User:Ericmetro/沙盒3:修订间差异
←页面内容被替换为:'test' |
无编辑摘要 |
||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
[[Image:Fallout shelter sign.jpg|thumb|250px|upright|A sign pointing to an old fallout shelter in [[New York City]].]] |
|||
test |
|||
{{nuclear weapons}} |
|||
A '''fallout shelter''' is an enclosed space specially designed to protect occupants from radioactive debris or [[nuclear fallout|fallout]] resulting from a [[nuclear explosion]]. Many such shelters were constructed as [[civil defense]] measures during the [[Cold War]]. |
|||
During a nuclear explosion, matter vaporized in the resulting fireball is exposed to neutrons from the explosion, absorbs them, and becomes [[radioactivity|radioactive]]. When this material condenses in the rain, it forms dust and light sandy materials that resembles ground [[pumice]]. The fallout emits [[Alpha particle|alpha]] and [[beta particle]]s, as well as [[gamma ray]]s. |
|||
Much of this highly radioactive material then falls to earth, subjecting anything within the line of sight to radiation, a significant [[radioactive contamination|hazard]]. A fallout shelter is designed to allow its occupants to minimize exposure to harmful fallout until radioactivity has decayed to a safer level. |
|||
Although many shelters still exist, some even being used as [[museum]]s, virtually all fallout shelters have been decommissioned since the fall of the [[Soviet Union]] in 1991.{{Citation needed|date=September 2011}} |
|||
==History== |
|||
[[Image:Fallout shelter photo.png|thumbnail|300px|right|Idealized American fallout shelter circa 1957.]] |
|||
During the [[Cold War]], many countries built fallout shelters for high-ranking government officials and crucial military facilities, such as [[Project Greek Island]] and [[Cheyenne Mountain nuclear bunker]] in the United States and Canada's [[Emergency Government Headquarters]]. Plans were made, however, to use existing buildings with sturdy below-ground-level basements as makeshift fallout shelters. These buildings were usually [[placard]]ed with the yellow and black [[trefoil]] sign. |
|||
The [[National Emergency Alarm Repeater]] (N.E.A.R.) program was developed in 1956 during the [[Cold War]] to supplement the existing siren [[warning systems]] and radio broadcasts in the event of a [[nuclear attack]]. The N.E.A.R. civilian alarm device was engineered and tested but the program was not viable and went defunct about 1966.<ref>[http://www.pbs.org/opb/historydetectives/pdf/709_near.pdf ]{{dead link|date=August 2012}}</ref> In the U.S. in September 1961, under the direction of [[Assistant Secretary of Defense for Homeland Defense and Americas' Security Affairs#Precedent|Steuart L. Pittman]], the federal government started the Community Fallout Shelter Program.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.civildefensemuseum.com/cdmuseum2/commun.html|title=Civil Defense Museum-Community Shelter Tours Main Page|publisher=www.civildefensemuseum.com|accessdate=2008-09-14}} |
|||
</ref><ref> |
|||
{{cite web|url=http://mywebtimes.com/archives/ottawa/display.php?id=366305|title=FALLOUT FEVER: Civil Defense shelters dotted area cities during the Cold War – My Web Times|publisher=mywebtimes.com|accessdate=2008-09-14}} |
|||
</ref> A letter from [[John F. Kennedy|President Kennedy]] advising the use of fallout shelters appeared in the September 1961 issue of ''[[Life (magazine)|Life]]'' magazine.<ref>[http://www.em.doe.gov/Publications/timeline_sep1961.aspx DOE.gov]</ref> |
|||
In November 1961 in ''[[Fortune (magazine)|Fortune]]'' magazine, an article by Gilbert Burck appeared that outlined the plans of [[Nelson Rockefeller]], [[Edward Teller]], [[Herman Kahn]], and [[Chet Holifield]] for an enormous network of concrete lined underground fallout shelters throughout the [[United States]] sufficient to shelter millions of people to serve as a refuge in case of [[nuclear war]].<ref>[[Fortune (magazine)|Fortune]] magazine November 1961 Pages 112–115 et al</ref> |
|||
American fallout shelters in the early 1960s were sometimes funded in conjunction with funding for other federal programs, such as [[urban renewal]] projects of the [[Federal Housing Authority]], examples being [[Barrington Plaza]], and other development projects of [[Los Angeles County Civil Defense and Disaster Commission]]er, [[Louis Lesser]], and were designed for large numbers of citizens.<ref>Los Angeles Times, November 15, 1961 “Board Asks Full Study of Shelters” [http://pqasb.pqarchiver.com/latimes/access/448218732.html?FMT=AI&FMTS=::ABS:AI:CITE:PAGE&type=historic&date=Nov+15%2C+1961&author=&pub=Los+Angeles+Times&desc=Board+Asks+Full+Study+of+Shelters]</ref><ref>[http://pqasb.pqarchiver.com/latimes/access/481412212.html?dids=481412212:481412212&FMT=ABS&FMTS=ABS:AI&type=historic&date=Oct+15%2C+1961&author=&pub=Los+Angeles+Times&desc=Apartment+Approved+as+Official+Fallout+Shelter&pqatl=google Los Angeles Times, Oct 15, 1961]</ref><ref>Los Angeles Times, December 3, 1961 “Businessman Appointed to CD Group” [http://pqasb.pqarchiver.com/latimes/access/481553932.html?FMT=AI&FMTS=::ABS:AI:CITE:PAGE&type=historic&date=Dec+03%2C+1961&author=&pub=Los+Angeles+Times&desc=Businessman+Appointed+to+CD+Group]</ref> |
|||
[[Switzerland]] built an extensive network of fallout shelters, not only through extra hardening of government buildings such as schools, but also through a building regulation that ensured that all residential building built after 1978 contained a nuclear shelter able to withstand a blast from a 12 megaton explosion at a distance of 700 metres.<ref name=wsj4>{{cite news|last=Ball|first=Deborah|title=Swiss Renew Push for Bomb Shelters|url=http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702304231204576405700994655570.html|accessdate=18 December 2012|newspaper=Wall Street Journal|date=June 25, 2011}}</ref> In addition, the Swiss government maintains large communal shelters (including the [[Sonnenberg Tunnel]]) stocked with over four months of food and fuel.<ref name=wsj4 /> The reference [[Nuclear War Survival Skills]] declared that, as of 1986, "Switzerland has the best civil defense system, one that already includes blast shelters for over 85 percent of all its citizens."<ref name=NWSS1>{{cite book|last=Kearny|first=Cresson H|title=Nuclear War Survival Skills|year=1986|publisher=Oak Ridge National Laboratory|location=Oak Ridge, TN|isbn=0-942487-01-X|pages=6–10|url=http://www.oism.org/nwss/s73p911.htm}}</ref> |
|||
Similar projects have been undertaken in [[Finland]], which requires all buildings with area over 600 m² to have an NBC shelter, and [[Norway]], which requires all buildings with an area over 1000 m² to have a shelter.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.lovdata.no/for/sf/jd/xd-19950315-0254.html |title=FOR 1995-03-15 nr 254: Forskrift om tilfluktsrom |publisher=Lovdata.no |date= |accessdate=2012-08-15}}</ref> |
|||
The former [[Soviet Union]] and other Eastern Bloc countries often designed their underground mass-transit and subway tunnels to serve as bomb and fallout shelters in the event of an attack. |
|||
In [[Switzerland]], most residential shelters are no longer stocked with the food and water required for prolonged habitation and a large number have been converted by the owners to other uses (e.g., [[wine cellar]]s, ski rooms, [[gyms]]).<ref name=wsj4 /> These shelters also provide a haven from natural disasters such as tornadoes and hurricanes, although [[Switzerland]] is rarely subject to such natural phenomena. |
|||
==Details of shelter construction== |
|||
[[Image:Väestönsuojan ovi.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Door to a light fallout shelter.]] |
|||
[[Image:Big_german_fire_door_1.png|thumb|left|Large German fire door, sealing a fallout/air raid shelter inside the basement parking garage of a hotel.]] |
|||
===Shielding=== |
|||
A basic fallout shelter consists of shields that reduce gamma ray exposure by a factor of 1000. The required shielding can be accomplished with 10 times the [[Radiation protection#Shielding design|thickness]] of any quantity of material capable of cutting gamma ray exposure in half. Shields that reduce gamma ray intensity by 50% (1/2) include 1 cm (0.4 inch) of lead, 6 cm (2.4 inches) of concrete, 9 cm (3.6 inches) of packed earth or 150 m (500 ft) of air. When multiple thicknesses are built, the shielding multiplies. Thus, a practical fallout shield is ten halving-thicknesses of packed earth, reducing gamma rays by approximately 1024 times (2<sup>10</sup>).<ref>{{cite web|url = http://www.derose.net/steve/guides/emergency/hardened.html|title=Halving-thickness for various materials|publisher="The Compass DeRose Guide to Emergency Preparedness - Hardened Shelters"}}</ref> |
|||
Usually, an expedient purpose-built fallout shelter is a trench; with a strong roof buried by c. 1 m (3 ft) of earth. The two ends of the trench have ramps or entrances at right angles to the trench, so that gamma rays cannot enter (they can travel only in straight lines). To make the overburden waterproof (in case of rain), a plastic sheet may be buried a few inches below the surface and held down with rocks or bricks.<ref name=NWSS6>{{cite book|last=Kearny|first=Cresson H|title=Nuclear War Survival Skills|year=1986|publisher=Oak Ridge National Laboratory|location=Oak Ridge, TN|isbn=0-942487-01-X|pages=37–45|url=http://www.oism.org/nwss/s73p916.htm}}</ref> |
|||
Blast doors are designed to absorb the shock wave of a nuclear blast, bending and then returning to their original shape.<ref name=lostworlds>{{Cite episode|title= Secret U.S. Bunkers|series=[[Lost Worlds (TV series)|Lost Worlds]]|network=The History Channel|date=August 29, 2007|number=18}}</ref> |
|||
===Climate control=== |
|||
Dry earth is a reasonably good thermal insulator, and over several weeks of habitation, a shelter will become dangerously hot.<ref name=NWSS7 /> The simplest form of effective fan to cool a shelter is a wide, heavy frame with flaps that swing in the shelter's doorway and can be swung from hinges on the ceiling. The flaps open in one direction and close in the other, pumping air. (This is a [[Kearny Air Pump]], or KAP, named after the inventor, [[Cresson Kearny]]) |
|||
Unfiltered air is safe, since the most dangerous fallout has the consistency of sand or finely ground pumice.<ref name=NWSS7 /> Such large particles are not easily ingested into the soft tissues of the body, so extensive filters are not required. Any exposure to fine dust is far less hazardous than exposure to the fallout outside the shelter. Dust fine enough to pass the entrance will probably pass through the shelter.<ref name=NWSS7>{{cite book|last=Kearny|first=Cresson H|title=Nuclear War Survival Skills |year= 1986|publisher=Oak Ridge National Laboratory|location=Oak Ridge, TN|isbn=0-942487-01-X |pages=51–56 |url=http://www.oism.org/nwss/s73p917.htm}}</ref> Some shelters, however, incorporate [[Chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear|NBC]]-filters for additional protection. |
|||
===Locations=== |
|||
Effective public shelters can be the middle floors of some tall buildings or parking structures, or below ground level in most buildings with more than 10 floors. The thickness of the upper floors must form an effective shield, and the windows of the sheltered area must not view fallout-covered ground that is closer than 1.5 km (1 mi). One of Switzerland's solutions is to utilise road tunnels passing through the mountains; with some of [[Sonnenberg Tunnel|these shelters]] being able to protect tens of thousands.<ref name=BBC1>{{cite news|last=Foulkes|first=Imogen|title=Swiss still braced for nuclear war|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/programmes/from_our_own_correspondent/6347519.stm|accessdate=15 August 2012|newspaper=BBC News, Switzerland|date=10 February 2007}}</ref> |
|||
Fallout shelters are not always underground. Above ground buildings with walls and roofs dense enough to afford a meaningful [[Radiation protection#Shielding design|protection factor]] can be used as a fallout shelter.<ref>Monteyne, David. ''Fallout Shelter: Designing for Civil Defense in the Cold War.'' Minneapolis: University of Minnesota, 2011. Print.</ref> |
|||
===Contents=== |
|||
A battery-powered radio may be helpful to get reports of fallout patterns and clearance. However, radio and other electronic equipment may be disabled by [[electromagnetic pulse]]. For example, even at the height of the cold war, [[Electromagnetic pulse#Practical considerations for nuclear EMP|EMP protection]] had been completed for only 125 of the approximately 2,771 radio stations in the United States [[Emergency Broadcast System]]. Also, only 110 of 3,000 existing Emergency Operating Centers had been protected against EMP effects.<ref name=NWSS4>{{cite book|last=Kearny|first=Cresson H|title=Nuclear War Survival Skills|year=1986|publisher=Oak Ridge National Laboratory|location=Oak Ridge, TN|isbn=0-942487-01-X|pages=24|url=http://www.oism.org/nwss/s73p914.htm}}</ref> The [[Emergency Broadcast System]] has since been supplanted in the United States by the [[Emergency Alert System]]. |
|||
The reference ''[[Nuclear War Survival Skills]]'' includes the following supplies in a list of "Minimum Pre-Crisis Preparations": one or more shovels, a pick, a bow-saw with an extra blade, a hammer, and 4-mil polyethylene film (also any necessary nails, wire, etc.); a homemade shelter-ventilating pump (a [[Kearny Air Pump|KAP]]); large containers for water; a plastic bottle of sodium hypochlorite bleach; one or two [[Kearny Fallout Meter|KFM]]s and the knowledge to operate them; at least a 2-week supply of compact, nonperishable food; an efficient portable stove; wooden matches in a waterproof container; essential containers and utensils for storing, transporting, and cooking food; a hose-vented 5-gallon can, with heavy plastic bags for liners, for use as a toilet; tampons; insect screen and fly bait; any special medications needed by family members; Pure [[potassium iodide]], a 2-oz bottle, and a medicine- dropper; A first-aid kit and a tube of antibiotic ointment; long-burning candles (with small wicks) sufficient for at least 14 nights; an [[Nuclear War Survival Skills#Light|oil lamp]]; a flashlight and extra batteries; and a transistor radio with extra batteries and a metal box to protect it from [[electro-magnetic pulse|EMP]].<ref name=NWSS17>{{cite book|last=Kearny|first=Cresson H|title=Nuclear War Survival Skills|year=1986|publisher=Oak Ridge National Laboratory|location=Oak Ridge, TN|isbn=0-942487-01-X|pages=133–134|url=http://www.oism.org/nwss/s73p927.htm}}</ref> |
|||
Inhabitants should have water on hand, 1-2 gallons per person per day. Water stored in bulk containers requires less space than water stored in smaller bottles.<ref>{{cite book|last=Hammes|first=JA|title=Fallout shelter survival research|year=1966|pages=154–159}}</ref> |
|||
====Kearny Fallout Meter==== |
|||
Commercially made [[Geiger counters]] are expensive and require frequent calibration. It is possible to construct an [[electroscope#Gold-leaf electroscope|electrometer]]-type radiation meter called the [[Kearny Fallout Meter]], which does not require batteries or professional calibration, from properly-scaled plans with just a coffee can or pail, gypsum board, [[monofilament line|monofilament fishing line]], and aluminum foil.<ref name=A>{{cite book|last=Kearny|first=Cresson H|title=The KFM, A Homemade Yet Accurate and Dependable Fallout Meter|year=1978|publisher=Oak Ridge National Laboratory|location=Oak Ridge, TN|url=http://www.ornl.gov/~webworks/cppr/y2001/rpt/112538.pdf}}</ref> Plans are freely available in the public domain in the reference [[Nuclear War Survival Skills]] by [[Cresson Kearny]].<ref name=NWSS11>{{cite book|last=Kearny|first=Cresson H|title=Nuclear War Survival Skills|year=1986|publisher=Oak Ridge National Laboratory|location=Oak Ridge, TN|isbn=0-942487-01-X|pages=95–100|url=http://www.oism.org/nwss/s73p921.htm}}</ref> |
|||
==Use== |
|||
Inhabitants should plan to remain sheltered for at least two weeks (with an hour out at the end of the first week – see Swiss Civil Defense guidelines (which was once part of Swiss Zivilschutz)), then work outside for gradually increasing amounts of time, to four hours a day at three weeks. The normal work is to sweep or wash fallout into shallow trenches to decontaminate the area. They should sleep in a shelter for several months. Evacuation at three weeks is recommended by official authorities.{{citation needed|date=August 2012}} |
|||
If available, inhabitants may take [[potassium iodide]] at the rate of 130 mg/day per adult (65 mg/day per child) as an additional measure to protect the thyroid gland from the uptake of dangerous radioactive iodine, a component of most fallout and reactor waste.<ref name=NWSS14>{{cite book|last=Kearny|first=Cresson H|title=Nuclear War Survival Skills|year=1986|publisher=Oak Ridge National Laboratory|location=Oak Ridge, TN|isbn=0-942487-01-X|pages=111–117|url=http://www.oism.org/nwss/s73p924.htm}}</ref> |
|||
{| style="float:right; clear:right; background:none; margin-left:1.2em;" |
|||
|- |
|||
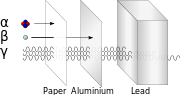
|[[File:Alfa beta gamma radiation penetration.svg|thumb|180px|right|Relative abilities of three different types of [[ionizing radiation]] to penetrate solid matter.]] |
|||
|- |
|||
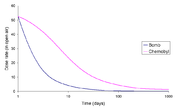
|[[Image:Protectionfactorchernobyl10cm.png|thumb|180px|right|The protection factor provided by '''10 cm of concrete shielding''' where the source is the idealised Chernobyl fallout.<ref name="OECD">Note that this image was drawn using data from the [http://atom.kaeri.re.kr/ton/nuc6.html ''OECD report''] and the second edition of ''The Radiochemical Manual''</ref>]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Image:Protectionfactorchernobyl20cm.png|thumb|180px|right|The protection factor provided by '''20 cm of concrete shielding''' where the source is the idealised Chernobyl fallout.<ref name="OECD"/>]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Image:Protectionfactorchernobyl30cm.png|thumb|180px|right|The protection factor provided by '''30 cm of concrete shielding''' where the source is the idealised Chernobyl fallout.<ref name="OECD"/>]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[File:Relativedoseratesnormalisedforday1.png|thumb|180px|right|Calculated relative gamma dose rates from atomic bomb and chernobyl fallout]] |
|||
|} |
|||
==Different types of radiation emitted by fallout== |
|||
===Alpha (α)=== |
|||
In the vast majority of accidents, and in all [[atomic bomb]] blasts, the threat due to beta and gamma emitters is greater than that posed by the alpha emitters in the fallout. Alpha particles are identical to a helium-4 nucleus (two protons and two neutrons), and travel at speeds in excess of 5% of the speed of light. [[Radiation#Alpha|Alpha particles]] have little penetrating power; most cannot penetrate through human skin. Avoiding direct exposure with fallout particles will prevent injury from alpha radiation.<ref name=NWSSC>{{cite book|last=Kearny|first=Cresson H|title=Nuclear War Survival Skills|year=1986|publisher=Oak Ridge National Laboratory|location=Oak Ridge, TN|isbn=0-942487-01-X|pages=45|url=http://www.oism.org/nwss/s73p916.htm}}</ref> |
|||
===Beta (β)=== |
|||
[[Radiation#Beta|Beta radiation]] consists of particles (high-speed electrons) given off by some fallout. Most beta particles cannot penetrate more than about 10 feet (3 m) of air or about {{frac|1|8}} inch (3 mm) of water, wood, or human body tissue; or a sheet of aluminum foil. Avoiding direct exposure with fallout particles will prevent most injuries from beta radiation.<ref name=NWSSD /> |
|||
The primary dangers associated with beta radiation are internal exposure from ingested fallout particles and beta burns from fallout particles no more than a few days old. [[Beta burn]]s can result from contact with highly radioactive particles on bare skin; ordinary clothing separating fresh fallout particles from the skin can provide significant shielding.<ref name=NWSSD>{{cite book |last=Kearny |first=Cresson H |title=Nuclear War Survival Skills |year=1986 |publisher=Oak Ridge National Laboratory |location=Oak Ridge, TN |isbn=0-942487-01-X |page=44 |url=http://www.oism.org/nwss/s73p916.htm}}</ref> |
|||
===Gamma (γ)=== |
|||
[[Radiation#Gamma|Gamma radiation]] penetrates further through matter than alpha or beta radiation. Most of the design of a typical fallout shelter is intended to protect against gamma [[electromagnetic radiation|rays]]. Gamma rays are better absorbed by materials with high atomic numbers and high density, although neither effect is important compared to the total mass per area in the path of the gamma ray. Thus, lead is only modestly better as a gamma shield than an equal mass of another shielding material such as aluminum, concrete, water or soil. |
|||
Some gamma radiation from fallout will penetrate into even the best shelters. However, the radiation dose received while inside a shelter can be significantly reduced with proper shielding. Ten [[Radiation protection#Shielding design|halving thicknesses]] of a given material can reduce gamma exposure to less than {{frac|1|1000}} of unshielded exposure.<ref name=NWSSE>{{cite book |last=Kearny |first=Cresson H |title=Nuclear War Survival Skills |year=1986 |publisher=Oak Ridge National Laboratory |location=Oak Ridge, TN |isbn=0-942487-01-X |pages=11–20 |url=http://www.oism.org/nwss/s73p912.htm}}</ref> |
|||
==Weapons versus nuclear accident fallout== |
|||
The bulk of the [[radioactivity]] in nuclear accident fallout is more long-lived than that in [[fallout|weapons fallout]]. A good table of the [[nuclide]]s, such as that provided by the [[Korean Atomic Energy Research Institute]], includes the [[Nuclear fission|fission]] yields of the different nuclides. From this data it is possible to calculate the isotopic mixture in the fallout (due to [[fission products]] in bomb fallout).{{citation needed|date=August 2012}} |
|||
==Other matters and simple improvements== |
|||
While a person's home may not be a purpose-made shelter, it could be thought of as one if measures are taken to improve the degree of [[Radiation protection|fallout protection]]. |
|||
===Measures to lower the beta dose=== |
|||
The main threat of [[Radiation#Beta|beta radiation]] exposure comes from ''[[hot particle]]s'' in contact with or close to the skin of a person. Also, swallowed or inhaled hot particles could cause [[beta burn]]s. As it is important to avoid bringing hot particles into the shelter, one option is to remove one's outer clothing, or follow other [[human decontamination|decontamination procedures]], on entry. Fallout particles will cease to be radioactive enough to cause beta burns within a few days following a nuclear explosion. The danger of gamma radiation will persist for far longer than the threat of beta burns in areas with heavy fallout exposure.<ref name=NWSSA>{{cite book|last=Kearny|first=Cresson H|title=Nuclear War Survival Skills|year=1986|publisher=Oak Ridge National Laboratory|location=Oak Ridge, TN|isbn=0-942487-01-X|pages=131|url=http://www.oism.org/nwss/s73p926.htm#Message2481}}</ref> |
|||
===Measures to lower the gamma dose rate=== |
|||
The gamma dose rate due to the contamination brought into the shelter on the clothing of a person is likely to be small (by wartime standards) compared to [[Radiation#Gamma|gamma radiation]] that penetrates through the walls of the shelter.<ref name=NWSSA /> The following measures can be taken to reduce the amount of gamma radiation entering the shelter: |
|||
* Roofs and gutters can be cleaned to lower the dose rate in the house. |
|||
* The top inch of soil in the area near the house can be either removed or dug up and mixed with the [[subsoil]]. This reduces the dose rate as the gamma rays have to pass through the topsoil before they can irradiate anything above. |
|||
* Nearby roads can be rinsed and washed down to remove dust and debris; the [[fallout]] would collect in the sewers and gutters for easier disposal. In [[Kiev]] after the [[Chernobyl accident]] a program of road washing was used to control the spread of radioactivity. |
|||
* Windows can be bricked up, or the sill raised to reduce the hole in the shielding formed by the wall. |
|||
* Gaps in the shielding can be blocked using containers of water. While water has a much lower density than that of lead, it is still able to shield some gamma rays. |
|||
* Earth (or other dense material) can be heaped up against the exposed walls of the building; this forces the gamma rays to pass through a thicker layer of shielding before entering the house. |
|||
* Nearby trees can be removed to reduce the dose due to fallout which is on the branches and leaves. It has been suggested by the US government that a fallout shelter should not be dug close to trees for this reason.<ref name=NWSSB>{{cite book|last=Kearny|first=Cresson H|title=Nuclear War Survival Skills|year=1986|publisher=Oak Ridge National Laboratory|location=Oak Ridge, TN|isbn=0-942487-01-X|pages=39|url=http://www.oism.org/nwss/s73p916.htm}}</ref> |
|||
==Fallout shelters in popular culture== |
|||
[[File:United States Fallout Shelter Sign.svg|200px|thumb|Fallout shelter sign of the United States]] |
|||
Fallout shelters feature prominently in the [[Robert A. Heinlein]] novel ''[[Farnham's Freehold]]'' (Heinlein built a fairly extensive shelter near his home in [[Colorado Springs, Colorado|Colorado Springs]] in 1963),<ref>[http://www.nitrosyncretic.com/rah/pm652-art-hi.html site: Robert A. Heinlein – Archives – PM 6/52 Article<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> ''Pulling Through'' by Dean Ing, ''[[A Canticle for Leibowitz]]'' by [[Walter M. Miller]] and ''[[Earth (Brin novel)|Earth]]'' by [[David Brin]]. |
|||
The ''[[The Twilight Zone (1959 TV series)|Twilight Zone]]'' episode "[[The Shelter (The Twilight Zone)|The Shelter]]", from a [[Rod Serling]] script, deals with the consequences of actually using a shelter. |
|||
In the ''[[Only Fools and Horses]]'' episode "[[The Russians Are Coming (Only Fools and Horses)|The Russians are Coming]]", Derek Trotter buys a lead fallout shelter, then decides to construct it in fear of an impending nuclear war caused by the Soviet Union (who were still active during the episode's creation). |
|||
The 1982 album ''[[The Nightfly]]'' by [[Donald Fagen]] features a song, 'New Frontier', about an early-1960s teenager enticing his girlfriend into spending a romantic weekend with him in his family's backyard fallout shelter. |
|||
In 1999 the [[film]] ''[[Blast from the Past (film)|Blast from the Past]]'' was released. It is a [[romantic comedy film]] about a [[nuclear physicist]], his wife, and son that enter a well-equipped, spacious fallout shelter during the 1962 [[Cuban Missile Crisis]]. They do not emerge until 35 years later, in 1997. The film shows their reaction to contemporary society. |
|||
In book 11 of the ''[[Cirque du Freak]]'' book series, Darren and Harkat must go into an alternate world. They then find a fallout shelter with post cards on the refrigerator from the late 1940s and realized that they had gone forward in time. |
|||
The [[Fallout series|''Fallout'' series]] of computer games depicts the remains of human civilization after an immensely destructive nuclear war; the United States of America had built underground vaults that were advertised to protect the general population against a nuclear attack, but were, in fact, grand social experiments that did little to protect their inhabitants. |
|||
''[[Paranoia (role-playing game)|Paranoia]]'', a role-playing game, takes place in a form of fallout shelter, which has become ruled by an insane computer. |
|||
The ''[[Metro 2033 (book)|Metro 2033]]'' book series by Russian author [[Dmitry Glukhovsky]] depicts survivors' life in the subway systems below Moscow and Saint-Petersburg after a global nuclear holocaust. |
|||
[[Cormac McCarthy]]'s book ''[[The Road]]'' and the accompanying movie has its main characters finding a shelter ([[bomb shelter|bomb]] or fallout) with uneaten rations. |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{Multicol}} |
|||
* [[Blast shelter]] |
|||
* [[Bomb shelter]] |
|||
* [[Bunker]] |
|||
* [[Collective protection]] |
|||
* [[Command center]] |
|||
* [[Continuity of government]] |
|||
* [[The Greenbrier]] |
|||
* [[Vivos (underground shelter)]] |
|||
* [[Ark Two Shelter]] |
|||
* [[Abo Elementary School]] |
|||
'''Nation specific:''' |
|||
* [[Diefenbunker]] |
|||
* [[Sonnenberg Tunnel]] |
|||
* [[Central Government War Headquarters]], The UKs Gov. War Headquarters at Corsham, Wiltshire. |
|||
* [[HANDEL]], UK's national attack warning system |
|||
{{Multicol-break}} |
|||
'''General:''' |
|||
* [[Fission product]] |
|||
* [[Retreat (survivalism)]] |
|||
* [[Survivalism]] |
|||
'''Publications:''' |
|||
* ''[[Fallout Protection]]'' |
|||
* ''[[Survival Under Atomic Attack]]'' |
|||
* ''[[Nuclear War Survival Skills]]'' |
|||
{{Multicol-end}} |
|||
== Notes and references== |
|||
{{Reflist|2}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
* [http://knol.google.com/k/bill-geerhart/an-indelible-cold-war-symbol/1uefuvb7s5ifz/12# History of the design of the Fallout Shelter Sign] |
|||
* [http://www.bomb-shelter.net/nuclear-weapons Fallout exposure based on size of bomb and distance from explosion. (www.bomb-shelter.net)] |
|||
* [http://www.undergroundbombshelter.com/bomb-shelter-questions.htm Bomb Shelter Questions and Answers (www.undergroundbombshelter.com)] |
|||
* [http://www.oism.org/nwss/s73p930.htm Nuclear War Survival Skills app. A: Instructions for Six Expedient Fallout Shelters] |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Fallout Shelter}} |
|||
[[Category:Civil defense]] |
|||
[[Category:Cold War sites]] |
|||
[[Category:Nuclear warfare]] |
|||
[[Category:Radioactivity]] |
|||
[[Category:Radiobiology]] |
|||
[[Category:Rooms]] |
|||
[[Category:Subterranea (geography)]] |
|||
[[Category:Survivalism]] |
|||
[[Category:Radiation protection]] |
|||
2014年5月29日 (四) 14:35的版本

| 核武器 |
|---|
 |
|
|
A fallout shelter is an enclosed space specially designed to protect occupants from radioactive debris or fallout resulting from a nuclear explosion. Many such shelters were constructed as civil defense measures during the Cold War.
During a nuclear explosion, matter vaporized in the resulting fireball is exposed to neutrons from the explosion, absorbs them, and becomes radioactive. When this material condenses in the rain, it forms dust and light sandy materials that resembles ground pumice. The fallout emits alpha and beta particles, as well as gamma rays.
Much of this highly radioactive material then falls to earth, subjecting anything within the line of sight to radiation, a significant hazard. A fallout shelter is designed to allow its occupants to minimize exposure to harmful fallout until radioactivity has decayed to a safer level.
Although many shelters still exist, some even being used as museums, virtually all fallout shelters have been decommissioned since the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991.[來源請求]
History

During the Cold War, many countries built fallout shelters for high-ranking government officials and crucial military facilities, such as Project Greek Island and Cheyenne Mountain nuclear bunker in the United States and Canada's Emergency Government Headquarters. Plans were made, however, to use existing buildings with sturdy below-ground-level basements as makeshift fallout shelters. These buildings were usually placarded with the yellow and black trefoil sign.
The National Emergency Alarm Repeater (N.E.A.R.) program was developed in 1956 during the Cold War to supplement the existing siren warning systems and radio broadcasts in the event of a nuclear attack. The N.E.A.R. civilian alarm device was engineered and tested but the program was not viable and went defunct about 1966.[1] In the U.S. in September 1961, under the direction of Steuart L. Pittman, the federal government started the Community Fallout Shelter Program.[2][3] A letter from President Kennedy advising the use of fallout shelters appeared in the September 1961 issue of Life magazine.[4]
In November 1961 in Fortune magazine, an article by Gilbert Burck appeared that outlined the plans of Nelson Rockefeller, Edward Teller, Herman Kahn, and Chet Holifield for an enormous network of concrete lined underground fallout shelters throughout the United States sufficient to shelter millions of people to serve as a refuge in case of nuclear war.[5]
American fallout shelters in the early 1960s were sometimes funded in conjunction with funding for other federal programs, such as urban renewal projects of the Federal Housing Authority, examples being Barrington Plaza, and other development projects of Los Angeles County Civil Defense and Disaster Commissioner, Louis Lesser, and were designed for large numbers of citizens.[6][7][8]
Switzerland built an extensive network of fallout shelters, not only through extra hardening of government buildings such as schools, but also through a building regulation that ensured that all residential building built after 1978 contained a nuclear shelter able to withstand a blast from a 12 megaton explosion at a distance of 700 metres.[9] In addition, the Swiss government maintains large communal shelters (including the Sonnenberg Tunnel) stocked with over four months of food and fuel.[9] The reference Nuclear War Survival Skills declared that, as of 1986, "Switzerland has the best civil defense system, one that already includes blast shelters for over 85 percent of all its citizens."[10]
Similar projects have been undertaken in Finland, which requires all buildings with area over 600 m² to have an NBC shelter, and Norway, which requires all buildings with an area over 1000 m² to have a shelter.[11]
The former Soviet Union and other Eastern Bloc countries often designed their underground mass-transit and subway tunnels to serve as bomb and fallout shelters in the event of an attack.
In Switzerland, most residential shelters are no longer stocked with the food and water required for prolonged habitation and a large number have been converted by the owners to other uses (e.g., wine cellars, ski rooms, gyms).[9] These shelters also provide a haven from natural disasters such as tornadoes and hurricanes, although Switzerland is rarely subject to such natural phenomena.
Details of shelter construction


Shielding
A basic fallout shelter consists of shields that reduce gamma ray exposure by a factor of 1000. The required shielding can be accomplished with 10 times the thickness of any quantity of material capable of cutting gamma ray exposure in half. Shields that reduce gamma ray intensity by 50% (1/2) include 1 cm (0.4 inch) of lead, 6 cm (2.4 inches) of concrete, 9 cm (3.6 inches) of packed earth or 150 m (500 ft) of air. When multiple thicknesses are built, the shielding multiplies. Thus, a practical fallout shield is ten halving-thicknesses of packed earth, reducing gamma rays by approximately 1024 times (210).[12]
Usually, an expedient purpose-built fallout shelter is a trench; with a strong roof buried by c. 1 m (3 ft) of earth. The two ends of the trench have ramps or entrances at right angles to the trench, so that gamma rays cannot enter (they can travel only in straight lines). To make the overburden waterproof (in case of rain), a plastic sheet may be buried a few inches below the surface and held down with rocks or bricks.[13]
Blast doors are designed to absorb the shock wave of a nuclear blast, bending and then returning to their original shape.[14]
Climate control
Dry earth is a reasonably good thermal insulator, and over several weeks of habitation, a shelter will become dangerously hot.[15] The simplest form of effective fan to cool a shelter is a wide, heavy frame with flaps that swing in the shelter's doorway and can be swung from hinges on the ceiling. The flaps open in one direction and close in the other, pumping air. (This is a Kearny Air Pump, or KAP, named after the inventor, Cresson Kearny)
Unfiltered air is safe, since the most dangerous fallout has the consistency of sand or finely ground pumice.[15] Such large particles are not easily ingested into the soft tissues of the body, so extensive filters are not required. Any exposure to fine dust is far less hazardous than exposure to the fallout outside the shelter. Dust fine enough to pass the entrance will probably pass through the shelter.[15] Some shelters, however, incorporate NBC-filters for additional protection.
Locations
Effective public shelters can be the middle floors of some tall buildings or parking structures, or below ground level in most buildings with more than 10 floors. The thickness of the upper floors must form an effective shield, and the windows of the sheltered area must not view fallout-covered ground that is closer than 1.5 km (1 mi). One of Switzerland's solutions is to utilise road tunnels passing through the mountains; with some of these shelters being able to protect tens of thousands.[16]
Fallout shelters are not always underground. Above ground buildings with walls and roofs dense enough to afford a meaningful protection factor can be used as a fallout shelter.[17]
Contents
A battery-powered radio may be helpful to get reports of fallout patterns and clearance. However, radio and other electronic equipment may be disabled by electromagnetic pulse. For example, even at the height of the cold war, EMP protection had been completed for only 125 of the approximately 2,771 radio stations in the United States Emergency Broadcast System. Also, only 110 of 3,000 existing Emergency Operating Centers had been protected against EMP effects.[18] The Emergency Broadcast System has since been supplanted in the United States by the Emergency Alert System.
The reference Nuclear War Survival Skills includes the following supplies in a list of "Minimum Pre-Crisis Preparations": one or more shovels, a pick, a bow-saw with an extra blade, a hammer, and 4-mil polyethylene film (also any necessary nails, wire, etc.); a homemade shelter-ventilating pump (a KAP); large containers for water; a plastic bottle of sodium hypochlorite bleach; one or two KFMs and the knowledge to operate them; at least a 2-week supply of compact, nonperishable food; an efficient portable stove; wooden matches in a waterproof container; essential containers and utensils for storing, transporting, and cooking food; a hose-vented 5-gallon can, with heavy plastic bags for liners, for use as a toilet; tampons; insect screen and fly bait; any special medications needed by family members; Pure potassium iodide, a 2-oz bottle, and a medicine- dropper; A first-aid kit and a tube of antibiotic ointment; long-burning candles (with small wicks) sufficient for at least 14 nights; an oil lamp; a flashlight and extra batteries; and a transistor radio with extra batteries and a metal box to protect it from EMP.[19]
Inhabitants should have water on hand, 1-2 gallons per person per day. Water stored in bulk containers requires less space than water stored in smaller bottles.[20]
Kearny Fallout Meter
Commercially made Geiger counters are expensive and require frequent calibration. It is possible to construct an electrometer-type radiation meter called the Kearny Fallout Meter, which does not require batteries or professional calibration, from properly-scaled plans with just a coffee can or pail, gypsum board, monofilament fishing line, and aluminum foil.[21] Plans are freely available in the public domain in the reference Nuclear War Survival Skills by Cresson Kearny.[22]
Use
Inhabitants should plan to remain sheltered for at least two weeks (with an hour out at the end of the first week – see Swiss Civil Defense guidelines (which was once part of Swiss Zivilschutz)), then work outside for gradually increasing amounts of time, to four hours a day at three weeks. The normal work is to sweep or wash fallout into shallow trenches to decontaminate the area. They should sleep in a shelter for several months. Evacuation at three weeks is recommended by official authorities.[來源請求]
If available, inhabitants may take potassium iodide at the rate of 130 mg/day per adult (65 mg/day per child) as an additional measure to protect the thyroid gland from the uptake of dangerous radioactive iodine, a component of most fallout and reactor waste.[23]
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Different types of radiation emitted by fallout
Alpha (α)
In the vast majority of accidents, and in all atomic bomb blasts, the threat due to beta and gamma emitters is greater than that posed by the alpha emitters in the fallout. Alpha particles are identical to a helium-4 nucleus (two protons and two neutrons), and travel at speeds in excess of 5% of the speed of light. Alpha particles have little penetrating power; most cannot penetrate through human skin. Avoiding direct exposure with fallout particles will prevent injury from alpha radiation.[25]
Beta (β)
Beta radiation consists of particles (high-speed electrons) given off by some fallout. Most beta particles cannot penetrate more than about 10 feet (3 m) of air or about 1⁄8 inch (3 mm) of water, wood, or human body tissue; or a sheet of aluminum foil. Avoiding direct exposure with fallout particles will prevent most injuries from beta radiation.[26]
The primary dangers associated with beta radiation are internal exposure from ingested fallout particles and beta burns from fallout particles no more than a few days old. Beta burns can result from contact with highly radioactive particles on bare skin; ordinary clothing separating fresh fallout particles from the skin can provide significant shielding.[26]
Gamma (γ)
Gamma radiation penetrates further through matter than alpha or beta radiation. Most of the design of a typical fallout shelter is intended to protect against gamma rays. Gamma rays are better absorbed by materials with high atomic numbers and high density, although neither effect is important compared to the total mass per area in the path of the gamma ray. Thus, lead is only modestly better as a gamma shield than an equal mass of another shielding material such as aluminum, concrete, water or soil.
Some gamma radiation from fallout will penetrate into even the best shelters. However, the radiation dose received while inside a shelter can be significantly reduced with proper shielding. Ten halving thicknesses of a given material can reduce gamma exposure to less than 1⁄1000 of unshielded exposure.[27]
Weapons versus nuclear accident fallout
The bulk of the radioactivity in nuclear accident fallout is more long-lived than that in weapons fallout. A good table of the nuclides, such as that provided by the Korean Atomic Energy Research Institute, includes the fission yields of the different nuclides. From this data it is possible to calculate the isotopic mixture in the fallout (due to fission products in bomb fallout).[來源請求]
Other matters and simple improvements
While a person's home may not be a purpose-made shelter, it could be thought of as one if measures are taken to improve the degree of fallout protection.
Measures to lower the beta dose
The main threat of beta radiation exposure comes from hot particles in contact with or close to the skin of a person. Also, swallowed or inhaled hot particles could cause beta burns. As it is important to avoid bringing hot particles into the shelter, one option is to remove one's outer clothing, or follow other decontamination procedures, on entry. Fallout particles will cease to be radioactive enough to cause beta burns within a few days following a nuclear explosion. The danger of gamma radiation will persist for far longer than the threat of beta burns in areas with heavy fallout exposure.[28]
Measures to lower the gamma dose rate
The gamma dose rate due to the contamination brought into the shelter on the clothing of a person is likely to be small (by wartime standards) compared to gamma radiation that penetrates through the walls of the shelter.[28] The following measures can be taken to reduce the amount of gamma radiation entering the shelter:
- Roofs and gutters can be cleaned to lower the dose rate in the house.
- The top inch of soil in the area near the house can be either removed or dug up and mixed with the subsoil. This reduces the dose rate as the gamma rays have to pass through the topsoil before they can irradiate anything above.
- Nearby roads can be rinsed and washed down to remove dust and debris; the fallout would collect in the sewers and gutters for easier disposal. In Kiev after the Chernobyl accident a program of road washing was used to control the spread of radioactivity.
- Windows can be bricked up, or the sill raised to reduce the hole in the shielding formed by the wall.
- Gaps in the shielding can be blocked using containers of water. While water has a much lower density than that of lead, it is still able to shield some gamma rays.
- Earth (or other dense material) can be heaped up against the exposed walls of the building; this forces the gamma rays to pass through a thicker layer of shielding before entering the house.
- Nearby trees can be removed to reduce the dose due to fallout which is on the branches and leaves. It has been suggested by the US government that a fallout shelter should not be dug close to trees for this reason.[29]
Fallout shelters in popular culture

Fallout shelters feature prominently in the Robert A. Heinlein novel Farnham's Freehold (Heinlein built a fairly extensive shelter near his home in Colorado Springs in 1963),[30] Pulling Through by Dean Ing, A Canticle for Leibowitz by Walter M. Miller and Earth by David Brin.
The Twilight Zone episode "The Shelter", from a Rod Serling script, deals with the consequences of actually using a shelter.
In the Only Fools and Horses episode "The Russians are Coming", Derek Trotter buys a lead fallout shelter, then decides to construct it in fear of an impending nuclear war caused by the Soviet Union (who were still active during the episode's creation).
The 1982 album The Nightfly by Donald Fagen features a song, 'New Frontier', about an early-1960s teenager enticing his girlfriend into spending a romantic weekend with him in his family's backyard fallout shelter.
In 1999 the film Blast from the Past was released. It is a romantic comedy film about a nuclear physicist, his wife, and son that enter a well-equipped, spacious fallout shelter during the 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis. They do not emerge until 35 years later, in 1997. The film shows their reaction to contemporary society.
In book 11 of the Cirque du Freak book series, Darren and Harkat must go into an alternate world. They then find a fallout shelter with post cards on the refrigerator from the late 1940s and realized that they had gone forward in time.
The Fallout series of computer games depicts the remains of human civilization after an immensely destructive nuclear war; the United States of America had built underground vaults that were advertised to protect the general population against a nuclear attack, but were, in fact, grand social experiments that did little to protect their inhabitants.
Paranoia, a role-playing game, takes place in a form of fallout shelter, which has become ruled by an insane computer.
The Metro 2033 book series by Russian author Dmitry Glukhovsky depicts survivors' life in the subway systems below Moscow and Saint-Petersburg after a global nuclear holocaust.
Cormac McCarthy's book The Road and the accompanying movie has its main characters finding a shelter (bomb or fallout) with uneaten rations.
See also
Nation specific:
|
General: Publications: |
Notes and references
- ^ [1][失效連結]
- ^ Civil Defense Museum-Community Shelter Tours Main Page. www.civildefensemuseum.com. [2008-09-14].
- ^ FALLOUT FEVER: Civil Defense shelters dotted area cities during the Cold War – My Web Times. mywebtimes.com. [2008-09-14].
- ^ DOE.gov
- ^ Fortune magazine November 1961 Pages 112–115 et al
- ^ Los Angeles Times, November 15, 1961 “Board Asks Full Study of Shelters” [2]
- ^ Los Angeles Times, Oct 15, 1961
- ^ Los Angeles Times, December 3, 1961 “Businessman Appointed to CD Group” [3]
- ^ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Ball, Deborah. Swiss Renew Push for Bomb Shelters. Wall Street Journal. June 25, 2011 [18 December 2012].
- ^ Kearny, Cresson H. Nuclear War Survival Skills. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. 1986: 6–10. ISBN 0-942487-01-X.
- ^ FOR 1995-03-15 nr 254: Forskrift om tilfluktsrom. Lovdata.no. [2012-08-15].
- ^ Halving-thickness for various materials. "The Compass DeRose Guide to Emergency Preparedness - Hardened Shelters".
- ^ Kearny, Cresson H. Nuclear War Survival Skills. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. 1986: 37–45. ISBN 0-942487-01-X.
- ^ Secret U.S. Bunkers. Lost Worlds. 第18集. August 29, 2007. The History Channel.
- ^ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Kearny, Cresson H. Nuclear War Survival Skills. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. 1986: 51–56. ISBN 0-942487-01-X.
- ^ Foulkes, Imogen. Swiss still braced for nuclear war. BBC News, Switzerland. 10 February 2007 [15 August 2012].
- ^ Monteyne, David. Fallout Shelter: Designing for Civil Defense in the Cold War. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota, 2011. Print.
- ^ Kearny, Cresson H. Nuclear War Survival Skills. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. 1986: 24. ISBN 0-942487-01-X.
- ^ Kearny, Cresson H. Nuclear War Survival Skills. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. 1986: 133–134. ISBN 0-942487-01-X.
- ^ Hammes, JA. Fallout shelter survival research. 1966: 154–159.
- ^ Kearny, Cresson H. The KFM, A Homemade Yet Accurate and Dependable Fallout Meter (PDF). Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. 1978.
- ^ Kearny, Cresson H. Nuclear War Survival Skills. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. 1986: 95–100. ISBN 0-942487-01-X.
- ^ Kearny, Cresson H. Nuclear War Survival Skills. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. 1986: 111–117. ISBN 0-942487-01-X.
- ^ 24.0 24.1 24.2 Note that this image was drawn using data from the OECD report and the second edition of The Radiochemical Manual
- ^ Kearny, Cresson H. Nuclear War Survival Skills. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. 1986: 45. ISBN 0-942487-01-X.
- ^ 26.0 26.1 Kearny, Cresson H. Nuclear War Survival Skills. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. 1986: 44. ISBN 0-942487-01-X.
- ^ Kearny, Cresson H. Nuclear War Survival Skills. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. 1986: 11–20. ISBN 0-942487-01-X.
- ^ 28.0 28.1 Kearny, Cresson H. Nuclear War Survival Skills. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. 1986: 131. ISBN 0-942487-01-X.
- ^ Kearny, Cresson H. Nuclear War Survival Skills. Oak Ridge, TN: Oak Ridge National Laboratory. 1986: 39. ISBN 0-942487-01-X.
- ^ site: Robert A. Heinlein – Archives – PM 6/52 Article
