摘要
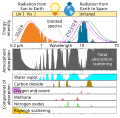
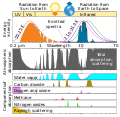
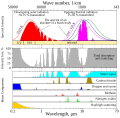
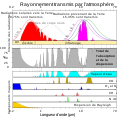
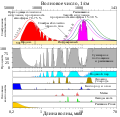
This figure shows the absorption bands in the Earth's atmosphere (middle panel) and the effect that this has on both solar radiation and upgoing thermal radiation (top panel). Individual absorption spectrum for major greenhouse gases plus Rayleigh scattering are shown in the lower panel.
Both the Earth and the Sun emit electromagnetic radiation (e.g. light) that closely follows a blackbody spectrum, and which can be predicted based solely on their respective temperatures. For the Sun, these emissions peak in the visible region and correspond to a temperature of ~5500 K. Emissions from the Earth vary following variations in temperature across different locations and altitudes, but always peak in the infrared.
The position and number of absorption bands are determined by the chemical properties of the gases present. In the present atmosphere, water vapor is the most significant of these greenhouse gases, followed by carbon dioxide and various other minor greenhouse gases. In addition, Rayleigh scattering, the physical process that makes the sky blue, also disperses some incoming sunlight. Collectively these processes capture and redistribute 25-30% of the energy in direct sunlight passing through the atmosphere. By contrast, the greenhouse gases capture 70-85% of the energy in upgoing thermal radiation emitted from the Earth surface.
Data sources and notes
The data used for these figures is based primarily on Spectral Calculator of GATS, Inc. archive copy at the Wayback Machine which implements the LINEPAK system of calculating absorption spectra (Gordley et al. 1994) from the HITRAN2004 (Rothman et al. 2004) spectroscopic database. To aid presentation, the absorption spectra were smoothed. Features with a bandwidth narrower than 0.5% of their wavelength may be obscured.
Calculations were done on the assumption of direct vertical transmission through an atmosphere with gas concentrations representative of modern day averages. In particular, absorption would be greater for radiation traveling obliquely through the atmosphere as it would encounter more gas.
The total scattering and absorption curve includes only the components indicated in the lower panel. These represent the vast majority of absorption contributing to the greenhouse effect and follow the treatment of Peixoto and Oort (1992), but other minor species such as carbon monoxide, nitric oxide and chloroflourocarbons (CFCs) have been omitted. Also omitted was scattering due to aerosols and other sources besides Rayleigh scattering.
The peaks in the blackbody spectra were adjusted to have the same height for ease in presentation.
许可协议
我,本作品著作权人,特此采用以下许可协议发表本作品:
 
|
本作品采用知识共享CC0 1.0 通用公有领域贡献许可协议授权。
|
| 采用本宣告发表本作品的人,已在法律允许的范围内,通过在全世界放弃其对本作品拥有的著作权法规定的所有权利(包括所有相关权利),将本作品贡献至公有领域。您可以复制、修改、传播和表演本作品,将其用于商业目的,无需要求授权。
http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.enCC0Creative Commons Zero, Public Domain Dedicationfalsefalse
|
References
- Gordley, Larry L., Benjamin T. Marshall, Allen D. Chu (1994). "LINEPAK: Algorithms for modeling spectral transmittance and radiance". Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer 52 (5): 563-580.
- L.S. Rothman, D. Jacquemart, A. Barbe, D. Chris Benner, M. Birk, L.R. Brown, M.R. Carleer, C. Chackerian Jr., K. Chance, L.H. Coudert, V. Dana, V.M. Devi, J.-M. Flaud, R.R. Gamache, A. Goldman, J.-M. Hartmann, K.W. Jucks, A.G. Maki, J.-Y. Mandin, S.T. Massie, J. Orphal, A. Perrin, C.P. Rinsland, M.A.H. Smith, J. Tennyson, R.N. Tolchenov, R.A. Toth, J. Vander Auwera, P. Varanasi, G. Wagner (2004). "The HITRAN 2004 molecular spectroscopic database". Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer 96: 139-204.
- Peixoto, Jose P. and Abraham H. Oort (1992年) 《 Physics of Climate》、Springer 国际标准书号: 0883187124.
Other versions
[编辑]
.svg:
-
英语 .svg
-
法语 .svg
-
马其顿语 .svg
-
俄语 .svg
-
韩语 .svg
.png:
-
英语 .png
-
法语 .png
-
波兰语 .png
-
日语 .png
-
阿拉伯语 .png