User:陳增澤/沙盒

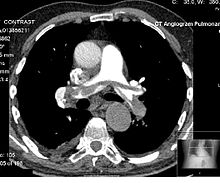
顯影電腦斷層掃瞄是需要使用顯影劑的電腦斷層掃描。 通常,用於電腦斷層掃描的顯影劑是基於碘(Iodinated contrast)的類型。這對於凸顯出類似血管之類的結構很有用,否則這些結構將很難從周圍的環境中劃出輪廓。 使用顯影劑還可以幫助醫師取得該組織的功能訊息[1] 。
對比劑自動跟蹤
[编辑]對比劑自動跟蹤技術(Bolus Tracking)是一種延時掃描技術,直到造影劑流入主動脈時才開始掃描。[2] 它根據血管使用感興趣區域(Region of interest,ROI),在一定的水平上跟蹤對比度的大小,當對比度達到某個水平後再使用電腦斷層掃描儀器進行跟蹤。也因此,影像的獲取速度會跟顯影劑在血管中移動的速度一樣快。 這種方法主要用於產生動脈影像,例如主動脈,肺動脈,腦動脈,頸動脈和肝動脈。
沖淡
[编辑]沖淡(Washout)是指最初在動脈注入的顯影劑,在隨後的靜脈或後期恢復到低密度的狀態。例如肝細胞在動脈時,由於是快速的動脈血,病灶處在動脈相時可以很快的立即顯影,不過顯影劑也很快就被沖淡了。[3] [4]
相位(Phases)
[编辑]有標準化的協定可用於注射顯影劑和獲取影像之間的時間間隔,以視覺化不同器官和其餘組織中對比度增強的狀態。[5] 其主要階段如下:[6]
| 相位 | 注射時間[6] | 追蹤時間[6] | 目的與發現[6] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 非增強電腦斷層掃描(Non-enhanced CT,縮寫:NECT) | - | - |
|
| 肺動脈相(Pulmonary arterial phase) | 6-13 秒[7] | - |
|
| 肺靜脈相(Pulmonary venous phase) | 17-24 秒[7] | - | |
| Early systemic arterial phase | 15-20 秒 | 立即 |
|
| 早期全身動脈期(Late systemicarterial phase) Sometimes also called "arterial phase" or "early venous portal phase" |
35-40 秒 | 15-20 秒 |
|
| Pancreatic phase | 30[9] or 40[10] - 50[10] 秒 | 20-30 秒 |
|
| Hepatic (most accurate) or late portal phase | 70-80 秒 | 50-60 秒 |
|
| Nephrogenic phase | 100 秒 | 80 秒 |
|
| Systemic venous phase | 180 秒 | 160 秒 |
|
| Delayed phase Sometimes called "wash out phase" or "equilibrium phase" |
6[6]-15 秒 | 6[6]-15 秒 |
|
CT血管攝影是在感興趣的血管的位置和corresponding phase階段拍攝的顯影電腦斷層掃瞄,以檢測血管疾病。 例如,腹部主動脈血管造影是在腹部水平的動脈期進行的,例如:可用於檢測主動脈夾層。[11]
劑量
[编辑]
成人
[编辑]下表顯示了正常體重成年人的劑量。 但是,對於有碘顯影劑風險的患者,如過敏反應,顯影劑誘發的腎病,對甲狀腺功能的影響或藥物不良相互作用,可能需要調整甚至停止使用劑量。
| 情況 | 碘濃度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 mg/ml | 350 mg/ml | 370 mg/ml | ||
| 腦部CT | 95ml[12] | 80 ml[12] | 75 ml[12] | |
| 胸部CT | 整體 | 70 - 95 ml[notes 1] | 60 - 80 ml[notes 1] | 55 - 75 ml[notes 1] |
| CT肺血管造影 | 20 ml[notes 2] | 17 ml[notes 2] | 15 ml[notes 2] | |
| 腹部CT | 整體 | 70 ml[12] | 60 ml[12] | 55 ml[12] |
| 肝 | 55 ml[notes 3] | 45 ml[notes 3] | 40-45 ml[notes 3] | |
| CT 電腦斷層血管攝影術 | 25 ml[notes 4] | 20 ml[notes 4] | ||
對於體重不正常的人,應調整劑量,在這種情況下,調整應與人的淨體重(英語:Lean body mass,LBM)成比例。 在肥胖症患者中,布爾公式是常被選擇的方法[13]
男性: 淨體重(LBM) = (0.407 × W) + (0.267 × H) − 19.2
女性: 淨體重(LBM)= (0.252 × W) + (0.473 × H) − 48.3
兒童
[编辑]用於兒童的標準劑量:[14]
| 情況 | 碘濃度 | |
|---|---|---|
| 300 mg/ml | 350 mg/ml | |
| 一般情況 | 2.0 ml/kg | 1.7 ml/kg |
| 腦部、頸部或胸部的CT | 1.5 ml/kg | 1.3 ml/kg |
不利影響
[编辑]碘顯影劑可能會引起過敏反應,顯影劑則可能引起腎臟疾病或甲狀腺功能亢進症。 但是,碘顯影劑沒有絕對會發生的副作用,因此需要謹慎衡量風險及使用它帶來的好處。[15] 通常,其放射劑量可能會增加誘發的癌症的風險。 注射碘顯影劑有時可能導致其外滲(英語:Extravasation (intravenous))[16]。
Notes
[编辑]- ^ 1.0 1.1 1.2 0.3–0.4 gI/kg in a 70kg individual, according to:
- Iezzi, Roberto; Larici, Anna Rita; Franchi, Paola; Marano, Riccardo; Magarelli, Nicola; Posa, Alessandro; Merlino, Biagio; Manfredi, Riccardo; Colosimo, Cesare. Tailoring protocols for chest CT applications: when and how?. Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology. 2017, 23 (6): 420–427. ISSN 1305-3825. PMC 5669541
 . PMID 29097345. doi:10.5152/dir.2017.16615.
. PMID 29097345. doi:10.5152/dir.2017.16615.
- Iezzi, Roberto; Larici, Anna Rita; Franchi, Paola; Marano, Riccardo; Magarelli, Nicola; Posa, Alessandro; Merlino, Biagio; Manfredi, Riccardo; Colosimo, Cesare. Tailoring protocols for chest CT applications: when and how?. Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology. 2017, 23 (6): 420–427. ISSN 1305-3825. PMC 5669541
- ^ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Using dual energy CTA (such as 90/150SnkVp), according to:
- Leroyer, Christophe; Meier, Andreas; Higashigaito, Kai; Martini, Katharina; Wurnig, Moritz; Seifert, Burkhardt; Keller, Dagmar; Frauenfelder, Thomas; Alkadhi, Hatem. Dual Energy CT Pulmonary Angiography with 6g Iodine—A Propensity Score-Matched Study. PLOS ONE. 2016, 11 (12): e0167214. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5132396
 . PMID 27907049. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0167214.
. PMID 27907049. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0167214.
- Leroyer, Christophe; Meier, Andreas; Higashigaito, Kai; Martini, Katharina; Wurnig, Moritz; Seifert, Burkhardt; Keller, Dagmar; Frauenfelder, Thomas; Alkadhi, Hatem. Dual Energy CT Pulmonary Angiography with 6g Iodine—A Propensity Score-Matched Study. PLOS ONE. 2016, 11 (12): e0167214. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5132396
- ^ 3.0 3.1 3.2 The liver generally needs an enhancement of at least 30 HU for proper evaluation according to:
- Multislice CT 3. Springer-Verlag Berlin and Heidelberg GmbH & Co. KG. 2010. ISBN 9783642069680.
- Bae, Kyongtae T. Intravenous Contrast Medium Administration and Scan Timing at CT: Considerations and Approaches. Radiology. 2010, 256 (1): 32–61. ISSN 0033-8419. PMID 20574084. doi:10.1148/radiol.10090908
 .
.
- ^ 4.0 4.1 CT-angiography in a 70kg person, with 100-150 mg I/kg by using 80 kVp, mAs-compensation for constant CNR, fixed injection duration adapted to scan time, automatic bolus tracking and a saline chaser, according to:
- Nyman, Ulf. Contrast Medium-Induced Nephropathy (CIN) Gram-Iodine/GFR Ratio to Predict CIN and Strategies to Reduce Contrast Medium Doses. 2012. doi:10.5772/29992
 .
.
- Nyman, Ulf. Contrast Medium-Induced Nephropathy (CIN) Gram-Iodine/GFR Ratio to Predict CIN and Strategies to Reduce Contrast Medium Doses. 2012. doi:10.5772/29992
References
[编辑]- ^ Webb, W. Richard; Brant, Wiliam E.; Major, Nancy M. Fundamentals of Body CT. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2014: 152. ISBN 9780323263580 (英语).
- ^ 主動脈剝離.
- ^ 螺旋式電腦斷層掃描儀對鑑別肝細胞癌與肝血管瘤的應用.
- ^ Choi, Jin-Young; Lee, Jeong-Min; Sirlin, Claude B. CT and MR Imaging Diagnosis and Staging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Part II. Extracellular Agents, Hepatobiliary Agents, and Ancillary Imaging Features. Radiology. 2014, 273 (1): 30–50. ISSN 0033-8419. PMC 4263770
 . PMID 25247563. doi:10.1148/radiol.14132362.
. PMID 25247563. doi:10.1148/radiol.14132362.
- ^ Bae, Kyongtae T. Intravenous Contrast Medium Administration and Scan Timing at CT: Considerations and Approaches. Radiology. 2010, 256 (1): 32–61. ISSN 0033-8419. PMID 20574084. doi:10.1148/radiol.10090908
 .
.
- ^ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Robin Smithuis. CT contrast injection and protocols. Radiology Assistant. [2017-12-13].
- ^ 7.0 7.1 Page 584 in: Ákos Jobbágy. 5th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering 14 - 18 September 2011, Budapest, Hungary. Volume 37 of IFMBE Proceedings. Springer Science & Business Media. 2012. ISBN 9783642235085.
- ^ Pavan Nandra. Introducing the use of Flash CTPA; how does it compare to standard CTPA?. Postering. 2018.
- ^ Raman SP, Fishman EK. Advances in CT Imaging of GI Malignancies.. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2012, 5 (3 Suppl 1): S4–9. PMC 3413036
 . PMID 22876336.
. PMID 22876336.
- ^ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Otto van Delden and Robin Smithuis. Pancreas - Carcinoma. Radiology Assistant. [2017-12-15].
- ^ Page 424 in: Stuart E. Mirvis, Jorge A Soto, Kathirkamanathan Shanmuganathan, Joseph Yu, Wayne S Kubal. Problem Solving in Emergency Radiology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2014. ISBN 9781455758395.
- ^ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 New Zealand Datasheet (PDF). New Zealand Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority. [2018-10-16].
- ^ Caruso, Damiano; De Santis, Domenico; Rivosecchi, Flaminia; Zerunian, Marta; Panvini, Nicola; Montesano, Marta; Biondi, Tommaso; Bellini, Davide; Rengo, Marco; Laghi, Andrea. Lean Body Weight-Tailored Iodinated Contrast Injection in Obese Patient: Boer versus James Formula. BioMed Research International. 2018, 2018: 1–6. ISSN 2314-6133. PMC 6110034
 . PMID 30186869. doi:10.1155/2018/8521893.
. PMID 30186869. doi:10.1155/2018/8521893.
- ^ Nievelstein, Rutger A. J.; van Dam, Ingrid M.; van der Molen, Aart J. Multidetector CT in children: current concepts and dose reduction strategies. Pediatric Radiology. 2010, 40 (8): 1324–1344. ISSN 0301-0449. PMC 2895901
 . PMID 20535463. doi:10.1007/s00247-010-1714-7.
. PMID 20535463. doi:10.1007/s00247-010-1714-7.
- ^ Stacy Goergen. Iodine-containing contrast medium. InsideRadiology - The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists. [2019-02-22]. Page last modified on 26/7/2017
- ^ Hrycyk J, Heverhagen JT, Böhm I. What you should know about prophylaxis and treatment of radiographic and magnetic resonance contrast medium extravasation. Acta Radiol. 2019, 60 (4): 496–500. PMID 29896979. doi:10.1177/0284185118782000.
External links
[编辑]- CT with IV contrast in low renal function. Radlines.org.
號角
號角是一種管狀的樂器,形狀往往是彎曲的,在古代,號角是通是用獸角製作而成,而現代的號角通常是由金屬製作而成。
號角在古代的軍旅中通常被用作發號施令或提振士氣的樂器,使用方式是對號角比較狹窄的一端吹奏,由寬度比較大的另一端發出聲音。
在部分情況,號角的吹孔往往是圓錐的形狀,不像其他銅管樂器呈顯寬度大於長度的扁平狀。
二維多平面重建(英語:2D Multiplanar reconstruction,MPR),是被大量用於分析電腦斷層掃描影像的技術。可用於在正交平面(冠狀,矢狀,軸向或傾斜,選擇任意平面)中重建影像,這可以幫助醫療人員建立解剖結構在多個平面的視覺效果。
在醫學影像中,要進行3D重建,最容易的方式是將所有的橫切面推疊起來,而支援MPR的軟體可以從各種不同的角度切割物體(像是縱切面)。
例子
[编辑]以牙科為例,當牙醫使用使用Cone Beam CT(錐狀斷層掃描(Cone-beam Computerized Tomography))等掃描技術,於電腦中建立3D影像後,從而可以利用立體渲染技術看出完整的口腔結構,而使用二維多平面重建 (MPR)技術可在任意平面及斜面中重建影像,這可以幫助牙醫師觀察牙齒在各個角度的解剖結構,而這種效益是僅使用一般影像顯示技術所無法實作的。
支援MPR的軟體
[编辑]
| 開發者 | Autodesk |
|---|---|
| 首次发布 | 2009年2月 |
| 当前版本 | 2.2(2016年9月21日[1]) |
| 操作系统 | Windows 7 OS X 10.7 or later iOS |
| 类型 | 三维繪圖軟體 |
| 许可协议 | 免費軟體 |
| 网站 | www |
Autodesk 123D是由Autodesk開發的免費3D建模工具,除了基本的繪圖和建模功能外,亦包含堆疊、排列、切割等進階功能。
2017年,Autodesk表示不會再更新Autodesk 123D,除了Autodesk 123D Circuits以外,所有的套件皆以停產,並由Tinkercad,Fusion 360和ReMake取代。
Autodesk 123D的套件
[编辑]Autodesk 123D包含以下套件:
- Catch: 從相機拍攝的不同角度的多張照片中建立3D模型。
- Sculpt+:可雕塑3D模型。
- Make: 可將3D模型轉換成多張2D的切片影像。
- Design: 建立簡易的3D模型。
- Creature: 可以在iPad上建立Creature。
- Circuits: 可模擬麵包板與電路設計。
- Tinkercad: 建立3D列印的工具。
- MeshMixer: 處理多邊形的工具。
暫存頁面(個人用):
羅素的茶壺
循環論證
特例假設
神的存在性
燃素說
科拉超深鑽孔
戴森球
恆星
月球空心說
地球空洞說
大霹靂
偽科學
我們現在不知道,將來也不知道
泛神論
量子纏結
觀測者效應
宇宙
宇宙的終極命運
大撕裂
大擠壓
熱寂
重力奇異點
黑洞資訊悖論
紅移
事件視界
事件視界望遠鏡
黑洞
時間
奧伯斯佯謬
人擇原理
地球殊異假說平庸原理
費米悖論
超常現象
一次打擊
意外絞刑悖論
動畫物理學
LATEX
自由意志
生命的意義
智能设计
恐怖谷理论
技术奇异点
巴納姆效應
喀爾文主義預定論
聖誕節休戰
決定論
※藍光濾波※討論貢獻 2021年4月25日 (日) 10:56 (UTC)
- ^ Autodesk 123D Design. Autodesk 123D Design. Autodesk, Inc. [March 27, 2017].
