曼尼普爾語
外觀
此條目可參照英語維基百科相應條目來擴充。 (2022年10月10日) |
| 曼尼普爾語 | |
|---|---|
| ꯃꯤꯇꯩ ꯂꯣꯟ | |
| 母語國家和地區 | 印度東北、孟加拉國、緬甸 |
母語使用人數 | 超過150萬,當中絕大部份位於印度[1] |
| 語系 | |
| 文字 | 曼尼普爾文(Meitei Mayek)[2],但現時主要用孟加拉文來書寫。 |
| 官方地位 | |
| 作為官方語言 | 印度曼尼普爾邦 |
| 語言代碼 | |
| ISO 639-2 | mni |
| ISO 639-3 | 兩者之一:mni – 曼尼普爾語omp – 古曼尼普爾語 |
| 語言學家列表 | omp Old Manipuri |
| Glottolog | mani1292[3] |
| 瀕危程度 | |
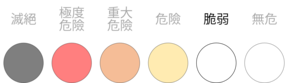
| 聯合國教科文組織認定的瀕危語言[4] 脆弱(UNESCO) | |
曼尼普爾語,又稱梅泰語(曼尼普爾語:ꯃꯤꯇꯩ ꯂꯣꯟ,羅馬化:Meitei lon、pangal-lol)是印度東北部喜馬拉雅山區東南部的曼尼普爾邦的官方語言及共通語,屬於漢藏語系。曼尼普爾語亦有在阿薩姆邦、特里普拉邦及孟加拉與緬甸通行。它已成為了曼尼普爾邦內各民族間的重要團結要素,因為各民族靠這種語言來互相溝通。
曼尼普爾語有獨特的文字——曼尼普爾文(Meitei Mayek),運用該種文字書寫的最古老的文獻溯源於13世紀。
留意曼尼普爾語跟比什努普里亞-曼尼普爾語(ইমার ঠার/বিষ্ণুপ্রিয়া মণিপুরী)是兩種完全不同的語言:比什奴普萊利亞-曼尼普爾語是一種印度-雅利安語支的語言,但同樣通行於印度東北部、緬甸及孟加拉一帶,而且現時同樣使用孟加拉文來書寫。
方言
[編輯]曼尼普爾語有三種方言:
- Meiteieg (meitei)
- Loieg (loi)
- Pangaleg (pangal)
語音
[編輯]此章節需要擴充。 (2008年5月) |
文法
[編輯]此章節需要擴充。 (2008年5月) |
書寫系統
[編輯]曼尼普爾語有獨特的文字——曼尼普爾文(Meitei Mayek),運用該種文字書寫的最古老的文書大約在11世紀到12世紀左右,但到18世紀就沒有再使用。從1891年英國開始在印度的管治時,曼尼普爾語開始採用孟加拉文來書寫,直到現在。不過,現時有建議要恢復使用曼尼普爾文。
參看
[編輯]註釋
[編輯]- ^ 引自印度2001年人口統計資料
- ^ A Manipuri Grammar, Vocabulary, and Phrase Book - 1888 Assam Secretariat Press
- ^ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian (編). Manipuri. Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. 2016.
- ^ UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in danger, UNESCO
參考文獻
[編輯]文化
[編輯]- Brara, N. Vijaylakshmi. (1998). Politics, society, and cosmology in India's North East. Delphi: Oxford University Press.
- Budha, W. (1992). Indigenous games of the Meiteis. Manipur: Wangkeimayum Publications.
- Singh, M. Kirti. (1988). Religion and culture of Manipur. Delhi: Manas Publications.
- Singh, M. Kirti. (1993). Folk culture of Manipur. Delhi: Manas Publications.
語言
[編輯]- Bhat, D. N. S.; & Ningomba, S. (1997). Manipuri grammar. Munich: Lincom Europa.
- Chelliah, Shobhana L. (1990). Experiencer subjects in Manipuri. In V. M. Manindra & K. P. Mohanan (Eds.), Experiencer subjects in South Asian languages (pp. 195-211). Stanford: The Center for the Study of Language and Information.
- Chelliah, Shobhana L. (1992). Tone in Manipuri. In K. L. Adams & T. J. Hudak (Eds.), Papers from the first annual meeting of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society 1991 (pp. 65-85). Tempe, AZ: Arizona State University.
- Chelliah, Shobhana L. (1992). Bracketing paradoxes in Manipuri. In M. Aronoff (Ed.), Morphology now (pp. 33-47). Albany: State University of New York Press.
- Chelliah, Shobhana L. (1994). Morphological change and fast speech phenomena in the Manipuri verb. In K. L. Adams & T. J. Hudak (Eds.), Papers from the second annual meeting of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society 1992 (pp. 121-134). Tempe, AZ: Arizona State University.
- Chelliah, Shobhana L. (1997). A grammar of Meithei. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter. ISBN 0-19-564331-3.
- Chelliah, Shobhana L. (2002). Early Meithei manuscripts. In C. I. Beckwith (Ed.), Medieval Tibeto-Burman languages: PIATS 2000: Tibetan studies: Proceedings of the ninth seminar of the International Association of Tibetan Studies, Leiden 2000 (pp. 59-71). Leiden, Netherlands: Brill.
- Chelliah, Shobhana L. (2002). A glossary of 39 basic words in archaic and modern Meithei. In C. I. Beckwith (Ed.), Medieval Tibeto-Burman languages: PIATS 2000: Tibetan studies: Proceedings of the ninth seminar of the International Association of Tibetan Studies, Leiden 2000 (pp. 189-190). Leiden, Netherlands: Brill.
- Chelliah, Shobhana L. (2004). Polysemy through metonymy: The case of Meithei pi 'grandmother'. Studies in Language, 28 (2), 363-386.
- Singh, Ningthoukhongjam Khelchandra. (1964). Manipuri to Manipuri & English dictionary.
外部連結
[編輯]維基百科提供如下語言版本:曼尼普爾語維基百科