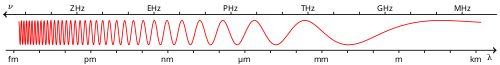
兆赫輻射



兆赫輻射(英語:Terahertz radiation),又稱THz波或兆赫茲,包含了頻率為0.3到3 THz的電磁波。此頻段屬遠紅外光,高於微波波段的頻率,[1]對應的波長範圍從1mm到0.1mm(或100μm),所以也叫作「亞毫米波段」(submillimeter waves)。
目前,國際上對兆赫茲輻射已達成如下共識,即兆赫茲是一種新的、有很多獨特優點的輻射源;兆赫茲技術是一個非常重要的交叉前沿領域,給技術創新、國民經濟發展和國家安全提供了一個非常誘人的機遇。它之所以能夠引起人們廣泛的關注、有如此之多的應用,首先是因為物質的兆赫茲光譜(包括透射譜和反射譜)包含著非常豐富的物理和化學信息,所以研究物質在該波段的光譜對於物質結構的探索具有重要意義;其次是因為兆赫茲脈衝光源與傳統光源相比具有很多獨特的性質。[2]
簡介[編輯]
THz波(兆赫茲波)或稱為THz射線(兆赫茲射線)是從1980年代中後期,才被正式命名的,在此以前科學家們將統稱為遠紅外射線。兆赫茲波是指頻率在0.1THz到10THz範圍的電磁波,波長大概在0.03到3mm範圍,介於微波與紅外之間。實際上,早在一百年前,就有科學工作者涉及過這一波段。在1896年和1897年,Rubens和Nichols就涉及到這一波段,紅外光譜到達9um(0.009mm)和20um(0.02mm),之後又有到達50um的記載。之後的近百年時間,遠紅外技術取得了許多成果,並且已經產業化。但是涉及兆赫茲波段的研究結果和數據非常少,主要是受到有效兆赫茲產生源和靈敏探測器的限制,因此這一波段也被稱為THz間隙。隨著80年代一系列新技術、新材料的發展,特別是超快技術的發展,使得獲得寬帶穩定的脈衝THz源成為一種准常規技術,THz技術得以迅速發展,並在實際範圍內掀起一股THz研究熱潮。
產生源[編輯]
自然產生源[編輯]
兆赫茲輻射是任意溫度高於約10K的物體的黑體輻射的一部分。
人工產生源[編輯]
在2012年,幾種兆赫茲輻射的產生源有:
- 迴旋管(gyrotron)
- 反向波振盪器(backward wave oscillator, "BWO")
- 遠紅外雷射(far infrared laser, "FIR laser")
- 肖特基二極體(Schottky diode)
- 量子級聯雷射器[3][4][5][6]
- 自由電子雷射(FEL)
- 同步輻射光源
- photomixing sources
研究[編輯]
無線數據通訊紀錄[編輯]
在2012年5月,日本東京工業大學的研究團隊使用T-射線的無線數據傳輸創下新的紀錄,發表在Electronics Letters[7],並建議在未來以此做為數據傳輸的頻率。該團隊的概念驗證裝置使用諧振穿隧二極體(RTD),其電壓下降時的電流增加造成二極體「共振」,並產生THz波段的波。使用該RTD,研究人員發送出542 GHz的訊號,得到的數據傳輸速率是每秒3 Gigabits。該展示速度比當時主流的Wi-Fi 802.11n標準快20倍,比之前11月份的數據傳輸設置的紀錄快一倍[8]。THz Wi-Fi可能僅能在大約10米(33英尺)範圍內工作,但「理論上」數據傳輸速度可以高達100 Gbit/s。[9]
安全[編輯]
參見[編輯]
引用和注釋[編輯]
- ^ DanielBaroletabFrançoisChristiaenscMichael R.Hamblinde. Infrared and skin: Friend or foe. [2022-01-08]. (原始內容存檔於2022-02-28).
- ^ 強烈兆赫茲輻射 (頁面存檔備份,存於網際網路檔案館),亞太日報,2013年12月18日
- ^ Köhler, Rüdeger; Alessandro Tredicucci, Fabio Beltram, Harvey E. Beere, Edmund H. Linfield, A. Giles Davies, David A. Ritchie, Rita C. Iotti, Fausto Rossi. Terahertz semiconductor-heterostructure laser. Nature. 2002-05-09, 417: 156–159 [2011-10-26]. Bibcode:2002Natur.417..156K. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 12000955. doi:10.1038/417156a.
- ^ Scalari, G.; C. Walther, M. Fischer, R. Terazzi, H. Beere, D. Ritchie, J. Faist. THz and sub-THz quantum cascade lasers. Laser & Photonics Review. 2009-02-24, 3: 45–66 [2011-10-27]. ISSN 1863-8880. doi:10.1002/lpor.200810030.
- ^ Lee, Alan W. M.; Qi Qin, Sushil Kumar, Benjamin S. Williams, Qing Hu, John L. Reno. Real-time terahertz imaging over a standoff distance(>25 meters). Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89 (14): 141125. Bibcode:2006ApPhL..89n1125L. ISSN 0003-6951. doi:10.1063/1.2360210.
- ^ Fathololoumi, S.; E. Dupont, C.W.I. Chan, Z.R. Wasilewski, S.R. Laframboise, D. Ban, A. Matyas, C. Jirauschek, Q. Hu, H. C. Liu. Terahertz quantum cascade lasers operating up to ~200 K with optimized oscillator strength and improved injection tunneling. Optics Express. 2012-02-13, 20 (4): 3866–3876 [2012-03-21]. Bibcode:2012OExpr..20.3866F. doi:10.1364/OE.20.003866. [失效連結]
- ^ K. Ishigaki, M. Shiraishi, S. Suzuki, M. Asada, N. Nishiyama, and S. Arai. Direct intensity modulation and wireless data transmission characteristics of terahertz-oscillating resonant tunneling diodes. Electronics Letters. 10 May 2012, 48 (10): 582–3. doi:10.1049/el.2012.0849.
- ^ Chacksfield, Marc. Scientists show off the future of Wi-Fi – smash through 3Gbps barrier. Tech Radar. 16 May 2012 [16 May 2012]. (原始內容存檔於2012-11-25).
- ^ Milestone for Wi-Fi with 'T-rays'. BBC News. 16 May 2012 [16 May 2012]. (原始內容存檔於2012-10-17).
延伸閱讀[編輯]
- Quasioptical Systems: Gaussian Beam Quasioptical Propagation and Applications, Paul F. Goldsmith, IEEE Press(1997)
- Sensing with Terahertz Radiation, ed. Daniel Mittleman, Springer(2002)
- Terahertz Spectroscopy: Principles and Applications, ed. Susan L. Dexheimer, CRC Press(2007)
- Principles of Terahertz Science and Technology, Yun-Shik Lee, Springer(2008)
- Introduction to THz Wave Photonics, Xi-Cheng Zhang and Jingzhou Xu, Springer(2009)
- Terahertz Technology: Fundamentals and Applications, Ali Rostami, Hassan Rasooli and Hamed Baghban, Springer(2011)
外部連結[編輯]
- Terahertz radiation: applications and sources by Eric Mueller
- Terahertz profile on Google Scholar(頁面存檔備份,存於網際網路檔案館)
- 兆赫茲科學技術及其應用的新發展[永久失效連結] by 劉盛綱,鍾任斌 《電子科技大學學報》
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|