异炔诺酮
外观
 | |
 | |
| 臨床資料 | |
|---|---|
| 商品名 | Enovid (with mestranol), others |
| 其他名稱 | Norethynodrel; Noretinodrel Norethinodrel; NYD; SC-4642; NSC-15432; 5(10)-Norethisterone; 17α-Ethinyl-19-nor-5(10)-testosterone; 17α-Ethynyl-δ5(10)-19-nortestosterone; 17α-Ethynylestr-5(10)-en-17β-ol-3-one; 19-Nor-17α-pregn-5(10)-en-20-yn-17β-ol-3-one |
| 给药途径 | 口服给药 |
| 藥物類別 | Progestin; Progestogen; Estrogen |
| ATC碼 | |
| 藥物動力學數據 | |
| 血漿蛋白結合率 | Noretynodrel: to albumin and not to SHBG or CBG[1] |
| 药物代谢 | Liver, intestines (hydroxylation, isomerization, conjugation)[1][3] |
| 代謝產物 | • 3α-Hydroxynoretynodrel[2] • 3β-Hydroxynoretynodrel[2] • Norethisterone[2][1][3] • Ethinylestradiol[3][4]• Conjugates[3] |
| 生物半衰期 | Very short (< 30 minutes)[5] |
| 排泄途徑 | Breast milk: 1%[6] |
| 识别信息 | |
| |
| CAS号 | 68-23-5 |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.620 |
| 化学信息 | |
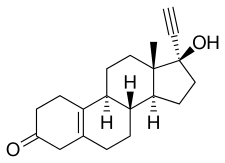
| 化学式 | C20H26O2 |
| 摩尔质量 | 298.419 g/mol |
| 3D模型(JSmol) | |
| |
| |
异炔诺酮(英語:Noretynodrel 或 英語:norethynodrel,商品名:Enovid等)是一种黄体制剂药物,过去被用于口服避孕药以及治疗一些妇科疾病,但现在已不再使用[3][6][7][8]。异炔诺酮和炔诺酮的不同之处在于双键位于5(10)号位而非4(5)号位。
参考文献
[编辑]- ^ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Kuhl H. Pharmacokinetics of oestrogens and progestogens. Maturitas. September 1990, 12 (3): 171–97. PMID 2170822. doi:10.1016/0378-5122(90)90003-O.
- ^ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Jin Y, Duan L, Chen M, Penning TM, Kloosterboer HJ. Metabolism of the synthetic progestogen norethynodrel by human ketosteroid reductases of the aldo-keto reductase superfamily. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 129 (3–5): 139–44. PMC 3303946
 . PMID 22210085. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.12.002.
. PMID 22210085. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.12.002.
- ^ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Kuhl H. Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration (PDF). Climacteric. 2005,. 8 Suppl 1: 3–63 [2019-06-30]. PMID 16112947. doi:10.1080/13697130500148875. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2016-08-22).
- ^ Kuhl H. Pharmacology of Progestogens (PDF). J Reproduktionsmed Endokrinol. 2011, 8 (1): 157–177 [2019-07-10]. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2016-10-11).
- ^ Hammerstein J. Prodrugs: advantage or disadvantage?. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1990, 163 (6 Pt 2): 2198–203. PMID 2256526.
- ^ 6.0 6.1 Sweetman, Sean C. (编). Sex hormones and their modulators. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference 36th. London: Pharmaceutical Press. 2009: 2120–2121. ISBN 978-0-85369-840-1.
- ^ Jucker. Progress in Drug Research / Fortschritte der Arzneimittelforschung / Progrès des recherches pharmaceutiques. Birkhäuser. 21 December 2013: 85–88 [2019-06-30]. ISBN 978-3-0348-7065-8. (原始内容存档于2021-03-14).
- ^ Lara Marks. Sexual Chemistry: A History of the Contraceptive Pill. Yale University Press. 2010: 74–75. ISBN 978-0-300-16791-7.
