使用者:Heihaheihaha/尺神經
| 尺神經(Ulnar nerve) | |
|---|---|
 點擊放大圖片-尺神經見於左下角 | |
 左上肢的神經(尺神經見於前臂,圖中左側) | |
| 基本資訊 | |
| 來源 | C8, T1 (內側束的分支) |
| 支配 | 尺側腕屈肌 指深屈肌尺側半 小魚際肌 第三和第四蚓狀肌 [[[小指短屈肌(手)|小指屈肌]] ]骨間背側肌 骨間掌側肌 拇內收肌 等 |
| 標識字符 | |
| 拉丁文 | nervus ulnaris |
| 《神經解剖學術語》 [在維基數據上編輯] | |
在人體解剖學中,尺神經行走於尺骨旁的一根神經,肘關節的尺側副韌帶與尺神經有關。該神經是人體最大的不受骨和肌肉保護的神經,其損傷較為常見。[1]該神經直接連接到小拇指、無名指的尺側半(與小拇指相鄰的半側),支配這些神經的掌側、指尖的前部和後部,可能遠至甲床。
在彎曲手臂的情況下撞擊肱骨內側髁可能刺激該神經並引起類似電擊的短暫疼痛。[2]
走行
[編輯]手臂
[編輯]尺神經起自脊神經C8-T1的神經根(有時也包含來自外側索的C7的纖維)。[3][4]然後成為臂叢的內側束的一部分,沿著肱動脈內側下降至肱二頭肌肌腱附著點(肱骨內側邊中間5厘米處)。之後,它穿過內側肌間隔膜進入臂後區內側,伴尺神經旁血管在肱骨的後內側走行,由尺神經溝經過內上髁穿過橈側腕屈肌起點至前臂內側份,可用手觸及。[5]
前臂
[編輯]The ulnar nerve is not a content of the cubital fossa. It enters the anterior (flexor) compartment of the forearm between the two heads of flexor carpi ulnaris,[4] and lies along the lateral border of the flexor carpi ulnaris.[4] The ulnar nerve runs between the flexor digitorum superficialis (laterally) and flexor digitorum profundus medially. Near the wrist, it courses superficial to the flexor retinaculum of hand, but covered by volar carpal ligament to enter the hand.[5]
In the forearm it gives off the following branches:[6]:700
- 肌支——供應一塊半肌肉(尺側腕屈肌和趾深屈肌的內側半)[5]
- 掌支——起自前臂中部並供應小魚際隆起處的皮膚[5]
- 背支——起自距腕關節上方7.5厘米處,向後繞行,供應尺側一個半手指的近端皮膚及手指間相鄰區域的皮膚。[4][5]
- 關節支——至肘關節。[5]
手
[編輯]
Ulnar nerve enters the palm of the hand via the Guyon's canal, superficial to the flexor retinaculum and lateral to the pisiform bone.[5]
在前臂,尺神經發出以下分支:[6]
- Superficial branch of ulnar nerve - supplies the palmaris brevis and gives digital branches to the medial one and a half fingers.[5]
- Deep branch of ulnar nerve - It accompanies the deep branch of the ulnar artery. It passes backwards between the abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi, and opponens digiti minimi, supplying all the three muscles, and lying on the hook of hamate bone. It then turns laterally, supplying the 3rd and 4th lumbricals and all the palmar interossei muscles and dorsal interossei of the hand. It terminates by supplying the adductor pollicis.[5]
- Articular branches to the wrist.[5]
功能
[編輯]尺神經也被稱為「音樂家的神經」,因為它控制著手指的精細運動。[5]
感覺
[編輯]
尺神經還為第五指和第四指的內側半部分及相應的手掌部分提供感覺神經支配:
- 掌支——為前部皮膚和指甲提供皮膚神經支配。
- 背側皮支——為手背內側和內側1.5個手指的背側提供皮神經支配。
運動
[編輯]尺神經及其分支支配前臂和手部的以下肌肉:
- 當尺神經經過鷹嘴和肱骨內上髁之間時,發出一條通向肘關節的關節支。
- 在前臂,尺神經的肌支通過:
- 在手部,尺神經深支通過:[3]
- 小魚際肌群
- The third and fourth lumbrical muscles
- Dorsal interossei
- Palmar interossei
- Adductor Pollicis
- Flexor pollicis brevis (deep head)
- In the hand, via the superficial branch of ulnar nerve:
臨床意義
[編輯]尺神經可能在從臂叢的近端起點到手部的遠端分支之間的任何位置受到損傷。它是肘部周圍最常受損的神經。[7][8] 尺神經通常因局部創傷或物理壓迫(「神經受壓」)而受損。尺神經在不同水平的損傷會導致特定的運動和感覺功能缺失。
在肘部
[編輯]- Common mechanisms of injury: Cubital tunnel syndrome, fracture of the medial epicondyle of the humerus (causing direct ulnar nerve injury), fracture of the lateral epicondyle of the humerus (causing cubitus valgus with tardy ulnar nerve palsy), Driver's Elbow[9]
- 運動功能損傷:
- Weakness in flexion of the hand at the wrist, loss of flexion of ulnar half of digits, or the 4th and 5th digits, loss of ability to cross the digits of the hand. (Note: Motor deficit is absent or very minor in cubital tunnel syndrome as the ulnar nerve is compressed in the cubital tunnel, rather than transected.)
- Presence of a claw hand deformity when the hand is at rest, due to hyperextension of the 4th and 5th digits at the metacarpophalangeal joints, and flexion at the interphalangeal joints.
- Weakness of adduction of the thumb, which may be assessed by the presence of Froment's sign.
- Sensory deficit: Loss of sensation or paresthesiae in ulnar half of the palm and dorsum of hand, and the medial 1½ digits on both palmar and dorsal aspects of the hand
在腕部
[編輯]- 常見機制:穿透性傷口、Guyon管囊腫(及其他病變)[10]
- 運動功能損傷:
- 尺側半部分手指(第4和第5指)屈曲能力喪失,手指交叉功能喪失。
- 感覺功能缺失:手掌尺側半部分以及掌面內側1½個手指的感覺喪失或感覺異常,背側無影響。手背未受影響是因為尺神經的後皮支在前臂較高處分支,並未到達手腕。
在嚴重情況下,可能需要通過手術重新定位或「釋放」神經,以防止進一步損傷。
其它圖像
[編輯]-
示脊神經臂叢
-
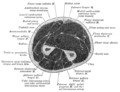
上臂中部橫截面
-
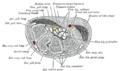
前臂中部橫截面
-
橈骨和尺骨遠端橫截面
-
手腕、手指橫截面
-
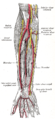
尺動脈和橈動脈
-
右臂叢神經(鎖骨下部分)位於腋窩;下面和前面觀
-
右上肢正面觀,示骨骼、動脈和神經的表面投影
-
右上肢後面觀,示骨骼、神經的體表投影
-
尺神經
-
尺神經標記於圖中
-
尺神經
-
尺神經
-
尺神經
-
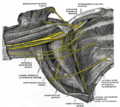
臂叢深層解剖前外側觀
另見
[編輯]本條目使用了部分解剖術語。
參考文獻
[編輯]- ^ N, Catena; Mg, Calevo; D, Fracassetti; D, Moharamzadeh; C, Origo; M, De Pellegrin. Risk of Ulnar Nerve Injury During Cross-Pinning in Supine and Prone Position for Supracondylar Humeral Fractures in Children: A Recent Literature Review. European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology: Orthopedie Traumatologie. 2019, 29 (6): 1169–1175 [2020-05-22]. PMID 31037406. S2CID 139108013. doi:10.1007/s00590-019-02444-0 (英語).
- ^ Why Does Hitting Your Funny Bone Hurt So Much?. www.houstonmethodist.org. [2024-04-02] (英語).
- ^ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Bonfiglioli, Roberta; Mattioli, Stefano; Violante, Francesco S., Lotti, Marcello; Bleecker, Margit L. , 編, Chapter 22 - Occupational mononeuropathies in industry, Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Occupational Neurology (Elsevier), 2015-01-01, 131: 411–426 [2020-10-25], ISBN 9780444626271, PMID 26563800, doi:10.1016/b978-0-444-62627-1.00021-4 (英語)
- ^ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Rea, Paul, Rea, Paul , 編, Chapter 3 - Neck, Essential Clinically Applied Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System in the Head and Neck (Academic Press), 2016-01-01: 131–183 [2020-10-25], ISBN 978-0-12-803633-4, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-803633-4.00003-x (英語)
- ^ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 Krishna, Garg. 8 - Arm. BD Chaurasia's Human Anatomy (Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical) Volume 1 - Upper limb and thorax Fifth. India: CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd. 2010: 91,110,111. ISBN 978-81-239-1863-1.
- ^ 6.0 6.1 Ellis, Harold; Susan Standring; Gray, Henry David. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone. 2005: 726. ISBN 0-443-07168-3.
- ^ Selby, Ronald; Safran, Marc; O'brien, Stephen. Practical Orthopaedic Sports Medicine & Arthroscopy, 1st edition: Elbow Injuries. msdlatinamerica.com. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2007 [2014-09-30]. (原始內容存檔於2014-10-06).
- ^ Minieka, Michael; Nishida, Takashi, Benzon, Honorio T.; Raja, Srinivasa N.; Molloy, Robert E.; Liu, Spencer S. , 編, Chapter 54 - Entrapment Neuropathies, Essentials of Pain Medicine and Regional Anesthesia (Second Edition) (Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone), 2005-01-01: 426–432 [2020-10-25], ISBN 978-0-443-06651-1, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-06651-1.50058-7 (英語)
- ^ Waldman, Steven D., Waldman, Steven D. , 編, Chapter 44 - Driver's Elbow, Atlas of Uncommon Pain Syndromes (Third Edition) (Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders), 2014-01-01: 126–129 [2020-10-25], ISBN 978-1-4557-0999-1, doi:10.1016/b978-1-4557-0999-1.00044-7 (英語)
- ^ Fuller, Geraint; Manford, Mark, Fuller, Geraint; Manford, Mark , 編, Common peripheral nerve lesions, Neurology (Third Edition) (Churchill Livingstone), 2010-01-01: 106–107 [2020-10-25], ISBN 978-0-7020-3224-0, S2CID 88836902, doi:10.1016/b978-0-7020-3224-0.00054-9 (英語)
外部連結
[編輯]- Cubital Tunnel Support Forums 網際網路檔案館的存檔,存檔日期2022-10-04.
- Anatomy figure: 05:03-15 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The major subdivisions and terminal nerves of the brachial plexus."
- Anatomy figure: 07:04-04 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Anterior view of the nerves, vessels, and superficial tendons that cross the left wrist."
- Anatomy figure: 08:03-07 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Transverse section through the carpal tunnel and distal row of the carpal bones."
- 杜克大學醫學中心整形外科計畫中的Ulnar nerve
- 堪薩斯大學醫學中心的手部人體工學
- 圖譜:hand_plexus at the University of Michigan Health System - "Axilla, dissection, anterior view"
- Overview at neuro.wustl.edu
- Shoulder Ulnar Nerve Entrapment
- 網際網路檔案館的存檔,存檔日期2006-09-06.