组织蛋白酶K
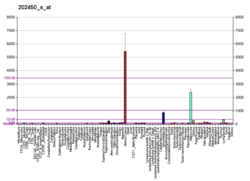
外观
组织蛋白酶K(英语:Cathepsin K),是一种在人体中由CTSK基因编码的酶。[7][8]
功能
[编辑]该基因编码的蛋白质是半胱氨酸组织蛋白酶,一种参与骨重塑和再吸收的溶酶体半胱氨酸蛋白酶。这种蛋白质是肽酶C1蛋白质家族的成员,主要在破骨细胞中表达。
组织蛋白酶K是一种蛋白酶,其特征在于其对激肽的高度特异性,与骨吸收有关。该酶分解代谢弹性蛋白、胶原蛋白和明胶的能力使其能够分解骨骼和软骨。这种分解代谢活动也是肺弹性丧失和肺气肿反冲的部分原因。组织蛋白酶K抑制剂在骨质疏松症的治疗中显示出巨大的潜力。在被称为受控组织蛋白酶同类相食的过程中,组织蛋白酶K被组织蛋白酶S降解。
临床意义
[编辑]组织蛋白酶K在很大一部分人类乳癌中表达,它可能有助于肿瘤侵袭性。[9]该基因的突变是致密性成骨不全症的原因,这是一种以骨质硬化和身材矮小为特征的常染色体隐性遗传病。[10]组织蛋白酶K也被发现在胶质母细胞瘤中过度表达。[11]
组织蛋白酶K的表达是某些癌症的特征,而其他癌症则没有。[12]组织蛋白酶K抗体已上市销售,用于研究该酶在各种细胞中的表达。[13][14][15]
默克公司在骨质疏松症的III期临床试验中使用了一种组织蛋白酶K抑制剂,奥达那替尼。2016年9月,默克公司在自行评估不良事件后宣布停止开发奥达那替尼,独立评估显示中风风险增加。[16][17]其他组织蛋白酶K抑制剂处于不同的发展阶段。[18][19]截至2017年10月,Medivir公司有一种组织蛋白酶K抑制剂MIV-711(L-006235[20][21][22]),在IIa期临床试验中,作为一种改善骨关节炎的药物。
参考文献
[编辑]- ^ 與组织蛋白酶K相關的疾病;在維基數據上查看/編輯參考.
- ^ 對Cathepsin K起作用的藥物;在維基數據上查看/編輯參考.
- ^ 3.0 3.1 3.2 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000143387 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ 4.0 4.1 4.2 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000028111 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ Human PubMed Reference:. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Mouse PubMed Reference:. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Entrez Gene: CTSK cathepsin K.
- ^ Inaoka T, Bilbe G, Ishibashi O, Tezuka K, Kumegawa M, Kokubo T. Molecular cloning of human cDNA for cathepsin K: novel cysteine proteinase predominantly expressed in bone. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. January 1995, 206 (1): 89–96. PMID 7818555. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1995.1013.
- ^ Duong LT, Wesolowski GA, Leung P, Oballa R, Pickarski M. Efficacy of a Cathepsin K Inhibitor in a Preclinical Model for Prevention and Treatment of Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 23 September 2014, 13 (12): 2898–909 [2 October 2016]. PMID 25249554. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0253
 . (原始内容存档于2019-08-24).
. (原始内容存档于2019-08-24).
- ^ CTSK cathepsin K [ Homo sapiens (human) ]. NCBI Gene. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine. 4 September 2016 [2 October 2016]. (原始内容存档于2022-10-31).
- ^ Verbovšek U, Motaln H, Rotter A, Atai NA, Gruden K, Van Noorden CJ, Lah TT. Expression Analysis of All Protease Genes Reveals Cathepsin K to Be Overexpressed in Glioblastoma. PLOS ONE. 30 October 2014, 9 (10): e111819. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9k1819V. PMC 4214761
 . PMID 25356585. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111819
. PMID 25356585. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111819  .
.
- ^ Argani, Pedram; et al. A Broad Survey of Cathepsin K Immunoreactivity in Human Neoplasms. American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 1 February 2013, 139 (2): 151–159. PMC 3957187
 . PMID 23355199. doi:10.1309/AJCPDTRTO2Z4UEXD.
. PMID 23355199. doi:10.1309/AJCPDTRTO2Z4UEXD.
- ^ Cathepsin K Antibodies. Novus Biologicals online catalog. Novus Biologicals, LLC. 2016 [2 October 2016]. (原始内容存档于2022-10-31).
- ^ Anti-Cathepsin K antibody (ab19027). Abcam plc online catalog. Abcam plc. 2016 [2 October 2016]. (原始内容存档于2022-10-31).
- ^ Anti-Cathepsin K Antibody (A5871). Antibodies.com online catalog. Antibodies.com Ltd. 2018 [16 January 2018]. (原始内容存档于2018-01-17).
- ^ Brömme, Dieter; Lecaille, Fabien. Cathepsin K inhibitors for osteoporosis and potential off-target effects. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 24 April 2009, 18 (5): 585–600. PMC 3110777
 . PMID 19388876. doi:10.1517/13543780902832661.
. PMID 19388876. doi:10.1517/13543780902832661.
- ^ Merck Provides Update on Odanacatib Development Program. Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. 2 September 2016 [1 October 2016]. (原始内容存档于2016-11-09).
- ^ Asagiri M, Hirai T, Kunigami T, Kamano S, Gober HJ, Okamoto K, Nishikawa K, Latz E, Golenbock DT, Aoki K, Ohya K, Imai Y, Morishita Y, Miyazono K, Kato S, Saftig P, Takayanagi H,. (2008). Cathepsin K-dependent toll-like receptor 9 signaling revealed in experimental arthritis. Science, 319(5863), 624-627.
- ^ Hussein, H., Ishihara, A., Menendez, M., & Bertone, A. (2014). Pharmacokinetics and bone resorption evaluation of a novel Cathepsin K inhibitor (VEL‐0230) in healthy adult horses. Journal of veterinary pharmacology and therapeutics.
- ^ MIV-711 for the treatment of ostheoarthritis. www.medivir.se. [2017-10-06]. (原始内容存档于6 October 2017) (英语).
- ^ Burston JJ, Xu L, Mapp PI, Grabowska U, Tunblad K, Lindström E, Chapman V. The Cathepsin K Inhibitor L-006235 Demonstrates Both Disease Modification and Attenuation of Pain Behaviour in the in the Mia Model of Osteoarthritis (PDF). www.medivir.se. April 2016 [6 October 2017]. (原始内容 (PDF)存档于6 October 2017).
- ^ Data monitoring committee gives "Go Ahead" in the MIV-711 osteoarthritis extension study (PDF). mb.cision.com. 14 September 2017 [2022-10-31]. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2022-08-21).
阅读
[编辑]- Motyckova G, Fisher DE. Pycnodysostosis: role and regulation of cathepsin K in osteoclast function and human disease.. Current Molecular Medicine. 2003, 2 (5): 407–21. PMID 12125807. doi:10.2174/1566524023362401.
- Troen BR. The regulation of cathepsin K gene expression.. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2006, 1068 (1): 165–72. Bibcode:2006NYASA1068..165T. PMID 16831915. S2CID 8117602. doi:10.1196/annals.1346.018.
- Del Nery E, Chagas JR, Juliano MA, et al. Evaluation of the extent of the binding site in human tissue kallikrein by synthetic substrates with sequences of human kininogen fragments.. The Biochemical Journal. 1996, 312 (1): 233–8. PMC 1136249
 . PMID 7492318. doi:10.1042/bj3120233.
. PMID 7492318. doi:10.1042/bj3120233. - Brömme D, Okamoto K. Human cathepsin O2, a novel cysteine protease highly expressed in osteoclastomas and ovary molecular cloning, sequencing and tissue distribution.. Biological Chemistry Hoppe-Seyler. 1995, 376 (6): 379–84. PMID 7576232. doi:10.1515/bchm3.1995.376.6.379.
- Gelb BD, Edelson JG, Desnick RJ. Linkage of pycnodysostosis to chromosome 1q21 by homozygosity mapping.. Nature Genetics. 1995, 10 (2): 235–7. PMID 7663521. S2CID 24297764. doi:10.1038/ng0695-235.
- Polymeropoulos MH, Ortiz De Luna RI, Ide SE, et al. The gene for pycnodysostosis maps to human chromosome 1cen-q21.. Nature Genetics. 1995, 10 (2): 238–9 [2022-10-31]. PMID 7663522. S2CID 11723845. doi:10.1038/ng0695-238. (原始内容存档于2022-10-31).
- Shi GP, Chapman HA, Bhairi SM, et al. Molecular cloning of human cathepsin O, a novel endoproteinase and homologue of rabbit OC2. (PDF). FEBS Letters. 1995, 357 (2): 129–34. PMID 7805878. S2CID 28099876. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(94)01349-6
 .
. - Inaoka T, Bilbe G, Ishibashi O, et al. Molecular cloning of human cDNA for cathepsin K: novel cysteine proteinase predominantly expressed in bone.. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 1995, 206 (1): 89–96. PMID 7818555. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1995.1013.
- Velasco G, Ferrando AA, Puente XS, et al. Human cathepsin O. Molecular cloning from a breast carcinoma, production of the active enzyme in Escherichia coli, and expression analysis in human tissues.. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1994, 269 (43): 27136–42. PMID 7929457. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)47135-9
 .
. - Li YP, Alexander M, Wucherpfennig AL, et al. Cloning and complete coding sequence of a novel human cathepsin expressed in giant cells of osteoclastomas.. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 1996, 10 (8): 1197–202. PMID 8585423. S2CID 41832979. doi:10.1002/jbmr.5650100809.
- Bossard MJ, Tomaszek TA, Thompson SK, et al. Proteolytic activity of human osteoclast cathepsin K. Expression, purification, activation, and substrate identification.. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996, 271 (21): 12517–24. PMID 8647860. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.21.12517
 .
. - Gelb BD, Shi GP, Chapman HA, Desnick RJ. Pycnodysostosis, a lysosomal disease caused by cathepsin K deficiency.. Science. 1996, 273 (5279): 1236–8. Bibcode:1996Sci...273.1236G. PMID 8703060. S2CID 7188076. doi:10.1126/science.273.5279.1236.
- Johnson MR, Polymeropoulos MH, Vos HL, et al. A nonsense mutation in the cathepsin K gene observed in a family with pycnodysostosis.. Genome Research. 1997, 6 (11): 1050–5. PMID 8938428. doi:10.1101/gr.6.11.1050
 .
. - Littlewood-Evans A, Kokubo T, Ishibashi O, et al. Localization of cathepsin K in human osteoclasts by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry.. Bone. 1997, 20 (2): 81–6. PMID 9028530. doi:10.1016/S8756-3282(96)00351-1.
- McGrath ME, Klaus JL, Barnes MG, Brömme D. Crystal structure of human cathepsin K complexed with a potent inhibitor.. Nature Structural Biology. 1997, 4 (2): 105–9. PMID 9033587. S2CID 22175354. doi:10.1038/nsb0297-105.
- Rood JA, Van Horn S, Drake FH, et al. Genomic organization and chromosome localization of the human cathepsin K gene (CTSK).. Genomics. 1997, 41 (2): 169–76. PMID 9143491. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4614.
- Gelb BD, Shi GP, Heller M, et al. Structure and chromosomal assignment of the human cathepsin K gene.. Genomics. 1997, 41 (2): 258–62. PMID 9143502. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4631.
- Gomes RA, Juliano L, Chagas JR, Hial V. Characterization of kininogenase activity of an acidic proteinase isolated from human kidney.. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 1997, 75 (6): 757–61. PMID 9276160. doi:10.1139/cjpp-75-6-757.
- Thompson SK, Halbert SM, Bossard MJ, et al. Design of potent and selective human cathepsin K inhibitors that span the active site.. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 1998, 94 (26): 14249–54. PMC 24926
 . PMID 9405598. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.26.14249
. PMID 9405598. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.26.14249  .
. - Gelb BD, Willner JP, Dunn TM, et al. Paternal uniparental disomy for chromosome 1 revealed by molecular analysis of a patient with pycnodysostosis.. The American Journal of Human Genetics. 1998, 62 (4): 848–54. PMC 1377035
 . PMID 9529353. doi:10.1086/301795.
. PMID 9529353. doi:10.1086/301795.
图集
[编辑]外部链接
[编辑]- The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: C01.036
- 医学主题词表(MeSH):Cathepsin+K