傅科摆
此条目可参照英语维基百科相应条目来扩充。 |


傅科摆(英语:Foucault pendulum、Foucault's pendulum),是依据法国物理学家莱昂·傅科命名的,用以证明地球自转的一种简单设备。虽然人们长久以来都知道地球在自转,但傅科摆第一次以简单的实验予以证明。
今天,它在许多科学博物馆和大学内是很受欢迎的展品[1]
实验
[编辑]这个实验的装置包括一个高大的、在任意垂直平面上振荡的单摆。单摆摆动的方向会因为地球本身的周日转动而改变。这是因为单摆的摆动平面,像陀螺仪一样,当地球转动时仍会在空间中保持固定的方向。傅科摆于1851年2月首度次在巴黎天文台的子午仪室公开展示 。几个星期之后,傅科制做了他最著名的单摆,他在巴黎先贤祠的拱顶下以67米长的钢索悬挂着一颗28千克重的铅锤。这个单摆的摆动平面以每小时顺时针方向11°,以31.7小时环绕一圈。1855年,这个单摆被移到法国国立工艺学院的国立工艺博物馆。在2010年4月6日[2],在国立工艺博物馆悬挂铅锤的钢索断裂,使单摆和博物馆的大理石地板受到无法修补的损坏[3]。

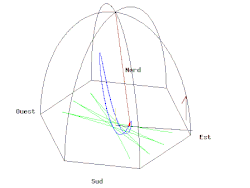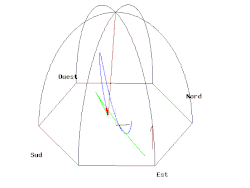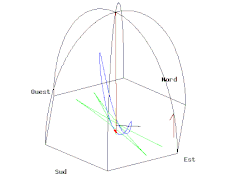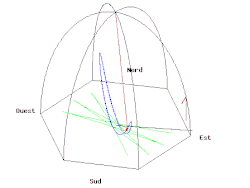
无论是在南极或北极,当单摆下面的地球以一个恒星日旋转了一周,摆的振荡平面相对于恒星是固定不变的。所以相对于地球,在南极或北极的摆的振荡平面以一天的时间,分别以顺时针或逆时针方向旋转了一周。当傅科摆被悬挂在赤道上,摆的振荡平面相对于地球是固定不变的,也就是说观察不到傅科摆现象。在其它的纬度上,这个摆的摆动平面相对于地球逐渐旋转,但比极地要慢;角速度, (每恒星日以顺时针方向旋转的角度),是正比于纬度 的正弦值:
- 日
此处,在赤道以北和以南的纬度分别以正值和负值来显示。例如,在南纬30°的傅科摆,会以2天的周期逆时针旋转360°。
为了证明地球的自转没有错综复杂的物理,而只与纬度有关,傅科在1852年的实验使用了一个陀螺仪。陀螺仪的转子直接追踪著恒星,由于没有单摆的几何不对称性,使它不受制于作用在单摆上不平衡的科里奥利力,所以无论在地球上的任何纬度,经过一天之后,可以观察到它的转轴仍然指向原来的方向。
傅科摆的架设需要很小心,因为不确定的结构可能会导致额外的转向,并被误认为是地球的影响。摆的初始启动非常重要,传统的操作方法是用火焰烧断暂时束缚住铅锤的棉线,以避免不必要的侧向运动。空气阻力会使振荡衰减,因此博物馆的傅科摆经常会结合电磁的或其它驱动装置来保持铅锤摆动;其它的则会定期重新启动。而在后者的情况,每次启动的仪式可能作为一场表演来执行。
世界各地的傅科摆
[编辑]世界各地有为数不少的傅科摆,许多都在大学、科学中心和天文馆,最特别、著名和突出的一个位于曼哈顿的联合国大会大楼。
这个实验也曾经在南极进行过。
参考资料
[编辑]- ^ Oprea, John. Geometry and the Foucault Pendulum. Amer. Math. Monthly. 1995, 102: 515–522 [2018-03-04]. doi:10.2307/2974765. (原始内容存档于2015-04-02).
- ^ Le pendule de Foucault perd la boule. [2010-12-14]. (原始内容存档于2010-07-10).
- ^ Foucault's pendulum is sent crashing to Earth http://www.timeshighereducation.co.uk/story.asp?storycode=411529 (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
延伸阅读
[编辑]- Arnold, V.I. Mathematical Methods of Classical Mechanics. Springer. 1989: 123. ISBN 0-387-96890-3.
- Marion, Jerry B.; Thornton, Stephen T. Classical dynamics of particles and systems 4th. Brooks Cole. 1995: 398–401. ISBN 0-03-097302-3.
- Persson, Anders O. The Coriolis Effect: Four centuries of conflict between common sense and mathematics, Part I: A history to 1885 (PDF). History of Meteorology. 2005, 2 [2010-12-14]. (原始内容 (PDF)存档于2014-04-11).
相关条目
[编辑]外部链接和书目提要
[编辑]- Julian Rubin, "The Invention of the Foucault Pendulum" (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆), Following the Path of Discovery, 2007, retrieved 2007-10-31. Directions for repeating Foucault's experiment, on amateur science site.
- Wolfe, Joe, "A derivation of the precession of the Foucault pendulum (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)".
- "The Foucault Pendulum (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)", derivation of the precession in polar coordinates.
- "The Foucault Pendulum (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)" By Joe Wolfe, with film clip and animations.
- "Foucault's Pendulum (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)" by Jens-Peer Kuska with Jeff Bryant, Wolfram Demonstrations Project: a computer model of the pendulum allowing manipulation of pendulum frequency, Earth rotation frequency, latitude, and time.
- "Webcam Kirchhoff-Institut für Physik, Universität Heidelberg (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)".
- California academy of sciences, CA Portuguese Web Archive的存档,存档日期2016-05-25 Foucault pendulum explanation, in friendly format
- Foucault pendulum model Exposition including a tabletop device that shows the Foucault effect in seconds.
- Foucault, M. L., Physical demonstration of the rotation of the Earth by means of the pendulum, Franklin Institute, 2000, retrieved 2007-10-31. Translation of his paper on Foucault pendulum.
- Tobin, William "The Life and Science of Léon Foucault" (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆).
- Bowley, Roger. Foucault's Pendulum. Sixty Symbols. Brady Haran for University of Nottingham. 2010 [2018-03-04]. (原始内容存档于2020-05-06).
- Foucault-inga Párizsban (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) Foucault's Pendulum in Paris – video of the operating Foucault's Pendulum in the Panthéon (匈牙利文).
- Pendolo nel Salone (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) The Foucault Pendulum inside Palazzo della Ragione in Padova, Italy
- Daliga, K., Przyborski, M., & Szulwic, J. Foucault's Pendulum. Uncomplicated Tool in the Study of Geodesy and Cartography, EDULEARN15 Proceedings - 7th International Conference on Education and New Learning Technologies, Barcelona, Spain, ISBN 978-84-606-8243-1, 2015



