User:JKessvinJ/沙盒/Wales Referrendum
 | |
| 北愛爾蘭歸屬公投 | 1973年 |
|---|---|
| 英國歐共體成員身份公投 | 1975年 |
| 蘇格蘭憲政公投 | 1979年 |
| 威爾斯憲政公投 | 1979年 |
| 蘇格蘭憲政公投 | 1997年 |
| 威爾斯憲政公投 | 1997年 |
| 大倫敦政府公投 | 1998年 |
| 北愛爾蘭貝爾法斯特協議公投 | 1998年 |
| 東北英格蘭憲政公投 | 2004年 |
| 威爾斯憲政公投 | 2011年 |
| 英國選擇投票制公投 | 2011年 |
| 苏格兰独立公投 | 2014年 |
| 英國去留歐盟公投 | 2016年 |
1997年威爾斯權力下放公投是英國政府於1997年9月18日在威爾斯全境舉行的一場立法前公民投票,目的是確認威爾斯選民是否支持成立一威爾斯地方議會,而給與當地某程度的自治。此公投源於工黨於1997年大選時的競選承諾,並在工黨政府第一届任期期間依據《1997年公投(蘇格蘭與威爾斯)法令》舉行。這是當地繼1979年後就權力下放議題所作的第二次公投——選民於第一次公投以絕大比數票否決設立地方議會。
公投結果為支持一方以些微票數險勝。英國政府亦因公投通過而通過《1998年威爾斯政府法令》,並於1999年正式成立威爾斯國民議會。
,目的是讓蘇格蘭選民決定是否從大不列顛及北愛爾蘭聯合王國獨立。
就是否支持成立蘇格蘭議會及交由其選出新的蘇格蘭政府進行的公民表決,是次公投源於為工黨黨派於當選後為實現競選承諾而推動。這是繼1979年當地就同一議題所作的第二次公投,投票率達到60.4%。
The Welsh devolution referendum of 1997 was a pre-legislative referendum held in Wales on 18 September 1997 over whether there was support for the creation of a National Assembly for Wales, and therefore a degree of self-government. The referendum was a Labour manifesto commitment and was held in their first term after the 1997 election under the provisions of the Referendums (Scotland and Wales) Act 1997. This was the second referendum held in Wales over the question of devolution: the first referendum was held in 1979 and was defeated by a large majority.
The referendum resulted in a narrow majority in favour, which led to the passing of the Government of Wales Act 1998 and the formation of the National Assembly for Wales in 1999.
背景[编辑]
A referendum was held in 1979 (with a parallel referendum in Scotland) proposing the creation of a Welsh Assembly, under James Callaghan's Labour government. The referendum stipulated that a Welsh Assembly would be created if supported by 50% of votes cast and 40% of the total electorate. The Scottish referendum achieved the first condition but not the second, while the Welsh referendum was defeated by almost a 4:1 majority. Indeed, although the Labour Party had committed itself to devolution in 1974 (following the advice of the Royal Commission on the Constitution) several Welsh Labour MPs (including Neil Kinnock) were very much opposed.
The 1979 referendum had been such a resounding defeat that it killed off any prospects of devolution in Wales for a generation. The almost wholly anti-devolution, unionist Conservative Party won the 1979 general election (though Welsh Labour remained the largest party in Wales, the Conservatives only won 11 out of 36 seats in Wales)[1] and remained in government until 1997. Over this time, the Conservative Party became increasingly unpopular in Wales. The Conservatives mostly appointed English MPs representing English constituencies to the post of Secretary of State for Wales, including William Hague and John Redwood (who famously attempted to mime the words to the Welsh national anthem at the 1993 Welsh Conservative Party conference.[2])
A commitment to the creation of a Welsh Assembly with executive powers was again put into the Labour Party manifesto for the 1992 general election.[3] The Labour Party shaped its policy of a Welsh Assembly under the guidance of Shadow Welsh Secretary Ron Davies and Welsh Office spokesmen Win Griffiths and Rhodri Morgan. In March 1996, Ron Davies signed an agreement with Alex Carlile, the Leader of the Welsh Liberal Democrats, which committed both parties to support a "Yes" vote in a Welsh devolution referendum in the event of a Labour victory at the 1997 general election. The agreement was made in the context of a potential Lib-Lab pact should Labour not win an overall majority.
There was no inter-party Constitutional Convention in Wales to define devolution as there had been in Scotland. Labour's initial proposal to elect a Welsh Assembly using the traditional first-past-the-post system was reversed in late-1996 in favour of the Additional Member System. This change was vital in order to gain the support of Plaid Cymru and the Welsh Liberal Democrats in the event of a referendum.
Referendum question[编辑]
Unusually for a referendum just as in the 1997 Scottish devolution referendum the electorate was asked to vote on two statements rather than a question which corresponded to the following proposal. The statements were issued both in English and Welsh.
Parliament has decided to consult people in Wales on the Government's proposals for a Welsh Assembly:
Mae'r Senedd wedi penderfynu ymgynghori pobl yng Nghymru ar gynigion y Llywodraeth ar gyfer Cynulliad i Gymru:
- I agree there should be a Welsh Assembly
- Yr wyf yn cytuno y dylid cael Cynulliad i Gymru
or
- I do not agree there should be a Welsh Assembly
- Nid wyf yn cytuno y dylid cael Cynulliad i Gymru
(To be marked by a single (X))
Campaign[编辑]
The official Yes campaign, Yes for Wales, was supported by Labour, the Liberal Democrats and Plaid Cymru, though they also ran their own individual campaigns.[4] Labour anti-devolution MPs (including Llew Smith, among others[5]) were subject to a tight parliamentary whip to ensure that the Labour Party was seen to be publicly behind the campaign. Yes for Wales placed a large emphasis on grassroots involvement in the campaign, with sectoral groups such as "Pensioners say Yes", and local branches throughout Wales.[6]
Prominent campaigners for a Yes vote included Labour politicians Leighton Andrews, Ron Davies, Alun Michael, Rhodri Morgan, Andrew Davies, Peter Hain, Hywel Francis, Edwina Hart and Val Feld; Liberal Democrat politicians Michael German, Jenny Randerson, Kirsty Williams and Peter Black; Plaid Cymru politicians Dafydd Wigley, Cynog Dafis Ieuan Wyn Jones and Leanne Wood; and academic Russell Deacon.
The official No campaign, Just Say NO, was chaired by Nick Bourne, then-Conservative "Chief Spokesman in Wales". The No campaign lacked the structure and finance of the Yes campaign, and suffered from the fact that the Conservatives' landslide defeat at the 1997 general election meant there were no Conservative MPs (and therefore no MPs supporting the No campaign) in Wales. Additionally, the No campaign in 1997 did not have the support of local authorities; the fact that the Conservatives had reduced layers of local government from two to one in 1994 meant that this was not an issue as it had been in 1979.
Result[编辑]
| 選項 | 票數 | % |
|---|---|---|
| I agree that there should be a Welsh Assembly Yr wyf yn cytuno y dylid cael Cynulliad i Gymru |
559,419 | 50.30 |
| I do not agree that there should be a Welsh Assembly Nid wyf yn cytuno y dylid cael Cynulliad i Gymru |
552,698 | 49.70 |
| 有效票 | 1,112,117 | 99.64 |
| 無效或空白票 | 3,999 | 0.36 |
| 總票數 | 1,116,116 | 100.00 |
| 已登記選民及投票率 | 2,222,533 | 50.22 |
Note: In Wales under the Welsh Language Act 1993 the Welsh language has equal status with the English language.
The overall result was declared in the Royal Welsh College of Music and Drama in Cardiff. The proceeding officer was Professor Eric Sunderland. The results of all 22 local authority areas were announced individually, and the result was close enough that everything in fact hung on the announcement from Carmarthenshire, which carried the Yes vote.[7] The difference between the 'agree' and 'disagree' vote was 6,721.[8]
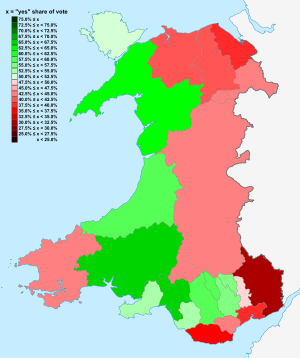
Results by unitary authority[编辑]
| Council Area | Turnout | Votes | Proportion of votes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agree Cytuno |
Disagree Anghytuno |
Agree Cytuno |
Disagree Anghytuno | |||
| Anglesey | 56.9% | 15,649 | 15,095 | 50.9% | 49.1% | |
| Blaenau Gwent | 49.3% | 15,237 | 11,928 | 56.1% | 43.9% | |
| Bridgend | 50.6% | 27,632 | 23,172 | 54.4% | 45.6% | |
| Caerphilly | 49.3% | 34,830 | 28,841 | 55.7% | 44.3% | |
| Cardiff | 46.9% | 47,527 | 59,589 | 44.4% | 55.6% | |
| Carmarthenshire | 56.4% | 49,115 | 26,119 | 65.5% | 34.5% | |
| Ceredigion | 56.8% | 18,304 | 12,614 | 59.2% | 40.8% | |
| Conwy | 51.5% | 18,369 | 26,521 | 40.9% | 59.1% | |
| Denbighshire | 49.7% | 14,271 | 20,732 | 40.5% | 59.5% | |
| Flintshire | 41.0% | 17,746 | 28,707 | 38.2% | 61.8% | |
| Gwynedd | 59.8% | 35,425 | 19,859 | 64.1% | 35.9% | |
| Merthyr Tydfil | 49.5% | 12,707 | 9,121 | 58.2% | 41.8% | |
| Monmouthshire | 50.5% | 10,592 | 22,403 | 32.1% | 67.9% | |
| Neath Port Talbot | 51.9% | 36,730 | 18,463 | 66.5% | 33.5% | |
| Newport | 45.9% | 16,172 | 27,017 | 37.5% | 62.5% | |
| Pembrokeshire | 52.6% | 19,979 | 26,712 | 42.8% | 57.2% | |
| Powys | 56.2% | 23,038 | 30,966 | 42.7% | 57.3% | |
| Rhondda Cynon Taff | 49.9% | 51,201 | 36,362 | 58.5% | 41.5% | |
| Swansea | 47.1% | 42,789 | 39,561 | 53.0% | 47.0% | |
| Torfaen | 45.5% | 15,756 | 15,854 | 49.8% | 50.2% | |
| Vale of Glamorgan | 54.3% | 17,776 | 30,613 | 35.5% | 64.5% | |
| Wrexham | 42.4% | 18,574 | 22,449 | 44.3% | 55.7% | |
See also[编辑]
- Referendums in the United Kingdom
- Referendums (Scotland & Wales) Act 1997
- 1997 Scottish devolution referendum
- 2011 Welsh devolution referendum
- Yes for Wales
- Senedd
- Welsh Devolution
References[编辑]
- ^ UK Election statistics 1945-2003 (PDF).
- ^ - YouTube. www.youtube.com.
- ^ Labour Party 1992 election manifesto. (原始内容存档于2013-12-09).
- ^ Welsh Referendum. www.bbc.co.uk.
- ^ Welsh Referendum. www.bbc.co.uk.
- ^ Welsh Referendum. www.bbc.co.uk.
- ^ Welsh Referendum. bbc.co.uk. [2017-09-18].
- ^ How Welsh devolution has evolved over two decades. 18 September 2017 –通过www.bbc.co.uk.
External links[编辑]
Template:Welsh devolution Template:Welsh elections Template:United Kingdom local elections, 1997 Template:Opinion polling for Senedd elections