阿爾隆
| 阿尔隆 Arlon(法語) Aarlen(荷蘭語) Arel(德語) Arel(盧森堡語) | |
|---|---|
| 坐标:49°41′N 05°49′E / 49.683°N 5.817°E | |
| 国家 | |
| 社群 | |
| 大区 | |
| 省 | |
| 区 | 阿爾隆區(区府) |
| 片区 | |
| 政府 | |
| • 市长 | 樊尚·马格努斯 (Arlon 2030) |
| • 执政党 | MRMC-ARLON 2030 |
| 面积 | |
| • 总计 | 119.06 平方公里(45.97 平方英里) |
| 面积排名 | 比利时市镇第43位 |
| 海拔 | 348 公尺(1,142 英尺) |
| 最高海拔 | 468 公尺(1,535 英尺) |
| 最低海拔 | 267 公尺(876 英尺) |
| 人口(2022年1月1日) | |
| • 總計 | 30,818人 |
| • 排名 | 比利时市镇第80位 |
| • 密度 | 259人/平方公里(670人/平方英里) |
| 居民称谓 | 法语: Arlonais(男性) Arlonaise(女性) 荷兰语: Aarlenaar(男性) Aarlense(女性) |
| 时区 | CET(UTC+01:00) |
| • 夏时制 | CEST(UTC+02:00) |
| 邮政编码 | 6700, 6704, 6706 |
| NIS编码 | 81001 |
| 电话区号 | 063 |
| 網站 | arlon.be |
| 资料最后更新:2023-06-16 | |
阿尔隆(法語:Arlon,发音:[aʁlɔ̃] (ⓘ);荷蘭語:Aarlen,发音:[ˈaːrlə(n)] (ⓘ);德語:Arel,发音:[ˈaːʁəl] (ⓘ);盧森堡語:Arel,发音:[ˈaːʀəl] (ⓘ)),比利时瓦隆大区盧森堡省城市,同时也是该省省会与同名区区府,通行法语,是比利时法语社群的一部分。其市镇面积119.06平方千米,人口30,818人(2022年1月1日),是该省人口最多的市镇。
阿尔隆位于比卢边境,东与卢森堡大公国接壤,是阿尔隆地区的首府。阿尔隆是比利时最古老的城市之一,其城市起源可追溯至罗马高卢时期。阿尔隆历史上为卢森堡伯国与大公国的一部分,传统语言为卢森堡语(阿尔隆方言),但其如今已式微。今天,该市已成为所在地区的商业、行政、教育和工业中心[1][2]。
地名
[编辑]
词源
[编辑]该地曾以如下名称在史料里出现:Orolauno(300年左右)、Orol[aunenses](1-4世纪)、Erlont(931-956年)、[de] Arlo(1052年)、Areleonis(11世纪)、Arlon(1095年)、Aralune(1175年、1182年)、Arelunenis(1176年)、Herlons(1189年)、Erluns(1202年)、Arlunz(1214年)、Arlunenis(1214年)[3]。以Orolauno为例,其第一个语素“Oro”可能来自凯尔特语“are”,意为“在…前面”,“在…附近”,亦出现于“Armor”(阿摩尔)、“Armorique”(阿摩里卡)、“Arles”(阿尔勒)等地名中,对应古愛爾蘭語“air”、威尔士语“er”和布列塔尼语“ar”;第二个语素“launo”含义尚未明确,其可能指的是凯尔特人的一位泉神[4]。
各语名称
[编辑]比利时的官方语言为荷蘭語、法语和德语。阿尔隆的官方语言为法语,其法语名为“Arlon”。在比利时另外两种官方语言中,阿尔隆的荷兰语名为“Aarlen”(阿尔伦),德语名为“Arel”(阿勒尔)[5][6],不过其如今在德语中的常用名与其德语维基百科条目名均为其法语名“Arlon”[7][8]。
阿尔隆当地的传统语言为卢森堡语(阿尔隆方言),其卢森堡语名为“Arel”[9]。阿尔隆附近地区的其他地方语言为瓦隆语和洛林语(戈姆方言),其瓦隆语名为“Årlon”[10],洛林语戈姆方言名为“Ièrlon”[11]。
居民称谓词与形容词
[编辑]在法语中,阿尔隆的居民称谓词为“Arlonais”(男性)、“Arlonaise”(女性),形容词同为“arlonais”但首字母常小写。在荷兰语中,阿尔隆的居民称谓词为“Aarlenaar”(男性)[12]、“Aarlense”(女性)[13],形容词为“Aarlens”[14]。
中文译名
[编辑]“Arlon”的通行中文译名为“阿尔隆”。中国大陆方面,“Arlon”在《世界地名翻译大辞典》《世界地名译名词典》与《法国地图册》均译作“阿尔隆”[15][16][17]。台湾方面,“Arlon”在國家教育研究院乐词网译作“亞倫”[18],不过其并不常用,台湾常用译名亦为“阿爾隆”[19][20][21][22][23]。
历史
[编辑]古典时代
[编辑]
阿尔隆起源于古罗马时期的比利時高盧定居点奥罗劳努姆,位于兰斯、特里尔和科隆之间羅馬道路的十字路口,与图尔奈和通厄伦同为比利时最古老的城市[1]。1-3世纪,阿尔隆在瑟穆瓦河两岸蓬勃发展,出土的各类文物印证了古罗马时期这里的辉煌[1]。罗马帝国末期,高卢因日耳曼人的入侵而陷入动荡[1]。3世纪末,高卢罗马人开始在克尼普申山周围建造城墙以防日耳曼人的入侵[1][24]。尼普顿塔和朱庇特塔为该城墙的两座罗马塔,建于400年左右,分别于1948年和2009年出土[25][26]。
中世纪
[编辑]
5世纪中叶,法蘭克人占领了阿尔隆,之后西羅馬帝國灭亡,阿尔隆先后由墨洛溫、加洛林和洛塔林吉亚统治。870年,阿尔隆依《梅尔森条约》归西法兰克国王秃头查理,此时与今天拼写相同的“Arlon”一称就已出现[1]。9世纪,阿尔隆及其周边地区成为了一个伯国。1065年,阿尔隆伯爵瓦勒良二世成为林堡伯爵瓦勒良一世[27],阿尔隆和林堡两伯国自此联合。1214年,林堡的瓦勒良三世与卢森堡女伯爵埃尔梅辛德一世结婚。1221年,瓦勒良三世之父亨利三世逝世,瓦勒良三世成为林堡公爵与阿尔隆侯爵(称阿尔隆的瓦勒良四世),阿尔隆伯国升格为阿尔隆侯国[28][29][註 1]。1226年,瓦勒良三世去世,阿尔隆侯国由其子亨利五世继承。1247年,亨利五世之母埃尔梅辛德一世去世,亨利五世成为卢森堡伯爵[30]。阿尔隆脱离了林堡,并入了卢森堡。1291年,加尔默罗会信徒定居阿尔隆[1]。1353年,卢森堡伯国升格为公国。1441年,卢森堡女公爵哥利茲的伊莉莎白将卢森堡公国割让给勃艮第公爵菲利普三世,阿尔隆随之归勃艮第统治,成为勃艮第属尼德兰的一部分[1]。
近现代
[编辑]

15世纪末,阿尔隆随勃艮第归哈布斯堡王朝统治,成为哈布斯堡尼德兰的一部分。查理五世统治时期,卢森堡成为了法国人和西班牙人的战场,阿尔隆处于战乱和动荡中[1]。1556年,尼德兰归哈布斯堡王朝西班牙支系所有,阿尔隆成为西屬尼德蘭的一部分。1558年,吉斯公爵弗朗索瓦在蒂永维尔围城战中取胜,之后又攻占了阿尔隆,将其洗劫一空并烧毁[31][1]。16世纪末至17世纪初,阿尔隆屡遭袭击和火灾[1]。1604年,一支荷兰军队进攻了阿尔隆并将城墙摧毁,之后城墙按意大利样式重建[1]。1621年,嘉布遣会在克尼普申山顶修建了一座修道院[1]。1660年,一场大火烧毁了这座城市,圣马丁教堂葬于火海[1]。1681年,法国国王路易十四的军队攻占了阿尔隆,总督决定建造一座新的教区教堂和一堵新的城墙,费用由法国国王承担[1]。1682年,阿尔隆的城墙被拆除,发展出了新的街区[1]。1683年,路易十四发动了重盟战争,次年攻占了卢森堡公国。1697年,阿尔隆随卢森堡公国依《赖斯韦克条约》重归哈布斯堡西班牙[1]。1700年,西班牙哈布斯堡王朝绝嗣,次年西班牙王位繼承戰爭爆发。1714年,卢森堡公国依《烏得勒支和約》归哈布斯堡王朝奥地利支系所有,阿尔隆成为奥属尼德兰的一部分。1785年,一场大火席卷了整座城市,故此前的建筑今天在市中心完全消失[1]。
法国大革命战争期间,1793年和1794年,法国和奥地利两度在阿尔隆开战。1795年,法国吞并奥属尼德兰,卢森堡公国终结,阿尔隆随之再度归法国统治,隶属于新设的森林省阿尔隆县(Canton d'Arlon),阿尔隆为该县县治[32]。1796年,加尔默罗会和嘉布遣会被驱逐[1]。1800年2月17日,森林省划分为4个区,阿尔隆及阿尔隆县隶属于卢森堡区[33]。1815年,拿破仑在滑铁卢战役败北,法兰西第一帝国覆灭,法国在大革命战争和拿破仑战争时期兼并的领土被划出。依《维也纳会议》,卢森堡大公国成立,加入德意志邦聯,与荷蘭聯合王國组成共主邦聯,阿尔隆成为卢森堡大公国的一部分。依荷兰联合王国1822年和1823年的皇家法令,卢森堡大公国划分为8个行政区(district),阿尔隆县隶属于阿尔隆行政区,但阿尔隆并不隶属于该行政区,其具有城市地位[32][34]。
1830年,比利时从荷蘭聯合王國独立,卢森堡大公国由比利时控制。1839年,卢森堡大公国依《伦敦条约》被瓜分,阿尔隆及其周边地区划入比利时,成为比利时卢森堡省,阿尔隆为省会[1]。1858年,布鲁塞尔-阿尔隆铁路开始全线运营,次年接入卢森堡,阿尔隆人口随着公务员和铁路工人的大量涌入而增加[1][35]。

1907-1914年,阿尔隆修建了新的圣马丁教堂,这便是今天的阿尔隆圣马丁教堂[1]。第一次世界大战期间,1914年8月26日,德军处决了133名平民(其中包括108名来自罗西尼奥勒的流离失所者),摧毁了100座建筑物[36]。第二次世界大战期间,1940年5月10日,盟军进入比利时,法国第3龙骑兵团和第2装甲车团(2e Régiment d'automitrailleuses)守卫阿尔隆[37]。上午,德军第10装甲师抵达阿尔隆郊区,但被法军击退[37]。为了不耽误时间,第10装甲师北上离开了阿尔隆。当天晚些时候,阿尔隆被歐根·里特爾·馮·肖伯特的第7军攻占[38]。1942年,阿尔隆市议会遭解散[1]。1944年9月10日,由诺曼·科塔少将指挥的美國陸軍第28步兵師解放了阿尔隆[39]。
1977年1月1日,阿尔隆与市镇博内尔特、吉尔什、欧泰尔巴、特尔尼什、安什和原属于市镇阿希的村庄富什和桑蓬及原属于市镇沃尔克朗日的村庄塞斯利什合并,组成了今天的阿尔隆市镇。
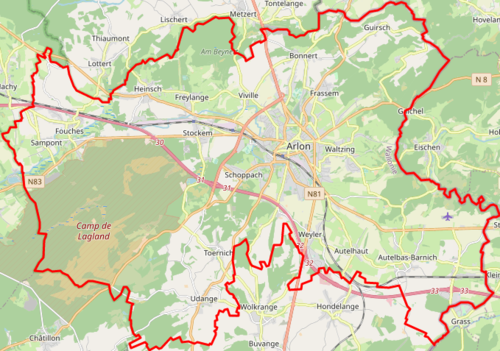
地理
[编辑]阿尔隆位于比利时、瓦隆大区与卢森堡省东南部,比卢边境,距离瓦隆大区首府那慕爾110千米[40],距离比利时首都布鲁塞尔166千米[41]。与阿尔隆接壤的市镇包括:梅桑西、圣莱热、埃塔勒、阿拜、阿泰尔特、贝克里希、哈布施特、施泰因福特、凯尔任、加尼希[42]。
阿尔隆坐标49°41'1"N, 5°49'0"E,市镇面积119.06平方千米,在比利时所有市镇中排名第43位。境内海拔在268-476米之间,平均海348米[43],属于依海拔高度划分的上比利时(la haute Belgique)地区[44]。
阿尔隆是比利时洛林地区的一部分,以阿尔隆为中心的历史与文化地区被称为“阿尔隆地区”。
-
阿尔隆的OSM定位图
-
阿尔隆的OSM定位图(含周围城镇)
-
阿尔隆的OSM地形图
地形
[编辑]阿尔隆市区地形以平原为主,斯托凯姆山位于市镇西部,海拔386米。克尼普申山是当地的一座小山丘,也是阿尔隆古城的历史中心区。
地质
[编辑]阿尔隆地区覆盖着含铁砾石,其延伸至比卢边境,在砂质粘土中以颗粒、结核或块状出现,无差别分布于各种侏罗纪地层中[45]。
水文
[编辑]
阿尔隆位于默兹河与莱茵河流域交界处,瑟穆瓦河发源于市中心,梅桑西河发源于市镇南部,属于默兹河流域;艾施河流经市镇东南比卢交界处,其支流克莱尔方丹河与欧泰尔巴河发源于市镇内,属于莱茵河流域[46]。
土地使用
[编辑]2021年,阿尔隆市镇面积119.06平方千米,其中树林面积30.90平方千米,建筑用地面积29.90平方千米,住宅用地面积7.64平方千米,工业用地面积0.82平方千米,采石场、矿井、矿山等用地面积0.14平方千米,商业用地面积0.93平方千米,公共服务(不包含交通、通信与科技基础设施)用地面积1.55平方千米,混合用途用地面积9.59平方千米,交通、通信用地面积7.96平方千米,科技基础设施用地面积0.09平方千米,游憩用地及其他开放空间面积1.18平方千米[47]。
气候
[编辑]根据柯本气候分类法,同比利时多数地区一样,阿尔隆属于温带海洋性气候(Cfb)[48]。阿尔隆是一座降水量大的城市,即便在最干燥的月份也有许多降水。阿尔隆年平均气温为8.9℃,年平均降雨量为1117.4毫米。
| 阿尔隆 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 月份 | 1月 | 2月 | 3月 | 4月 | 5月 | 6月 | 7月 | 8月 | 9月 | 10月 | 11月 | 12月 | 全年 |
| 平均高温 °C(°F) | 3.9 (39.0) |
5.0 (41.0) |
8.9 (48.0) |
12.9 (55.2) |
17.6 (63.7) |
20.5 (68.9) |
22.9 (73.2) |
22.4 (72.3) |
17.9 (64.2) |
13.4 (56.1) |
7.8 (46.0) |
4.5 (40.1) |
13.0 (55.4) |
| 日均气温 °C(°F) | 1.0 (33.8) |
1.5 (34.7) |
4.8 (40.6) |
7.9 (46.2) |
12.2 (54.0) |
15.1 (59.2) |
17.3 (63.1) |
17.0 (62.6) |
13.3 (55.9) |
9.5 (49.1) |
4.8 (40.6) |
2.0 (35.6) |
8.9 (48.0) |
| 平均低温 °C(°F) | −1.8 (28.8) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
0.8 (33.4) |
3.0 (37.4) |
7.2 (45.0) |
10.1 (50.2) |
12.1 (53.8) |
11.6 (52.9) |
8.5 (47.3) |
5.6 (42.1) |
1.9 (35.4) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
4.8 (40.6) |
| 平均降水量 mm(英寸) | 126.1 (4.96) |
96.3 (3.79) |
96.7 (3.81) |
70.7 (2.78) |
78.1 (3.07) |
80.2 (3.16) |
74.4 (2.93) |
76.9 (3.03) |
81.3 (3.20) |
105.3 (4.15) |
103.4 (4.07) |
128.1 (5.04) |
1,117.4 (43.99) |
| 平均降水天数 | 14.5 | 11.7 | 14.0 | 10.5 | 11.8 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 11.0 | 12.3 | 14.0 | 14.4 | 146.4 |
| 月均日照時數 | 45 | 73 | 124 | 172 | 202 | 206 | 227 | 213 | 149 | 103 | 47 | 39 | 1,599 |
| 数据来源:比利时皇家气象研究所[49] | |||||||||||||
自然生态
[编辑]
阿尔隆属于大陆生物地理区域[50]。阿尔隆当前森林以亚自然古森林(Forêt ancienne subnaturelle)、古森林转针叶林(Transformation résineuse de forêt ancienne)、种植阔叶林(Boisement feuillu)和种植针叶林(Boisement résineux)为主[51]。
为促进森林地区旅游发展,瓦隆政府引入“阿登森林”概念并将其划分为4个区域,阿尔隆与邻近的8个市镇属于昂利耶大森林(La Grande Forêt d'Anlier)[52][53]。
在有关生物研究与保护的地点方面,阿尔隆有55个具有重大生物学意义的地点(SGIB)、1个具有科学意义的地下洞穴(CSIS)、4个核准自然保护区(RNA)和3个国有自然保护区(RND)[54]。阿尔隆有5个Natura 2000保护区[55],分布于市镇西部与东南部[56],占市镇面积的25.1%[57]。
2019年10月,环保人士在绍帕克采沙场SGIB建立了阿尔隆保卫区,目的是阻止由市际组织IDELUX和市长樊尚·马格努斯规划的经济园区的建设,保护该SGIB,使其免受城市化影响。2021年3月15日,该保卫区被拆除警察[58]。
自然灾害
[编辑]洪水
[编辑]阿尔隆的洪水风险地区主要在郊区,且风险等级以极低危为主,城中心基本无洪水风险地区[59][60][61]。2014年7月29日,阿尔隆发生洪水,二十余辆汽车受损[62][63]。
区划
[编辑]- 行政
阿尔隆是比利时瓦隆大区盧森堡省阿爾隆區的一个市镇(享有城市称号),NIS编码81001。
今天的阿尔隆市镇于1977年1月1日由原阿尔隆与市镇欧泰尔巴、博内尔特、吉尔什、安什、特尔尼什外加原属于市镇阿希的村庄富什和桑蓬及原属于市镇沃尔克朗日的村庄塞斯利什合并而成。合并前的各市镇(含原阿尔隆)成为了今阿尔隆市镇的片区,村庄富什和桑蓬属于安什片区,村庄塞斯利什属于阿尔隆片区。
| 阿尔隆各片区信息 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 片区名称 | 面积 (km²) | 人口 (2022年) | 邮政编码 | NIS编码 | |
| 阿尔隆 Arlon |
8.94 | 16479 | 6700 | 81001A | |
| 欧泰尔巴 Autelbas |
24.16 | 2547 | 6706 | 81001B | |
| 安什 Heinsch |
39.07 | 5554 | 6700 | 81001C | |
| 博内尔特 Bonnert |
17.81 | 4863 | 6700 | 81001D | |
| 吉尔什 Guirsch |
8.32 | 275 | 6704 | 81001E | |
| 特尔尼什 Toernich |
20.77 | 1060 | 6700 | 81001F | |
| 来源:比利时统计局[64] | |||||
| 阿尔隆各片区地点 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 片区 | 地点 | |
| 阿尔隆 Arlon |
市中心外加塞斯利什 | |
| 欧泰尔巴 Autelbas |
欧泰尔巴、巴尔尼什、欧泰洛、比雷勒、克莱尔方丹、斯泰嫩、斯泰尔珀尼什、韦莱尔 | |
| 安什 Heinsch |
安什、弗雷朗日、绍帕克、斯托凯姆外加富什和桑蓬 | |
| 博内尔特 Bonnert |
博内尔特、弗拉塞姆、塞姆里什、维维尔、瓦尔桑 | |
| 吉尔什 Guirsch |
吉尔什、埃克布斯 | |
| 特尔尼什 Toernich |
特尔尼什、于当日 | |
- 邮政与电信
阿尔隆邮政编码为6700、6704、6706,其中阿尔隆、博内尔特、安什(含富什和桑蓬)、特尔尼什片区为6700,吉尔什片区为6704,欧泰尔巴片区为6706。阿尔隆电话区号为063。
- 立法与司法
在选举方面,阿尔隆属于法语选举团(歐洲議會選舉)、卢森堡选区(联邦选举)、阿尔隆-马尔什昂法梅讷-巴斯托涅-维尔通-讷沙托选区(瓦隆尼亚议会选举)、阿尔隆省级选区(省议会选举)和阿尔隆选举县(Canton d'Arlon,市镇级以上选举时各选区的细分选区)。
在司法方面,阿尔隆属于卢森堡司法区,该司法区范围与卢森堡省相同。2014年之前,阿尔隆属于阿尔隆司法区。
- 警务与救援
在警务方面,阿尔隆属于阿尔隆-阿泰尔特-阿拜-马特朗日警区。
在消防救援方面,阿尔隆属于卢森堡救援区,该救援区范围与卢森堡省相同。
- 其他
比利时统计局将领土划分为若干统计区(secteur statistique)以便统计,阿尔隆市镇划分为70个统计区[65];瓦隆评估、预测和统计研究所(IWEPS)将瓦隆大区领土划分为若干统计街区(quartiers statistiques)[66],阿尔隆市镇划分为27个统计街区[67]。
为进行水务管理,瓦隆大区划分为4个水务大区(district)和若干个水务区(secteur),阿尔隆属于马尔什水务区(District de Marche)[68]。
比利时划分为14个农业区,阿尔隆属于侏罗地区(région jurassique)农业区[69]。瓦隆大区划分为9个农业地理区(Zones agro-géographiques),阿尔隆属于洛林(Lorraine)农业地理区[70]。
在宗教方面,阿尔隆属于天主教那慕尔教区和阿尔隆總鐸區[71][72],下分若干堂区[73]。
与比利时其他所有地区一样,阿尔隆的时区为UTC+01:00、UTC+02:00(夏令时)。
政治
[编辑]

阿尔隆是比利时瓦隆大区盧森堡省阿爾隆區的一个市镇,也是卢森堡省的省会与阿尔隆区的区府。在比利时三个社群中,阿尔隆属于比利时法语社群。
在歐洲議會選舉方面,阿尔隆属于法语选举团,选举歐洲議會議員。在联邦选举方面,阿尔隆属于卢森堡选区,选举众议员。在瓦隆尼亚议会选举方面,阿尔隆属于阿尔隆-马尔什昂法梅讷-巴斯托涅-维尔通-讷沙托选区,选举瓦隆尼亚议会议员。在省议会选举方面,阿尔隆属于阿尔隆省级选区,选举卢森堡省议员。此外,比利时分为210个选举县,用作市镇级以上选举时各选区的细分选区,阿尔隆属于阿尔隆选举县(Canton d'Arlon)。
| 层级 | 超國家 | 国家 | 社群 | 大区 | 省 | 区 | 市镇 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 区划 | 阿爾隆區 | 阿尔隆 | |||||||
| 行政机构 | 欧盟委员会 | 比利時聯邦政府 | 法语社群政府 | 瓦隆政府 | 卢森堡省理事会 | 无 | 阿尔隆市镇理事会 | ||
| 立法 | 议会 | 欧洲议会 | 众议院 | 法语社群议会 | 瓦隆尼亚议会 | 卢森堡省议会 | 无 | 阿尔隆市议会 | |
| 选区 | 法语地区选区 (法语选举团) |
卢森堡选区 | 无 | 阿尔隆-马尔什昂法梅讷- 巴斯托涅-维尔通-讷沙托选区 |
阿尔隆省级选区 | 无 | 阿尔隆 | ||
| 选举 | 歐洲議會選舉 | 联邦选举 | 无 | 瓦隆尼亚议会选举 | 卢森堡省议会选举 | 无 | 市议会选举 | ||
市镇政治
[编辑]阿尔隆市议会负责管理所有与市镇利益相关的事务,并审议上级机关提交的其他事项。阿尔隆市议会由29名成员组成:市长、六名市政官[註 2]和二十二名市议员,分属Arlon 2030(行动者党在阿尔隆的分支)、MRMC(革新运动党在阿尔隆的分支)、ECOLO+(生态党在阿尔隆的分支)和Pour vouS(社会党在阿尔隆的分支)四个党派,其中Arlon 2030和MRMC为执政党,ECOLO+和Pour vouS为反对党[74][75]。
阿尔隆市镇理事会为阿尔隆的市镇行政机构,由市长、六名市政官[註 2]、一名社会福利公共中心(CPAS)主席和一名市镇总干事组成,负责市镇日常管理,执行市议会的决议与上级机关颁布的法令[76][77]。
阿尔隆的现任市长为樊尚·马格努斯(Vincent Magnus)先生,所属党派为Arlon 2030。
| 阿尔隆市镇委员会 | ||
| 姓名 | 职务 | 党派 |
|---|---|---|
| 樊尚·马格努斯 Vincent Magnus |
市长 | Arlon 2030 |
| 卡琳·施米特-勒孔特 Carine Schmit Lecomte |
第一市政官 | MRMC |
| 卡马尔·米特里 Kamal Mitri |
第二市政官 | Arlon 2030 |
| 迪迪埃·拉福热 Didier Laforge |
第四市政官 | Arlon 2030 |
| 安娜·拉梅施 Anne Lamesch |
第五市政官 | Arlon 2030 |
| 奥利维耶·瓦尔桑 Olivier Waltzing |
市政官 | MRMC |
| 阿兰·德沃姆 Alain Deworme |
CPAS主席 | MRMC |
| 塞德里克·勒克莱尔 Cédric Leclercq |
市镇总干事 | Les Engagés |
历任市长
[编辑]以下为1830年以来阿尔隆历任市长列表:
| 阿尔隆历任市长 | ||
| 市长 | 任期 | 党派 |
|---|---|---|
| 让·尼古拉·罗西尼翁 Jean-Nicolas Rossignon |
1830—1838年 | Parti Libéral |
| 夏尔·普林茨 Charles Printz |
1838—1843年 | Parti Libéral |
| 皮埃尔·霍伦费尔茨 Pierre Hollenfeltz |
1843—1880年 | Parti Libéral |
| 约瑟夫·内策 Joseph Netzer |
1880—1901年 | Parti Libéral |
| 努马·恩施-特施 Numa Ensch-Tesch |
1901—1921年 | Parti Libéral |
| 保罗·勒泰 Paul Reuter |
1921—1949年 | Parti Libéral |
| 朱尔·马索内 Jules Massonnet |
1949—1958年 | Parti Libéral |
| 夏尔·西蒙 Charles Simon |
1958—1976年 | PSC |
| 让·戈菲内 Jean Goffinet |
1977—1982年 | PRL |
| 费尔南·阿塞尔博恩 Fernand Asselborn |
1983—1985年 | PS |
| 让·戈菲内 Jean Goffinet |
1986—1988年 | PRL |
| 居伊·拉尔西耶 Guy Larcier |
1989—1992年 | PS |
| 让·戈菲内 Jean Goffinet |
1993—1994年 | PRL |
| 居伊·拉尔西耶 Guy Larcier |
1995—2006年 | PS |
| 雷蒙·比朗 Raymond Biren |
2007—2012年 | cdH |
| 樊尚·马格努斯 Vincent Magnus |
2013年至今 | ARLON 2030 |
选举结果
[编辑]以下为1976年-2018年阿尔隆市议会选举结果:
| 1976年-2018年阿尔隆市议会选举结果 | |||||||||||||||||
| 党派 | 1976年10月10日[78] | 1982年10月10日 | 1988年10月9日 | 1994年10月9日 | 2000年10月8日 | 2006年10月8日[79] | 2012年10月14日[80] | 2018年10月14日 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 得票率 / 席位 | % | 27 | % | 27 | % | 27 | % | 27 | % | 27 | % | 29 | % | 29 | % | 29 | |
| PSC1 / UC2 / CDH3 / Arlon 20304 |
33.591 | 9 | 37.712 | 11 | 311 | 9 | 34.951 | 11 | 29.791 | 9 | 40.053 | 12 | 37.173 | 11 | 39.094 | 12 | |
| PS1 / Bourgmestre2 / Pour vouS3 |
25.91 | 7 | 23.771 | 7 | 26.881 | 8 | 28.711 | 8 | 26.151 | 8 | 30.362 | 9 | 26.11 | 8 | 15.683 | 4 | |
| ECOLO1/Ecolo+2 | - | 4.841 | 0 | 5.931 | 1 | 6.891 | 1 | 12.851 | 3 | 9.481 | 2 | 15.161 | 4 | 22.802 | 7 | ||
| PRL1/MR2 | 21.931 | 6 | 30.381 | 9 | 26.221 | 7 | 24.191 | 7 | 25.451 | 7 | 20.112 | 6 | 21.582 | 6 | 22.432 | 6 | |
| GERONS | - | - | 9.97 | 2 | 5.27 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| UDC | 18.58 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||
| 其他* | - | 3.3 | 0 | - | - | 5.75 | 0 | - | - | - | |||||||
| 总票数 | 15099 | 15383 | 15559 | 15754 | 16573 | 17206 | 17345 | 18144 | |||||||||
| 投票率 % | 92.88 | 91.88 | 92.14 | 91.69 | 87.67 | 89.18 | |||||||||||
| 空白票和无效票比率 % | 4.09 | 6.44 | 5.98 | 6.07 | 9.03 | 7.53 | 7.92 | 9.26 | |||||||||
经济
[编辑]阿尔隆是所在地区的工商业中心,費列羅、宜家、迪卡侬等多家大型企业在阿尔隆设店设厂。由于毗邻卢森堡大公国,阿尔隆吸引了许多投资者和希望在此长居的人[81]。
阿尔隆工商联合会(ACIA)与“阿尔隆市中心”(Arlon Centre-Ville)是阿尔隆的非营利组织(asbl),前者成立于1930年,致力于促进阿尔隆的商业发展,全年会组织许多活动,如大型夏季销售、主题和季节性商业活动及省级建筑展[82][83];后者致力于提高市中心的吸引力,推动城市商业经济发展,提升城市环境质量、加强城市移动性、接待能力与城市活力[84][85]。市际组织IDELUX管理当地的公共项目[86]。
阿尔隆设有4个经济活动区(zone d'activité économique),其中3个由IDELUX管理,1个由阿尔隆市经济局管理[87]。
商业
[编辑]
阿尔隆市中心是众多商铺、餐馆及企业的所在地,为当地传统消费购物区[88]。市区西部有比利时最大的露天购物中心Hydrion,占地33,000平方米,有40家商店入驻[89]。
每周四上午,阿尔隆市中心开设每周市场。三至十月的每月第一个星期日,阿尔隆市中心开设跳蚤市场[90]。
企业
[编辑]2021年,阿尔隆缴纳增值税的企业有1382家,其中农林渔企业79家(占比5.7%),建筑企业122家(占比8.8%),机动车销售维修企业282家(占比20.4%),住宿餐饮企业136家(占比9.8%),科技企业216家(占比15.6%),教育企业60家(占比4.3%),健康和社会服务企业90家(占比6.5%),艺术、娱乐、休闲企业67家(占比4.8%),其他服务企业109家(占比7.9%),其他企业221家(占比16%)[91]。2022年,阿尔隆有6家企业破产[92]。
IDELUX为入驻企业提供帮扶[93]。
居民收入
[编辑]2020年,阿尔隆居民人均收入为22910欧元,与上一年相比增加3%[94],高于比利时(19671欧元)、瓦隆大区(18518欧元)与卢森堡省(19363欧元)[95]。2020年,阿尔隆报税人数16054人,与上一年相比增加0.9%[94]。报税者收入中位数为31779欧元,收入平均数为43373欧元,均高于瓦隆大区(24808欧元和32978欧元)[96][97]。
就业情况
[编辑]2019年,阿尔隆15-64岁人口(劳动适龄人口)20084人,其中劳动人口13061人,非劳动人口7023人[67]。2020年,阿尔隆15-64岁人口失业率为6.1%,高于比利时(5.6%)与卢森堡省(5.1%),低于瓦隆大区(7.4%)[98]。2022年,阿尔隆15-64岁人口行政失业率(taux de chômage administratif)为10.2%,低于瓦隆大区(12.8%)[99]。
2021年,阿尔隆有酬工作岗位中,工业占比9.6%,农林渔业占比0.1%,建筑业占比0.9%,贸易、运输、餐饮业占比20.4%,信息通信业占比0.4%,金融保险业占比1.1%,房地产业占比0.5%,专业与行政机构占比12.4%,行政、国防、教育、卫生、社会工作占比50.7%,其他服务占比3.9%。自雇人士中,自由职业占比36.4%,农渔业占比8.6%,工业与手工业占比16.8%,贸易与服务业占比36.7%,其他行业占比1.5%[67]。
财政
[编辑]2021年,阿尔隆的人均财政收入为2450.9欧元[100],人均财政支出为2182.8欧元[101],人均地方政府债务为2799.8欧元[102]。
军事
[编辑]拉格朗军营位于阿尔隆西部,占地近2500公顷[103],主要被比利时国防部用作射击场。这一地带也是Natura 2000保护区[104]。2021年,比利时女王储伊丽莎白公主在此参加了军事训练[105][106]。
人口
[编辑]阿尔隆是卢森堡省人口最多的市镇,但同时也是比利时十个省会城市中人口最少者。2022年,阿尔隆人口30818人,在比利时所有市镇中排名第43位,其中男性15394人(占比49.95%),女性15424人(占比50.05%),外籍人口5989人(占比19.43%,其中欧盟人口15.73%,非欧盟人口3.70%),人口密度258.8人/km²,人口平均年龄40.2岁[107][67]。
2021年,阿尔隆境内出生310人(174名男婴,136名女婴),死亡250人[108][109];粗出生率为10.1‰,人口增长率为1.40%,均高于瓦隆大区[110][111]。2012-2022年,阿尔隆人口增长率为8.94%(比利时为4.97%)[112]。
人口结构
[编辑]在人口结构方面,2022年阿尔隆18岁以下人口6175人(占比20.04%,其中男性3143人,女性3032人),18-64岁人口19684人(占比63.87%,其中男性10130人,女性9554人),65岁以上人口4959人(占比16.09%,其中男性2121人,女性2838人;百岁及以上人瑞4人,其中男性3人,女性1人)[113][114]。
外籍人口
[编辑]2022年外籍人口中,喀麦隆籍有121人(占比2.0%),西班牙籍232人(占比3.9%),法国籍1556人(占比26.0%),摩洛哥籍110人(占比1.8%),罗马尼亚籍463人(占比7.7%),俄罗斯籍112人(占比1.9%),意大利籍583人(占比9.7%),卢森堡籍514人(占比8.6%),葡萄牙籍998人(占比16.7%),其他籍1300人(占比21.7%)[115]。
住户类型
[编辑]在住户类型方面,2022年阿尔隆有子女的已婚伴侣2757户(占比19.5%),无子女的已婚伴侣2105户(占比14.9%),有子女的未婚伴侣874户(占比6.2%),无子女的未婚伴侣967户(占比6.8%),单亲家庭1358户(占比9.6%),一人户5818户(占比41.1%),其他类型住户254户(占比1.8%)[115]。
外籍人口[115]
阿尔隆市镇人口变化图

- 来源:比利时统计局。1831-1981年数据为各年12月31日数据,1990年及之后数据为各年1月1日数据;1977年市镇合并前的数据为各年各原市镇人口总合。
住户类型[115]
交通
[编辑]公路
[编辑]
两条高速公路经过阿尔隆南部:欧洲411公路和欧洲E25公路。两条公路并行,方向相反。
数条国道经过阿尔隆,其中属于第一公路网(premier réseau)的国道有N4,属于第二公路网(deuxième réseau)的国道有N40,属于第三公路网(troisième réseau)的国道有N81、N82和N83,属于第四公路网(quatrième réseau)的国道有N817、N844、N850、N852、N870、N881和N882。
2005年,阿尔隆境内的铺面道路共计329.4千米[116],其中高速公路14.9千米[117],大区道与省道75.9千米[118],市道238.6千米[119]。
铁路
[编辑]阿尔隆位于连接那慕爾与比卢边境村庄斯泰尔珀尼什的比利时162号铁路线上。阿尔隆火车站是阿尔隆的一座历史建筑,是所有在卢森堡工作的比利时人的重要跨境点。
阿尔隆站也是比利时165号铁路(阿蒂-默兹线)的终点站,该铁路于2007年重新开放,将阿尔隆与梅桑西、欧邦日、维尔通、弗洛朗维尔、贝尔特里和利布拉蒙-舍维尼连接。
除阿尔隆站外,阿尔隆境内还有欧泰尔巴站、富什站、斯泰尔珀尼什站、斯托凯姆站和维维尔站五个小型铁路车站。
-
阿尔隆站
-
斯托凯姆站
-
维维尔站
航空
[编辑]
阿尔隆斯泰尔珀尼什机场(國際民航組織機場代碼:EBAR)是阿尔隆的一座小型机场,位于斯泰尔珀尼什以北,是阿雷尔航空超轻型飞机俱乐部(club ULM Arel-Air)的活动场地[120]。
距离阿尔隆最近的民用航空机场是卢森堡机场,该机场距离阿尔隆市区约40千米,是卢森堡大公国唯一的国际机场。
城市公共交通
[编辑]
瓦隆尼亚交通运营商(TEC)为阿尔隆提供公共汽车服务[121],乘车可前往瓦隆大区各地与布鲁塞尔首都大区[122]。
其他道路
[编辑]RAVeL是瓦隆大区的一项倡议,旨在为行人、自行车骑行者、骑马者和行动不便者在情况允许的情况下创建一个道路网。项目成立于1995年10月,道路由纤道和废弃铁路改造而成。2014年,RAVeL获得“官方”地位[123]。阿尔隆的RAVeL起步较晚,直到2019年才落成第1千米[124]。
共享交通工具
[编辑]截至2023年,服务于阿尔隆的共享汽车运营商有Cambio、Cozywheels[125],尚未有共享自行车与共享电动滑板车/摩托车运营商进驻[126]。
车辆统计
[编辑]
2022年,阿尔隆有各类车辆共20209辆,其中乘用车15855辆,非乘用车4354辆[127];新车登记数量为1051辆[128],二手车登记数量为2210辆[129]。
2021年,阿尔隆没有汽车的家庭占比26.0%[130],有一辆汽车的家庭占比48.1%[131],有两辆汽车的家庭占比19.7%[132],有三辆及以上汽车的家庭占比4.2%[133]。
交通事故
[编辑]2021年,阿尔隆发生交通事故60起,与上一年相比下降8%;伤亡77人,与上一年相比下降4%。伤亡者伤亡情况中,轻伤74人,重伤2人,事故后30日内不治者1人。各交通方式伤亡者中,汽车驾乘者60人,摩托车驾乘者2人,自行车骑行者3人,卡车驾乘者3人,行人4人,其他类型5人[134]。
社会
[编辑]健康
[编辑]阿尔隆医院(Hôpital d'Arlon),即圣约瑟夫医院(Clinique Saint-Joseph),是阿尔隆的一家较大规模的医院,隶属于南卢森堡医院联盟(Cliniques du Sud-Luxembourg)和Vivalia市际医疗保健公司。
2021年,阿尔隆每名专职同等资历全科医生平均服务人口数为1771人,高于瓦隆大区平均值(1092人)[135]。全科医生中,55岁及以上者的比例为55.0%,高于瓦隆大区(44.4%)[136]。
2022年,阿尔隆每1000名60岁及以上人士的疗养院(MR)与疗养护理院(MRS)床位为26张,低于瓦隆大区平均值(52张)[137]。
2011-2020年,阿尔隆居民潜在寿命损失年数(期望寿命为70岁)为3221,低于瓦隆大区平均值(3948)[138]。
教育
[编辑]2023年,阿尔隆有20所初等教育学校[139]、7所中等教育学校[140]、1所大学[141]、2所高等专业学院[142]、2所继续教育学校[143]、2所非全日制艺术学院[144]、2所特殊教育学校[145]。
2021-2022学年,阿尔隆各级教育机构注册学生中,幼儿园学童1167人[146],初等教育学校学生2681人[147],中等教育学校学生5282人[148]。
2017年,阿尔隆25岁及以上人口中有34.2%接受过高等教育[149]。
住房
[编辑]
2022年,阿尔隆共有各类住房15608套[151]。各类住房中,楼宇和公寓占比32.1%[152],封闭式房屋占比19.2%[153],半封闭式房屋占比17.3%[154],开放式房屋、农场、城堡占比25.4%[155],商业用房占比2.5%[156],其他建筑物占比3.4%[157]。
2020年,阿尔隆各类住房的中位数价格为219250欧元(瓦隆大区为175000欧元)[158],房屋的中位数价格为265000欧元(瓦隆大区为180000欧元)[159],公寓的中位数价格为177537欧元(瓦隆大区为155000欧元)[160]。同年,阿尔隆住房交易量为320[161],其中房屋184栋[162],公寓136套[163]。
2011年,阿尔隆各类住房中,自有住房占比63.3%[164],租房占比36.7%[165]。
殡葬
[编辑]2023年,阿尔隆共有17处墓地[166],3家殡葬公司[167]。阿尔隆公墓为当地的大型公墓。
劳动就业
[编辑]地区资格教育、培训、就业机构卢森堡省分区(IBEFE Luxembourg)、社会职业融入中心(CISP)、瓦隆交替式培训、自雇与中小企业协会卢森堡省分中心(Centre IFAPME Luxembourg)、瓦隆职业培训和就业办公室(Forem)等组织机构负责阿尔隆的就业和职业培训工作[168][169][170][171]。
社会保障
[编辑]比利时每个市镇均有一个社会福利公共中心(CPAS),为困难民众提供社会援助。2021年,阿尔隆社会福利公共中心人均支出507.5欧元[172]。
在阿尔隆有地方职业介绍所,其为比利时的非营利组织,为符合特定条件的困难民众提供简易工作[173]。
阿尔隆是社会凝聚力计划(Plan de cohésion sociale)参与市镇,该计划由瓦隆政府推出,致力于通过促进所有人有效享有基本权利来减少不稳定和不平等,使每个人都能在瓦隆大区过上有尊严的生活[174][175]。
爱心餐厅是1985年由法国喜剧演员科吕什创立于法国的非营利组织,旨在为无家可归者和低收入群体提供餐食。阿尔隆爱心餐厅(Resto du Cœur d'Arlon)与比利时爱心餐厅协会(Fédération des Restos du Cœur de Belgique)和阿尔隆市密切合作。在阿尔隆,全年周一至周五,需要帮助的人可以以每餐0.5欧元的价格获得由阿尔隆爱心餐厅提供的堂食或外卖餐食[176]。
“冬日阳光”(« Soleil d’hiver »)是阿尔隆的夜间收容所,于每年11月1日至次年3月31日开放。2017年起,该收容所能够依靠每年6万欧元的地区补贴来运作,此前则是依靠市政府的自有资金并在志愿者的帮助下运作[177]。
“我们的住所”(Nos Logis)是阿尔隆的非营利组织,其有35套公寓,为符合特定条件的困难民众提供过渡性住房[178]。
公共安全与司法
[编辑]治安
[编辑]阿尔隆警务方面由阿尔隆-阿泰尔特-阿拜-马特朗日警区负责。ESPAS是阿尔隆当地的机构,是瓦隆戒毒机构联合会(Fédito)的成员,负责预防、发现和限制家庭暴力、吸毒和犯罪行为,为酗酒者提供建议和支持[179][180]。
2022年,阿尔隆发生犯罪案件1884起,违规案件148起[181],每10000户住宅发生入室盗窃案件51.76起[182],每10000辆汽车发生被盗案件3.85起[183],每10000辆汽车发生车上物品盗窃案件71.97起[184],每10000个住户发生家庭暴力案件111.63起[185]。
消防救援
[编辑]阿尔隆消防救援方面由卢森堡救援区负责。2020年,该救援区内共发生各类火灾1504起[186]。
司法
[编辑]阿尔隆司法方面由卢森堡司法区负责。卢森堡省初审法院(Tribunal de première instance du Luxembourg)位于阿尔隆[187]。
2022年,阿尔隆有1709起刑事案件立案,1768起刑事案件结案,29起民事案件立案,38起民事案件结案[188]。
资源、能源与环境
[编辑]
资源
[编辑]市际组织IDELUX管理当地的水资源[189]。2017年,阿尔隆平均用水量为70立方米/(户/年)[190]。
能源
[编辑]2019年,阿尔隆能源总消耗量为986.8GWh[191],其中用电量为201.6GWh[192],天然气能源消耗量为166.6GWh[193],石油产品能源消耗量为565.1GWh[194],其他载体能源消耗量为53.6GWh[195]。能源供应中,可再生能源供电28.1GWh,可再生能源供热1.2GWh[67]。
阿尔隆是市长盟约签署市镇[196],该运动旨在提高市镇的能源效率和使用可再生能源。
环境
[编辑]2017-2019年,阿尔隆环境空气质量指标为-0.52,高于瓦隆大区平均水平(瓦隆大区为0,即基准数,指标小于0表示空气质量高于瓦隆大区平均水平,大于0则反之)[197]。
2021年,阿尔隆平均生活垃圾产生量为121.2千克/(人/年),低于瓦隆大区平均值(138.7千克/(人/年))[198]。市际组织IDELUX管理当地的垃圾[199]。
阿尔隆是市镇移动性计划(PCM)参与市镇[200],该计划旨在改善市镇的无障碍设施、移动性、道路安全和生活环境,减少噪音、空气污染[201]。
为维护河流及流域环境,瓦隆大区成立了14个河流协定(Contrats de Rivière)非营利组织,阿尔隆是瑟穆瓦-希耶尔河流协定(Contrat de Rivière Semois-Chiers)的成员[202]。
娱乐休闲
[编辑]加斯帕尔公园(Parc Gaspar)位于阿尔隆市中心,其原为加斯帕尔家族的私人花园,后被捐赠用作公园[203]。弗拉塞姆植物园(Arboretum de Frassem)位于北部的弗拉塞姆,建于1991年左右,占地2公顷,内有来自当地森林的50余种树木[204]。
阿尔隆“官方”露营地(Camping 'Officiel' Arlon)位于阿尔隆北部,N4国道旁,于每年3月1日至10月31日开放[205][206]。
GR步道是欧洲的长距离远足径网络。有三条GR步道经过阿尔隆:GR 15、GR 16和GR 129[207]。
Belarel是一条为步行者和骑行者创建的环路,长54千米,连接阿尔隆各村庄[208]。
体育
[编辑]2023年,阿尔隆共有53个体育组织,涵盖各类球类、射击、武术、水类、户外运动[209][210]。
阿尔隆没有比赛于高级别联赛的足球俱乐部。当地有阿尔隆足球俱乐部,其主队2022-2023赛季参加卢森堡省甲级足球联赛(比利时第六级别),其主场为隆维大街球场(Stade Avenue Longwy)[211]。
阿尔隆没有职业篮球俱乐部,阿尔隆皇家篮球联盟(Royal Basket Alliance Arlon)和阿尔隆青年(Junior Arlonais)为当地的两支业余篮球俱乐部[212]。
媒体
[编辑]瓦隆大区主要媒体均可在阿尔隆接收。其所在的卢森堡省的主要地方性媒体有《默兹报》、《未来报》卢森堡省版、七号广播(SEVEN RADIO)、Must Fm、南部广播(Radio Sud)和TV Lux[213]。
发展规划
[编辑]2021年,阿尔隆市政府同意实施市镇商业发展纲要(SCDC)[214]。
文化
[编辑]建筑
[编辑]2022年,阿尔隆共有12120座建筑,其中建于20世纪之前的建筑有2702座[151]。截至2023年,阿尔隆有33座建筑被列为比利时建筑遗产,4座建筑被列为瓦隆尼亚特殊建筑遗产[215]。众多历史悠久的建筑中,知名者有圣多纳教堂、圣马丁教堂、阿尔隆皇家阶梯、阿爾隆猶太會堂、欧泰尔巴城堡、阿尔隆树林城堡、吉尔什城堡和斯泰尔珀尼什城堡等。
广场
[编辑]
大广场(Grand Place)、利奥波德广场(Place Léopold)和阿斯特丽德广场(Square Astrid)为阿尔隆市中心的主要广场。利奥波德广场为前法院大楼(L'ancien palais de justice)和省府大楼(Palais provincial)所在地[216],如今一个新项目“利奥波德空间”(Espace Léopold)正在进行,计划将于2024年8月完工,广场将会被全面改造[217]。阿斯特丽德广场为纪念因车祸逝世的比利时女王阿斯特丽德而在其逝世不久后建立并以其命名。广场上的鸣鹿纪念碑是比利时雕塑家让·加斯帕尔的作品“森林的呼唤”(L'Appel de la Forêt)的放大版,于1936年秋天移至广场[218]。
墓园
[编辑]
阿尔隆公墓是当地的大型公墓,建于1853年,按天主教和犹太教分为两个区域,是瓦隆大区最古老的犹太人墓地[219][220]。旧公墓已于1852年弃用,今天此处仍有许多17-19世纪的十字架。所在区域有古罗马时期的遗址,现已建为考古公园[221][222]。
文化设施
[编辑]
阿尔隆的主要博物馆为阿尔隆考古博物馆和加斯帕尔博物馆,前者有许多罗马高卢和墨洛温遗迹,后者主要收藏艺术品。此外,阿尔隆还有自行车博物馆(Musée du cycle)、阿尔隆军事博物馆(Musée Militaire d'Arlon)、国际童军博物馆(Musée International du Scoutisme)和欧泰尔巴博物馆(Musée d'Autelbas)[223]。
阿尔隆市立图书馆(Bibliothèque communale d'Arlon)成立于1842年,后于1993年迁至文化之家(Maison de la Culture),藏有55000份纸质与电子书刊[224][225]。
文化之家(Maison de la Culture)是由瓦隆尼亚-布鲁塞尔联邦认可的文化中心,可举办演出、音乐会、课程和会议[226][227]。
美食
[编辑]五月酒是一种季节性的调味酒,为阿尔隆地区的特产,由摩泽尔白葡萄酒浸泡香车叶草花序制成[228]。五月酒皇家协会(Royale Confrérie du Maitrank)是阿尔隆当地的一个协会,旨在通过当地特色饮品五月酒来宣传推广这座城市[229][230]。
豆子羹是由豆角、土豆、培根和洋葱(可能会配以额外的蔬菜或肉类)烹饪而成的汤品,是卢森堡菜之一,亦通行于阿尔隆地区[231][232]。
-
一杯添加了草莓的五月酒
-
一碗豆子羹
节日、活动与习俗
[编辑]
阿尔隆狂欢节是阿尔隆当地的狂歡節,传统上于每年三月左右举办[233]。Les Aralunaires音乐节始于2009年,于每年四月或五月举办,主打独立音乐和新兴艺人[234][235]。
五月酒节于每年五月的第四个周末举办,旨在庆祝和品尝五月酒[236]。
Veni Vidi Orolaunum举办于每年九月的第一个周末,人们会通过重演营地、角斗、军事演习和展览工艺品来重现罗马高卢时代[237]。
鸣鹿节(Fête du cerf bramant)于每年九月底在阿斯特丽德广场(Square Astrid)举办,因广场上的鸣鹿纪念碑而得名。节日期间会举办狩猎号角音乐会,民众会得到由节日委员会免费分发的野生蘑菇汤[238]。
“四旬节豆子”是阿尔隆的民间传统。每年四旬节的第一个星期日,孩子们会去新婚夫妇那里唱“福至贵居,给我们四旬节的豆子吧”(盧森堡語:T ass Gléck an ärem Haus, Geheit d'Faaschtebounen erauset),讨到一些糖果和零钱[239][240]。
旅游
[编辑]
阿尔隆皇家旅游局(Royal Office du Tourisme d'Arlon)为阿尔隆当地的旅游事务机构,该旅游局已有百余年历史[241]。此外,比利时卢森堡省旅游协会(Fédération du Tourisme du Luxembourg belge)和阿尔隆地区旅游局(Maison du Tourisme du Pays d'Arlon)分别为为卢森堡省和阿尔隆地区的旅游事务机构,二者亦负责阿尔隆的旅游事务[242][243]。VISITWallonia是比利时的一个非营利组织(asbl),致力于在比利时国内外推广瓦隆尼亚地区旅游[244],亦会介绍宣传阿尔隆的风景和文化[245]。
阿尔隆地区旅游局网站列出了数个阿尔隆地区不容错过的项目,其中位于(或包括)阿尔隆的有罗马高卢遗址、五月酒、圣多纳教堂望景楼、圣马丁教堂和克莱尔方丹修道院遗址[246]。
在《米其林绿色指南》中,阿尔隆被列出的景点有阿尔隆考古博物馆、圣多纳教堂、罗马塔和罗马浴场,其中阿尔隆考古博物馆获得一星评级[247]。
在《米其林红色指南》中,阿尔隆共有3家餐厅被列出,其中1家餐厅获得一星评级[248]。
纹章与旗帜
[编辑]阿尔隆纹章被授予过两次,第一次于1818年11月18日由荷蘭聯合王國贵族高级委员会授予,第二次于1841年11月24日依比利时皇家法令授予[249]。该纹章来自卢森堡伯爵,最早可以追溯至1311年[250]。纹章图案背景银色与蓝色条纹,上面有一只佩戴金冠的叉尾红色狮子。与1818年的纹章相比,1841年的纹章将狮子爪子的颜色由金色改为了红色,以免与卢森堡纹章混淆[251]。
语言
[编辑]阿尔隆是比利时法语社群的一部分,官方语言和当地通行语言为法语。阿尔隆所在的阿尔隆地区的传统语言为卢森堡语阿尔隆方言,不过其如今已式微[252]。“阿尔隆地区和语言”(Arelerland a Sprooch)是阿尔隆当地一个协会,旨在弘扬阿尔隆地区卢森堡语文化[253]。
阿尔隆史上有很多德语人口,且直至一战,阿尔隆地区的文化语言都为德语。一战、二战后,德语因被限制、敌视而衰落[254]。
此外,在1846-1947年间,比利时人口普查会调查居民语言使用情况。1846年人口普查只问询当前使用的语言。自1866年起,人口普查会问询掌握的语言。自1910年起,人口普查不仅会问询掌握的语言,还问会及最常使用的语言,但没有具体说明是在哪种场合下最常使用(如私人、公共、职业)。
| 掌握的语言 | |||||||||||||||
| 年份 | 仅荷 | 荷法 | 仅法 | 法德 | 仅德 | 德荷 | 荷法德 | 无(其他语言) | 仅荷 | 荷法 | 仅法 | 法德 | 仅德 | 德荷 | 荷法德 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 人数 | 人数 | 人数 | 人数 | 人数 | 人数 | 人数 | 人数 | 比例 | 比例 | 比例 | 比例 | 比例 | 比例 | 比例 | |
| 1846 | 297 | 891 | 4 217 | 5,5 % | 16,5 % | 78,0 % | |||||||||
| 1866 | 54 | 104 | 591 | 2 622 | 1 994 | 14 | 46 | 0 | 1,0 % | 1,9 % | 10,9 % | 48,3 % | 36,8 % | 0,3 % | 0,8 % |
| 1880 | 31 | 148 | 1 047 | 2 899 | 2 593 | 0 | 42 | 0 | 0,5 % | 2,2 % | 15,5 % | 42,9 % | 38,4 % | 0,0 % | 0,6 % |
| 1890 | 5 | 126 | 1 501 | 4 161 | 2 002 | 5 | 229 | 0 | 0,1 % | 1,6 % | 18,7 % | 51,8 % | 24,9 % | 0,1 % | 2,9 % |
| 1900 | 99 | 242 | 1 919 | 6 055 | 1 059 | 2 | 179 | 489 | 1,0 % | 2,5 % | 20,1 % | 63,4 % | 11,1 % | 0,0 % | 1,9 % |
| 1910 | 91 | 351 | 2 684 | 6 747 | 1 552 | 4 | 141 | 442 | 0,8 % | 3,0 % | 23,2 % | 58,3 % | 13,4 % | 0,0 % | 1,2 % |
| 1920 | 51 | 285 | 4 522 | 5 159 | 572 | 0 | 209 | 404 | 0,5 % | 2,6 % | 41,9 % | 47,8 % | 5,3 % | 0,0 % | 1,9 % |
| 1930 | 20 | 263 | 6 831 | 3 366 | 320 | 2 | 212 | 373 | 0,2 % | 2,4 % | 62,0 % | 30,6 % | 2,9 % | 0,0 % | 1,9 % |
| 1947 | 5 | 387 | 8 710 | 1 268 | 31 | 1 | 395 | 383 | 0,0 % | 3,6 % | 80,7 % | 11,7 % | 0,3 % | 0,0 % | 3,7 % |
| 法:法语 · 荷:荷兰语 · 德:德语 来源:比利时公报 | |||||||||||||||
| 唯一使用或最常使用的语言 | ||||||
| 年份 | 荷兰语 | 法语 | 德语 | 荷兰语 | 法语 | 德语 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 人数 | 人数 | 人数 | 比例 | 比例 | 比例 | |
| 1910 | 165 | 3 568 | 7 837 | 1,4 % | 30,8 % | 67,7 % |
| 1920 | 130 | 7 502 | 3 166 | 1,2 % | 69,5 % | 29,3 % |
| 1930 | 84 | 9 398 | 1 532 | 0,8 % | 85,3 % | 13,9 % |
| 1947 | 55 | 10 629 | 80 | 0,5 % | 98,7 % | 0,7 % |
| 来源:比利时公报 | ||||||
宗教
[编辑]阿尔隆当地宗教信仰以天主教为主,不过同比利时各地一样正在减少。在区划方面,阿尔隆属于天主教那慕尔教区和阿尔隆總鐸區[71][72],下分若干堂区[73]。此外,阿尔隆有一座清真寺,属于阿尔隆穆斯林协会(Association des Musulmans d’Arlon)[255];亦有一座犹太会堂,即阿爾隆猶太會堂。
艺术
[编辑]音乐
[编辑]
《在克尼普申山上的阿尔隆》是阿尔隆地区和卢森堡大公国的一首传统民歌,歌词有卢森堡语和法语版本,被卢森堡省人认作该省的非官方国歌。阿尔隆圣多纳教堂的钟楼每小时都会奏起该歌的旋律[256]。
稻草乐队是一支来自阿尔隆的摇滚乐队,于2005年成立,2012年解散。伊尼米卡尔乐队是另一支来自阿尔隆的摇滚乐队,成立于2004年。
Les Aralunaires为当地一年一度的音乐节。
影视
[编辑]电影《敌人》《一个晚上,一辆列车》《临终遗言》《感謝上帝》和《淘气托托大冒险》拍摄于阿尔隆[257][258][259][260]。
以阿尔隆命名的事物
[编辑]
卢森堡和比利时有数条阿尔隆路(Route d'Arlon)和阿尔隆街(Rue d'Arlon)。
小行星1717“阿尔隆星”((1717) Arlon)是一颗绕太阳运转的小行星,于1954年1月8日由比利時皇家天文台发现,以阿尔隆命名。
荣誉与评价
[编辑]阿尔隆的片区与村庄吉尔什入选“瓦隆尼亚最美村庄”[261]。
人物
[编辑]
政治家阿尔弗雷德·贝特朗、宗教史学家及天主教会枢机朱利安·里斯、历史学家戈德弗鲁瓦·屈尔特、电影导演伯努瓦·拉米、画家卡米耶·朗贝尔、歌手让-吕克·丰克、诗人弗雷德里克·基泽尔、篮球运动员格扎维埃-罗贝尔·弗朗索瓦、足球运动员安东尼·莫里斯和蒂莫西·卡斯塔涅出生于阿尔隆,漫画家热拉尔·德瓦姆、政治家约瑟夫·米歇尔逝世于阿尔隆。
国际关系
[编辑]国际合作
[编辑]阿尔隆是跨境合作组织Tonicités的成员,其为由比、卢、法三国6个跨境城镇组成的网络,旨在促进成员地区经济、旅游和城市发展[262][263]。
友好城市
[编辑]截至2023年,阿尔隆共与5座城市互为友好城市关系[264]:
注释
[编辑]参考文献
[编辑]- ^ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 Arlon : 2000 ans d'histoire !. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-04]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-04) (法语).
- ^ Larousse, Éditions. Arlon - LAROUSSE. www.larousse.fr. [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-06) (法语).
- ^ Maurits Gysseling: Toponymisch Woordenboek (1960) p. 69. bouwstoffen.kantl.be. [2022-11-25]. (原始内容存档于2022-11-24).
- ^ 阿尔贝·多扎与夏尔·罗斯坦, Dictionnaire étymologique des noms de lieux en France, Librairie Guénégaud, Paris 1978 ISBN 2-85023-076-6
- ^ Dr. Paul Ostwald. Belgien. Springer-Verlag. 2013-12-19 [2023-06-09]. ISBN 978-3-663-16215-5. (原始内容存档于2023-06-14) (德语).
- ^ Alwin Fill, Alwin. Sustaining Language: Essays in Applied Ecolinguistics. LIT Verlag Münster. 2007 [2023-06-09]. ISBN 978-3-8258-9858-8. (原始内容存档于2023-06-15) (英语).
- ^ Maison du Tourisme des Landes von Arlon. visitwallonia.de. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (德语).
- ^ Andy. Arlon - die südlichste Provinzhauptstadt Belgiens. WAFFELREISEN. 2019-05-13 [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (de-DE).
- ^ Alfred Bertrang. Académie royale de Belgique , 编. Grammatik der Areler Mundart. 布鲁塞尔. 1921.
- ^ DTW: Motî walon-francès - Dictionnaire wallon-français - Walloon-French dictionary. dtw.walon.org. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13).
- ^ Michel Feltz. « SingulierS » Revue des parlers romans de la province de Luxembourg. 2011: 4.}
- ^ woordenlijst. woordenlijst.org. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2021-12-28).
- ^ woordenlijst. woordenlijst.org. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2021-12-28).
- ^ woordenlijst. woordenlijst.org. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2021-12-28).
- ^ 周定国 (编). 世界地名翻译大辞典. 北京: 中国对外翻译出版公司. 2007: 48. ISBN 978-7-5001-0753-8 (中文).
Arlon 阿尔隆 【比】
- ^ 民政部地名研究所 (编). 世界地名译名词典 上册 A-G. 北京: 中国社会出版社. 2017: 137. ISBN 978-7-5087-5525-0 (中文).
Arlon 阿尔隆 比 49°41'N 5°49'E
- ^ 中国地图出版社 (编). 荷兰 比利时 卢森堡地图册. 北京. 2010: 85. ISBN 978-7-5031-5312-9 (中文).
- ^ 樂詞網. terms.naer.edu.tw. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-08).
- ^ 歐盟比利時國立列日大學 HEC管理學院 (PDF). [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2023-06-08).
- ^ 臺灣:召回在比利時阿爾隆生產的健達產品 - 奧丁丁新聞 OwlNews. OwlNews. 2022-04-12 [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-08) (中文(臺灣)).
- ^ 三立新聞網. 染沙門氏菌疑因「健達出奇蛋」 台灣急下架360盒同廠貨 | 生活 | 三立新聞網 SETN.COM. www.setn.com. 2022-04-07 [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-08) (中文(臺灣)).
- ^ 健達奇趣蛋疑染沙門氏菌! 台灣也有同廠貨急下架. Yahoo News. 2022-04-08 [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (中文(臺灣)).
- ^ 精選書摘. 《解密突出部之役》:阿登戰役的一大爭議,在於盟軍竟無法預料到這次攻擊. The News Lens 關鍵評論網. 2019-04-10 [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-08) (中文(臺灣)).
- ^ Arlonide, géographie Arlon, Histoire. www.arlonide.be. [2023-06-04]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-04).
- ^ La Tour romaine Neptune (classée). Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-05]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-05) (法语).
- ^ La Tour Jupiter. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-05]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-05) (法语).
- ^ Familienstammbaum von Waleran 1er DE LIMBOURG Udon. Geneanet. [2023-06-05] (德语).
- ^ Farcy, Philippe. Wiltz, un très puissant fief d'Arlon. La Libre.be. 2023-06-05 [2023-06-05]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-06) (法语).
- ^ Familienstammbaum von Waleran Iii DE LUXEMBOURG de LIMBOURG. Geneanet. [2023-06-05] (德语).
- ^ Section Historique de L'Institut Grand-ducal de Luxembourg. Publications de la Section Historique de l'Institut G.-D. de Luxembourg: Volume 41. 1890 [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-05) (法语).
- ^ HISTOIRE.——LA VILLE DE LUXEMBOURG. (SUIT ET FIN.). [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-12).
- ^ 32.0 32.1 Canton d’Arlon. carnetsdenotes.fr. [2023-06-05]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-06).
- ^ Départements des Forêts. carnetsdenotes.fr. [2023-06-05]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-05).
- ^ De Philippe Vandermaelen. Dictionnaire géographique du Luxembourg. Etablissement géographique. 1838 [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-06) (法语).
- ^ Les origines des chemins de fer en Lorraine Belge (II) - Rixke Rail's Archives. rixke.tassignon.be. [2023-06-04]. (原始内容存档于2022-10-19).
- ^ John Horne; Alan Kramer. Tallandier , 编. 1914 Les atrocités allemandes. 2005: 483. ISBN 2-84734-235-4.
- ^ 37.0 37.1 Jean-Yves Mary. Heimdal , 编. Le Corridor des Panzers I. Bayeux. 2009: 87–88.
- ^ Jean-Yves Mary. Heimdal , 编. Le Corridor des Panzers I. Bayeux. 2009: 174.
- ^ Arlon (Aarlen) - Dalle en hommage aux libérateurs de la ville. bel-memorial.org. [2023-06-04]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-04).
- ^ Distance Arlon, BEL > Namur, BEL - Trajet aérien, trajet par route, point médian. fr.distance.to. [2022-11-26]. (原始内容存档于2022-11-26) (fr-fr).
- ^ Distance Arlon, BEL > Brussel, BEL - Trajet aérien, trajet par route, point médian. fr.distance.to. [2022-11-26]. (原始内容存档于2022-11-26) (fr-fr).
- ^ Arlon - geo.be. www.geo.be. [2022-11-26]. (原始内容存档于2022-11-27).
- ^ Carte topographique Arlon, altitude, relief. Cartes topographiques. [2022-11-27]. (原始内容存档于2022-11-27) (法语).
- ^ Description géographique de la Belgique | Belgium.be. www.belgium.be. [2022-11-27]. (原始内容存档于2023-08-15).
- ^ Carte géologique de Wallonie : 68/7-8, 69/5 Habay-la- Neuve - Arlon - Sterpenich (PDF). Service Public de Wallonie (法语).
- ^ Bassins versants - Série. geoportail.wallonie.be. [2023-06-18]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-19) (英语).
- ^ Utilisation du sol en Belgique à partir de 1980. 比利时统计局. [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (法语).
- ^ Météo et climat : Arlon (Belgique) - Quand partir à Arlon ?. Le planificateur de voyages. [2022-11-27]. (原始内容存档于2022-11-27).
- ^ Statistiques climatiques des communes belges (PDF). 比利时皇家气象研究所. [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2022-11-27) (法语).
- ^ SPW. Biodiversité - État de l'environnement wallon. Etat de l’environnement wallon. [2023-05-31]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-31) (法语).
- ^ Ancienneté des forêts actuelles. geoportail.wallonie.be. [2023-06-17]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-15) (英语).
- ^ La grande foret Anlier Ardennes belges slow tourisme. www.grandeforetdanlier.be. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-08).
- ^ Les Forêts d’Ardenne - Massifs forestiers. geoportail.wallonie.be. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09) (英语).
- ^ Recherche géographique | Sites | La biodiversité en Wallonie. biodiversite.wallonie.be. [2022-11-27]. (原始内容存档于2023-01-18) (法语).
- ^ Rechercher un site intéressant ou protégé | Sites | La biodiversité en Wallonie. biodiversite.wallonie.be. [2023-06-03]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-03).
- ^ Réseau Natura 2000 en vigueur - Série. geoportail.wallonie.be. [2023-06-17]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-17) (英语).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-14).
- ^ JVE. Arlon : la ZAD a été démantelée. La Libre.be. 2023-06-09 [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (法语).
- ^ Cartographie des zones soumises à l’aléa d’inondation en Wallonie (en vigueur). geoapps.wallonie.be. [2022-11-27]. (原始内容存档于2023-10-05).
- ^ Cartographies des zones inondables en Wallonie - Directive Inondation 2007/60/CE). geoapps.wallonie.be. [2022-11-27]. (原始内容存档于2023-10-05).
- ^ Cartographies des risques d’inondation en Wallonie - Directive Inondation 2007/60/CE. geoapps.wallonie.be. [2022-11-27]. (原始内容存档于2023-10-05).
- ^ Les habitants de la rue de la Semois à Arlon en ont assez d’être «sous l’eau». sudinfo.be. [2022-11-27]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-07) (法语).
- ^ Inondations: le niveau de crue a dépassé trois mètres par endroits. RTBF. [2022-11-27] (法语).
- ^ Population par secteur statistique | Statbel. statbel.fgov.be. [2023-06-16]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-16).
- ^ Population par secteur statistique | Statbel. statbel.fgov.be. [2023-06-16]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-16).
- ^ Quartiers statistiques wallons. geoportail.wallonie.be. [2023-05-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-11) (英语).
- ^ 67.0 67.1 67.2 67.3 67.4 IWEPS. WalStat - Détail de l'entité ARLON (Commune). walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-10).
- ^ Districts et secteurs administratifs de gestion de l'eau - Série. geoportail.wallonie.be. [2023-05-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-12) (英语).
- ^ Région agricole. geoportail.wallonie.be. [2023-06-17]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-17) (英语).
- ^ Zones agro-géographiques. geoportail.wallonie.be. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-08) (英语).
- ^ 71.0 71.1 Diocèse de Namur. www.diocesedenamur.be. [2023-05-09]. (原始内容存档于2013-09-08).
- ^ 72.0 72.1 Carte du doyenné d'Arlon. www.diocesedenamur.be. [2023-05-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-10).
- ^ 73.0 73.1 - Diocèse de Namur -. namur.diocese.be. [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13).
- ^ CONSEIL COMMUNAL. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-15]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-15) (法语).
- ^ conseil communal | CRISP asbl. [2023-06-15]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-15) (fr-FR).
- ^ Collège communal. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-15]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-15) (法语).
- ^ collège communal | CRISP asbl. [2023-06-15]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-15) (fr-FR).
- ^ 1976-2000:Verkiezingsdatabase Binnenlandse Zaken. Gearchiveerd 2021年10月5日.
- ^ 2006年结果: elections2006.wallonie.be:. Gearchiveerd 2018年1月9日.
- ^ 2012年结果: elections2012.wallonie.be
- ^ Développement socio-économique. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (法语).
- ^ Association Commerciale et Industrielle d'Arlon. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-12) (法语).
- ^ ACIA - Association Commerciale et Industrielle d'Arlon. ACIA. [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-09-20) (fr-FR).
- ^ Bienvenue dans le Centre-Ville d'Arlon - Page d'accueil. Arlon Centre-Ville. [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-12) (fr-FR).
- ^ Arlon Centre-ville asbl. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-12) (法语).
- ^ IDELUX Projets publics, partenaire de vos projets communaux | Projets communaux. www.idelux.be. [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13).
- ^ Zones d'activité économique. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (法语).
- ^ SCHÉMA COMMUNAL DE DÉVELOPPEMENT COMMERCIAL PHASE 1 - DIAGNOSTIC (PDF). [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2023-06-12).
- ^ Villes & centres commerciaux - Ardenne Belge Tourisme. www.ardennebelge.be. [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-12).
- ^ Marchés et brocantes. Maison du Tourisme du Pays d'Arlon. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (fr-FR).
- ^ Arlon | Statbel. statbel.fgov.be. [2023-05-25]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-17).
- ^ be.STAT. bestat.statbel.fgov.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-31).
- ^ IDELUX Développement, créateur de solutions | Pour l'entreprise. www.idelux.be. [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13).
- ^ 94.0 94.1 Arlon | Statbel. statbel.fgov.be. [2023-06-17]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-17).
- ^ Le revenu moyen des Belges s'élevait à 19.671 euros en 2020 | Statbel. statbel.fgov.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-28).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-31]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-05).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-31]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-31).
- ^ Taux d'activité, taux d'emploi et taux de chômage par commune calibrés sur l'enquête sur les forces de travail. Iweps. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-28) (fr-FR).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ HERCK, Christian VAN. Le camp de Lagland, à Arlon, est désormais interdit aux civils : les riverains se mobilisent. lavenir.net. 2023-06-01 [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (法语).
- ^ BE34058 - Camp militaire de Lagland | Rechercher un site intéressant ou protégé | Sites | La biodiversité en Wallonie. biodiversite.wallonie.be. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-03).
- ^ Breusegem, Charlotte Van. La princesse Elisabeth en camp militaire d’été à Arlon (photos). lavenir.net. 2023-06-13 [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (法语).
- ^ La princesse Elisabeth en formation au camp militaire d’Arlon: "Elle a eu droit à un lever aux aurores dans son bivouac". RTL Info. 2021-07-09 [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (法语).
- ^ Population par sexe et nationalité pour la Belgique et les régions, 2012 et 2022. bestat.statbel.fgov.be. [2022-12-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-01-16).
- ^ Naissances et fécondité | Statbel. statbel.fgov.be. [2022-12-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-03-21).
- ^ Mortalité générale | Statbel. statbel.fgov.be. [2022-12-06]. (原始内容存档于2018-06-18).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-15).
- ^ Arlon | Statbel. statbel.fgov.be. [2023-06-18]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-17).
- ^ Centenaires par sexe pour la Belgique et les régions, 2012 et 2022. bestat.statbel.fgov.be. [2022-12-06]. (原始内容存档于2022-12-20).
- ^ be.STAT. bestat.statbel.fgov.be. [2022-12-06]. (原始内容存档于2022-12-06).
- ^ 115.0 115.1 115.2 115.3 115.4 Arlon - Habitants | Statbel. statbel.fgov.be. [2022-12-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-17).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ ArelAir Asbl. [2023-05-10]. (原始内容存档于2023-09-24) (fr-FR).
- ^ Plan du sud de la province de Luxembourg (PDF). letec.be. [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2023-06-13) (法语).
- ^ Lignes du réseau TEC. geoportail.wallonie.be. [2023-05-15]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-15) (英语).
- ^ Son histoire. ravel.wallonie.be. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13).
- ^ Lux, T. V. Arlon se dote de son premier kilomètre de RAVEL - TV Lux. www.tvlux.be. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (fr-BE).
- ^ Offre. Autodelen. [2023-05-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-30) (fr-FR).
- ^ Solutions de mobilité intelligente - Arlon. Seety. [2023-05-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-09).
- ^ Arlon | Statbel. statbel.fgov.be. [2023-06-17]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-17).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-08).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ Arlon - Accidents de la circulation | Statbel. statbel.fgov.be. [2022-12-07]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-17).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-06).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-04).
- ^ Enseignement fondamental. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29) (法语).
- ^ Enseignement secondaire. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-03) (法语).
- ^ Enseignement supérieur universitaire. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-28) (法语).
- ^ Hautes écoles. www.mesetudes.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-09-12) (法语).
- ^ Enseignement.be - Annuaire des établissements d'enseignement de promotion sociale. Enseignement.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-28) (法语).
- ^ Enseignement.be - Annuaires des académies. Enseignement.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-28) (法语).
- ^ Enseignement spécialisé. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29) (法语).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-03).
- ^ Le niveau d’instruction cartographié | Statbel. statbel.fgov.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ Arlon. www.campus.uliege.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-30) (法语).
- ^ 151.0 151.1 Parc des bâtiments | Statbel. statbel.fgov.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-28).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-08).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-08).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-08).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-08).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-08).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-06-17]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-17).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-06-17]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-17).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-06-17]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-06-17]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-06-17]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-08).
- ^ Les cimetières sur le territoire communal. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-02]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-06) (法语).
- ^ Les meilleurs adresses pour Pompes Funebres Inhumations Et Cremations à Arlon - (Il y a 03 résultats pour votre recherche.) - Local Infobel.BE. local.infobel.be. [2023-06-02]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-02).
- ^ Instance Bassin Enseignement qualifiant - Formation - Emploi. www.ibefe-lux.be. [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (法语).
- ^ cisp – Forme-toi à ta sauce. [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-07-02) (fr-BE).
- ^ Arlon. IFAPME. 2023-05-08 [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-12) (法语).
- ^ Service Clientèle d'Arlon. Le Forem. [2023-06-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (fr-BE).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-06-17]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-17).
- ^ A.L.E. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09) (法语).
- ^ Plan de Cohésion Sociale. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09) (法语).
- ^ Plan de cohésion sociale 2020 - 2025 | Portail de la Cohésion sociale. cohesionsociale.wallonie.be. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09).
- ^ Resto du Coeur. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09) (法语).
- ^ Abri de nuit "Soleil d'hiver". Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09) (法语).
- ^ asbl Nos Logis. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09) (法语).
- ^ ESPAS. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09) (法语).
- ^ Membres effectifs - Fedito Wallonne. www.feditowallonne.be. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09).
- ^ Statistiques de criminalité | Statistiques. www.police.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (法语).
- ^ Carte avec données relatives | Statistiques. www.police.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-30) (法语).
- ^ Carte avec données relatives | Statistiques. www.police.be. [2023-05-29] (法语).[失效連結]
- ^ Carte avec données relatives | Statistiques. www.police.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29) (法语).
- ^ Carte avec données relatives | Statistiques. www.police.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29) (法语).
- ^ Statistiques des interventions 2020 - Zones de secours belges (PDF). [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2023-06-13).
- ^ Tribunal de première instance du Luxembourg | Cours & Tribunaux. www.rechtbanken-tribunaux.be. [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档于2023-10-14).
- ^ Les statistiques annuelles des cours et tribunaux - Données 2022 (PDF). [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2023-05-02).
- ^ IDELUX Eau, à votre écoute pour la gestion des eaux. www.idelux.be. [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-06-17]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-17).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-31]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-31).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-31]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-31]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-31]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-29]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ Politique de traitement, valorisation et recyclage des déchets : tri, recyparcs, collectes, bulles à verres, etc.. www.idelux.be. [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-14).
- ^ IWEPS. Catalogue des indicateurs statistiques - WALSTAT. walstat.iweps.be. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-29).
- ^ Mobilité. Plans communaux et intercommunaux de mobilité (PCM et PICM). Mobilité. [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-04) (中文).
- ^ Contrats de rivière de Wallonie - Série. geoportail.wallonie.be. [2023-05-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-09) (英语).
- ^ Le parc Gaspar. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-02]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-02) (法语).
- ^ L'Arboretum de Frassem. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09) (法语).
- ^ Homepage-FR. Camping Officiel Arlon. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (fr-FR).
- ^ Camping Officiel Arlon. Alan Rogers. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (英国英语).
- ^ - Reseau Sentiers de Grande randonnée en Wallonie. qgiscloud.com. [2023-05-15]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13).
- ^ Le Belarel. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (法语).
- ^ Annuaire — Ville d'Arlon. www.arlon.be. [2023-05-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-12) (法语).
- ^ Liste des clubs faisant partie de la Commission des Sports. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-05-12]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-14) (法语).
- ^ Stade. FC Arlon. [2023-05-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-09) (fr-BE).
- ^ Basket-ball. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-05-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-09) (法语).
- ^ Luxembourg | médias belges: presse, audiovisuel..... www.mediasrequest.com. [2023-05-15]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-17).
- ^ SPW. Schéma Communal de Développement Commercial d’Arlon : détermination des communes pour l’enquête publique - Willy BORSUS. Willy BORSUS - Vice-Président de la Wallonie. 2021-04-22 [2023-05-28]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-03) (法语).
- ^ Aménagement du territoire, Logement, Patrimoine et Énergie. lampspw.wallonie.be. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01).
- ^ L'ancien Palais de Justice. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09) (法语).
- ^ Espace Léopold. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09) (法语).
- ^ L’Appel de la Forêt – Arlon | BE-monumen. be-monumen.be. 2019-08-28 [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2020-09-19) (fr-FR).
- ^ Le cimetière. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-02]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-02) (法语).
- ^ Traces juives au Pays d'Arlon. Le Soir. 2005-10-22 [2023-06-02]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (法语).
- ^ Le vieux cimetière. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09) (法语).
- ^ Parc archéologique d'Arlon | Connaître la Wallonie. connaitrelawallonie.wallonie.be. [2023-06-09]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09).
- ^ Musées et Attractions. Maison du Tourisme du Pays d'Arlon. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (fr-FR).
- ^ Bibliothèque. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-05) (法语).
- ^ La Bibliothèque communale d'Arlon fête ses 30 ans. RTBF. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (法语).
- ^ Maison de la Culture. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-06) (法语).
- ^ La Maison de la Culture d'Arlon. Maison de la Culture d'Arlon. [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-09-20) (fr-FR).
- ^ Le Maitrank. Maison du Tourisme du Pays d'Arlon. 2020-08-28 [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (fr-FR).
- ^ Fêtes du Maitrank à Arlon - Confrérie. www.maitrank.be. [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-02).
- ^ Royale Confrérie du Maitrank d'Arlon – Porter haut et loin le renom de la ville d’ARLON.. [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-09-30) (fr-FR).
- ^ Goldstein, D.; Merkle, K.; Parasecoli, F.; Mennell, S. Culinary Cultures of Europe: Identity, Diversity and Dialogue. Council of Europe Pub. 2005: 282 [November 26, 2018]. ISBN 978-92-871-5744-7.
- ^ Sheehan, P. Luxembourg. Cultures of the World (Third Edition). Cavendish Square Publishing. 2017: 130 [November 26, 2018]. ISBN 978-1-5026-2738-4.
- ^ Carnaval. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (法语).
- ^ Infos – Les #Aralunaires23 | du 03.05 au 07.05 2023. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-07-25) (美国英语).
- ^ Evénements incontournables. Maison du Tourisme du Pays d'Arlon. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (fr-FR).
- ^ Fêtes du Maitrank à Arlon - Accueil. www.maitrank.be. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-10-07).
- ^ Week-end gallo-romain "Veni Vidi Orolaunum". Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (法语).
- ^ La fête du Cerf Bramant. www.ot-arlon.be. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2021-11-27).
- ^ Les Faaschtebounen. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (法语).
- ^ Lux, T. V. Arlon : Faaschtebounen - TV Lux. www.tvlux.be. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (fr-BE).
- ^ Royal Office du Tourisme d'Arlon. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (法语).
- ^ Qui sommes-nous?. Pro Luxembourg belge. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-07-30) (法语).
- ^ Accueil. Maison du Tourisme du Pays d'Arlon. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-07-16) (fr-FR).
- ^ VISITWallonia Wallonie Belgique Tourisme asbl et ses missions. visitwallonia.be. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (fr-BE).
- ^ Search results | VISITWallonia.be. visitwallonia.com. [2023-06-08] (英国英语).
- ^ Les Incontournables. Maison du Tourisme du Pays d'Arlon. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (fr-FR).
- ^ Arlon Tourist attractions - ViaMichelin. www.viamichelin.com. [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (英语).
- ^ Restaurants Michelin Arlon - Le Guide MICHELIN Belgique. MICHELIN Guide. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (fr-BE).
- ^ 利奥波德一世, Arrété N° 1138. qui confirme les armoiries de la commune d'Arlon., in Recueil des lois, décrets, ordonnances et règlements 24 (1841), p. 1539.
- ^ R. Hartemink, art. Arlon (2012-2015).. [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档于2018-04-09).
- ^ M. Servais, Armorial des provinces et des communes de Belgique, Luik, 1955, p. 391.
- ^ La langue luxembourgeoise en Belgique. luxembourg.public.lu. 19-09-2011 [2023-09-09]. 原始内容存档于2015-03-15 (法语).
- ^ sprooch.com. sprooch.com. [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-06).
- ^ MOUTON, PAR OLIVIER. La minorité belge oubliée. La Libre.be. [2023-05-10]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-10) (法语).
- ^ Inauguration ce dimanche de la nouvelle mosquée d’Arlon. RTBF. [2023-05-10]. (原始内容存档于2023-05-10) (法语).
- ^ L'église Saint Donat à Arlon (Belgique). Réalisations en Drone. 2017-02-23 [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-06) (fr-FR).
- ^ Jean-Pierre De Staercke. Benoît Lamy était mort sous les coups. L'Avenir. 29-05-2013 [20-09-2020]. 原始内容存档于2013年6月7日. .
- ^ Guiot, Jean-Jacques. Tourné à Arlon et Saint-Hubert, primé à Berlin. lavenir.net. 2023-06-01 [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (法语).
- ^ EDA. « Silence, on tourne au château ! ». lavenir.net. 2023-06-01 [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (法语).
- ^ Le film «Les blagues de Toto» a été en partie tourné à l’Athénée Royal d’Arlon. sudinfo.be. 2020-08-07 [2023-06-01]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-01) (法语).
- ^ Guirsch. Plus Beaux Villages de Wallonie. [2023-06-08]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-09) (fr-FR).
- ^ Réseau de villes Tonicités. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-14) (法语).
- ^ Tonicités – Les villes frontières. [2023-06-13]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-13) (美国英语).
- ^ Villes jumelées. Ville d'Arlon. [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-06) (法语).
- ^ Philippe Vandermaelen. Dictionnaire du Luxembourg. Hoffman. 1844 [2023-06-06]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-05) (法语).
- ^ Histoire de la vallée. Site d'Attert. [2023-06-05]. (原始内容存档于2023-06-05) (英语).