DuPhos
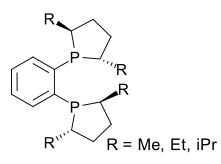
DuPhos是一種用於不對稱合成中的不對稱配體。DuPhos之名稱取自其研發公司(DuP,杜邦公司)和化合物的種類:膦雜環(Phos)。這種二膦配體首先由化學家M.J. Burk於1991年發現, [1][2] 並首次在不對稱氫化反應中,成功地將特定的烯基醯氨酯還原為胺基酸前體:
同期發現其他有機磷不對稱配體有諸如:DIPAMP、BINOL和Chiraphos,而後期發現了一批新的配體被證明比前者更具活性。
描述
[編輯]DuPhos配體由兩個2,5-烷基取代膦雜環(THF的磷類似物)通過1,2-苯橋連而成。這裡的烷基可以是:甲基、乙基、丙基或異丙基。DuPhos的類似物,雙(二甲基膦)乙烷或BPE配體[3][4] 相當於苯基橋被1,2-乙基所替代之產物。該兩種化合物都可通過相應的手性二醇化合物,轉化為環狀硫酸鹽,繼而與雙鋰二苯基膦反應製備獲得。DuPhos配體中,磷原子屬於富電子原子團,使形成的金屬絡合物具有強活性。磷原子還引入了一種假-手性,使對映體選擇性不受整個分子的化學構象影響。[5] DuPhos的另一種早期應用,是通過還原胺化反應合成非天然手性胺基酸:[6] 如先通過二苯甲酮和苯甲醯氯合成的腙得到亞胺,而後在DuPhos催化下發生不對稱氫化反應,最後脫去苯甲醯保護基得到非天然手性胺基酸產物:[7]
在早期的過渡金屬催化反應中,銠是常用的催化劑,直到在1995年才引入了釕催化劑,[8] 實例是氫化還原β-酮酯的羰基,合成手性的β-羥基酯:
應用
[編輯]DuPhos的一個不對稱合成實例為催化「脫氫華法林」氫化為華法林的反應:[9]
BozPhos配體
[編輯]使用硼烷二甲硫醚作為保護基,在過氧化氫條件下單氧化(R,R)-Me-Duphos即得到BozPhos。[11][12] 該配體可用於銅-催化的二有機鋅試劑對N-二苯基次磷醯亞胺的不對稱加成反應。
參考文獻
[編輯]- ^ Burk, Mark J. C2-symmetric bis(phospholanes) and their use in highly enantioselective hydrogenation reactions. Journal of the American Chemical Society (American Chemical Society (ACS)). 1991, 113 (22): 8518–8519. ISSN 0002-7863. doi:10.1021/ja00022a047.
- ^ Burk, Mark J.; Feaster, John E.; Nugent, William A.; Harlow, Richard L. Preparation and use of C2-symmetric bis(phospholanes): production of .alpha.-amino acid derivatives via highly enantioselective hydrogenation reactions. Journal of the American Chemical Society (American Chemical Society (ACS)). 1993, 115 (22): 10125–10138. ISSN 0002-7863. doi:10.1021/ja00075a031.
- ^ Burk, Mark J.; Feaster, John E.; Harlow, Richard L. New electron-rich chiral phosphines for asymmetric catalysis. Organometallics (American Chemical Society (ACS)). 1990, 9 (10): 2653–2655. ISSN 0276-7333. doi:10.1021/om00160a010.
- ^ Burk, Mark J.; Feaster, John E.; Harlow, Richard L. New chiral phospholanes; Synthesis, characterization, and use in asymmetric hydrogenation reactions. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry (Elsevier BV). 1991, 2 (7): 569–592. ISSN 0957-4166. doi:10.1016/s0957-4166(00)86109-1.
- ^ Crépy, Karen V. L.; Imamoto, Tsuneo. Recent Developments in Catalytic Asymmetric Hydrogenation Employing P-Chirogenic Diphosphine Ligands. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis (Wiley-Blackwell). 2003, 345 (12): 79–101. ISSN 1615-4150. doi:10.1002/adsc.200390031.
- ^ Burk, Mark J.; Feaster, John E. Enantioselective hydrogenation of the C:N group: a catalytic asymmetric reductive amination procedure. Journal of the American Chemical Society (American Chemical Society (ACS)). 1992, 114 (15): 6266–6267. ISSN 0002-7863. doi:10.1021/ja00041a067.
- ^ Burk, Mark J.; Martinez, Jose P.; Feaster, John E.; Cosford, Nick. Catalytic asymmetric reductive amination of ketones via highly enantioselective hydrogenation of the CN double bond. Tetrahedron (Elsevier BV). 1994, 50 (15): 4399–4428. ISSN 0040-4020. doi:10.1016/s0040-4020(01)89375-3.
- ^ Genêt, J.P.; Ratovelomanana-Vidal, V.; Caño de Andrade, M.C.; Pfister, X.; Guerreiro, P.; Lenoir, J.Y. Practical asymmetric hydrogenation of β-keto esters at atmospheric pressure using chiral Ru (II) catalysts. Tetrahedron Letters (Elsevier BV). 1995, 36 (27): 4801–4804. ISSN 0040-4039. doi:10.1016/0040-4039(95)00873-b.
- ^ Robinson, Andrea; Li, Hui-Yin; Feaster, John. The first practical asymmetric synthesis of R and S-Warfarin. Tetrahedron Letters (Elsevier BV). 1996, 37 (46): 8321–8324. ISSN 0040-4039. doi:10.1016/0040-4039(96)01796-0.
- ^ Hoerrner, R. Scott; Askin, David; Volante, R.P.; Reider, Paul J. A highly enantioselective asymmetric hydrogenation route to β-(2R,3S)-methyltryptophan. Tetrahedron Letters (Elsevier BV). 1998, 39 (21): 3455–3458. ISSN 0040-4039. doi:10.1016/s0040-4039(98)00604-2.
- ^ Alexandre Côté, Jean-Nicolas Desrosiers, Alessandro A. Boezio, and André B. Charette (2006). "Preparation of enantiomerically pure (R,R)-BozPhos". Org. Synth. 83: 1.
- ^ Jean-Nicolas Desrosiers, Alexandre Côté, Alessandro A. Boezio, and André B. Charette (2006). "Preparation of enantiomerically enriched (1S)-1-Phenylpropan-1-amine hydrochloride by a catalytic addition of diorganozinc reagents to imines". Org. Synth. 83: 5.




