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF09036(旧版) | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR015123 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
BCR基因(英語:BCR gene),或称断裂点簇集区(英語:breakpoint cluster region),是bcr-abl融合基因的组成部分之一,其与费城染色体的形成机制有关。
病理学[编辑]
一个22号染色体与9号染色体的相互易位作用而产生的费城染色体,它通常在慢性粒细胞性白血病患者体内发现。22号染色体的断裂点就在BCR基因中。这个易位作用产生了一种基于BCR基因和ABL基因进行编码而成的融合蛋白,其基因就位于9号染色体的断裂点上。尽管bcr-abl融合基因已经被广泛研究,但普通的BCR基因机制仍然不明。其蛋白产生一些丝氨酸或苏氨酸蛋白激酶活动,并是一类p21rac酶活化蛋白。[1]
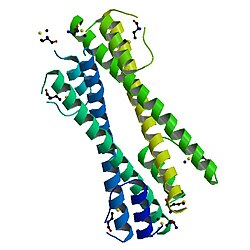
Bcr-Abl肿瘤蛋白齐聚反应域(Bcr-Abl oncoprotein oligomerisation domain)位于BCR的氨基端(N-terminus),其为BCR-ABL融合蛋白的齐聚反应必不可少的基因之一。Bcr-Abl肿瘤蛋白齐聚反应域包含一个短状氨基端α螺旋(alpha-1),一个灵活的转角(Turn)和一个长状的C型α螺旋(alpha-2)。其螺旋体转角使得两个α螺旋能够保持平行定向。这一单体分子的蛋白质结构域,通过一个反平行的卷轴螺旋(coiled coil)形成为一个蛋白质二聚体(protein dimer)。其中两个α螺旋彼此之间发生了结构域对换,其中一个α-1螺旋氨基端进行交换,并挤压另个单体上的α-2螺旋(alpha-2)。两个蛋白质二聚体随后形成一个四聚体(tetramer)[2]。
相互机制[编辑]
现今已经发现BCR基因与以下基因发生蛋白-蛋白交互作用(Protein-protein interaction):PTPN6[3]、XPB[4]、猫肉瘤癌基因[5][6]、GRB10[7]、CD117[8]、Grb2[6][7][9][10][11][12]、MLLT4[13]、Abl基因[11][14][15]、HCK[16][17]、SOS1[6][11]、PIK3CG[7][18][19]、CRKL[7][10][20][21]和桩蛋白[18][22]。
参考[编辑]
- ^ Entrez Gene: BCR breakpoint cluster region.
- ^ Zhao X, Ghaffari S, Lodish H, Malashkevich VN, Kim PS. Structure of the Bcr-Abl oncoprotein oligomerization domain. Nat. Struct. Biol. February 2002, 9 (2): 117–20. PMID 11780146. doi:10.1038/nsb747.
- ^ Liedtke, M; Pandey P, Kumar S, Kharbanda S, Kufe D. Regulation of Bcr-Abl-induced SAP kinase activity and transformation by the SHPTP1 protein tyrosine phosphatase. Oncogene (ENGLAND). Oct 1998, 17 (15): 1889–92. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 9788431. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202117.
- ^ Takeda, N; Shibuya M, Maru Y. The BCR-ABL oncoprotein potentially interacts with the xeroderma pigmentosum group B protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (UNITED STATES). Jan 1999, 96 (1): 203–7. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 15117
 . PMID 9874796. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.1.203.
. PMID 9874796. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.1.203.
- ^ Lionberger, J M; Smithgall T E. The c-Fes protein-tyrosine kinase suppresses cytokine-independent outgrowth of myeloid leukemia cells induced by Bcr-Abl. Cancer Res. (UNITED STATES). Feb 2000, 60 (4): 1097–103. ISSN 0008-5472. PMID 10706130.
- ^ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Maru, Y; Peters K L, Afar D E, Shibuya M, Witte O N, Smithgall T E. Tyrosine phosphorylation of BCR by FPS/FES protein-tyrosine kinases induces association of BCR with GRB-2/SOS. Mol. Cell. Biol. (UNITED STATES). Feb 1995, 15 (2): 835–42. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 231961
 . PMID 7529874.
. PMID 7529874.
- ^ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Bai, R Y; Jahn T, Schrem S, Munzert G, Weidner K M, Wang J Y, Duyster J. The SH2-containing adapter protein GRB10 interacts with BCR-ABL. Oncogene (ENGLAND). Aug 1998, 17 (8): 941–8. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 9747873. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202024.
- ^ Hallek, M; Danhauser-Riedl S, Herbst R, Warmuth M, Winkler A, Kolb H J, Druker B, Griffin J D, Emmerich B, Ullrich A. Interaction of the receptor tyrosine kinase p145c-kit with the p210bcr/abl kinase in myeloid cells. Br. J. Haematol. (ENGLAND). Jul 1996, 94 (1): 5–16. ISSN 0007-1048. PMID 8757502. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.1996.6102053.x.
- ^ Million, R P; Van Etten R A. The Grb2 binding site is required for the induction of chronic myeloid leukemia-like disease in mice by the Bcr/Abl tyrosine kinase. Blood (UNITED STATES). Jul 2000, 96 (2): 664–70. ISSN 0006-4971. PMID 10887132.
- ^ 10.0 10.1 Million, Ryan P; Harakawa Nari, Roumiantsev Sergei, Varticovski Lyuba, Van Etten Richard A. A direct binding site for Grb2 contributes to transformation and leukemogenesis by the Tel-Abl (ETV6-Abl) tyrosine kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. (United States). Jun 2004, 24 (11): 4685–95. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 416425
 . PMID 15143164. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.11.4685-4695.2004.
. PMID 15143164. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.11.4685-4695.2004.
- ^ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Puil, L; Liu J, Gish G, Mbamalu G, Bowtell D, Pelicci P G, Arlinghaus R, Pawson T. Bcr-Abl oncoproteins bind directly to activators of the Ras signalling pathway. EMBO J. (ENGLAND). Feb 1994, 13 (4): 764–73. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 394874
 . PMID 8112292.
. PMID 8112292.
- ^ Ma, G; Lu D, Wu Y, Liu J, Arlinghaus R B. Bcr phosphorylated on tyrosine 177 binds Grb2. Oncogene (ENGLAND). May 1997, 14 (19): 2367–72. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 9178913. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201053.
- ^ Radziwill, G; Erdmann R A, Margelisch U, Moelling K. The Bcr kinase downregulates Ras signaling by phosphorylating AF-6 and binding to its PDZ domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. (United States). Jul 2003, 23 (13): 4663–72. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 164848
 . PMID 12808105. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.13.4663-4672.2003.
. PMID 12808105. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.13.4663-4672.2003.
- ^ Ling, Xiaoyang; Ma Guozhen, Sun Tong, Liu Jiaxin, Arlinghaus Ralph B. Bcr and Abl interaction: oncogenic activation of c-Abl by sequestering Bcr. Cancer Res. (United States). Jan 2003, 63 (2): 298–303. ISSN 0008-5472. PMID 12543778.
- ^ Pendergast, A M; Muller A J, Havlik M H, Maru Y, Witte O N. BCR sequences essential for transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene bind to the ABL SH2 regulatory domain in a non-phosphotyrosine-dependent manner. Cell (UNITED STATES). Jul 1991, 66 (1): 161–71. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 1712671. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(91)90148-R.
- ^ Stanglmaier, M; Warmuth M, Kleinlein I, Reis S, Hallek M. The interaction of the Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase with the Src kinase Hck is mediated by multiple binding domains. Leukemia (England). Feb 2003, 17 (2): 283–9. ISSN 0887-6924. PMID 12592324. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2402778.
- ^ Lionberger, J M; Wilson M B, Smithgall T E. Transformation of myeloid leukemia cells to cytokine independence by Bcr-Abl is suppressed by kinase-defective Hck. J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES). Jun 2000, 275 (24): 18581–5. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10849448. doi:10.1074/jbc.C000126200.
- ^ 18.0 18.1 Salgia, R; Sattler M, Pisick E, Li J L, Griffin J D. p210BCR/ABL induces formation of complexes containing focal adhesion proteins and the protooncogene product p120c-Cbl. Exp. Hematol. (UNITED STATES). Feb 1996, 24 (2): 310–3. ISSN 0301-472X. PMID 8641358.
- ^ Skorski, T; Kanakaraj P, Nieborowska-Skorska M, Ratajczak M Z, Wen S C, Zon G, Gewirtz A M, Perussia B, Calabretta B. Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase activity is regulated by BCR/ABL and is required for the growth of Philadelphia chromosome-positive cells. Blood (UNITED STATES). Jul 1995, 86 (2): 726–36. ISSN 0006-4971. PMID 7606002.
- ^ Heaney, C; Kolibaba K, Bhat A, Oda T, Ohno S, Fanning S, Druker B J. Direct binding of CRKL to BCR-ABL is not required for BCR-ABL transformation. Blood (UNITED STATES). Jan 1997, 89 (1): 297–306. ISSN 0006-4971. PMID 8978305.
- ^ Kolibaba, K S; Bhat A, Heaney C, Oda T, Druker B J. CRKL binding to BCR-ABL and BCR-ABL transformation. Leuk. Lymphoma (SWITZERLAND). Mar 1999, 33 (1-2): 119–26. ISSN 1042-8194. PMID 10194128. doi:10.3109/10428199909093732.
- ^ Salgia, R; Li J L, Lo S H, Brunkhorst B, Kansas G S, Sobhany E S, Sun Y, Pisick E, Hallek M, Ernst T. Molecular cloning of human paxillin, a focal adhesion protein phosphorylated by P210BCR/ABL. J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES). Mar 1995, 270 (10): 5039–47. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 7534286. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.10.5039.
外部链接[编辑]
延伸阅读[编辑]
- Wang L, Seale J, Woodcock BE, Clark RE. e19a2-positive chronic myeloid leukaemia with BCR exon e16-deleted transcripts.. Leukemia. 2002, 16 (8): 1562–3. PMID 12145699. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2402600.