氟化铜
外观
| 氟化铜 | |
|---|---|

| |
| |

| |
| |
| IUPAC名 Copper difluoride | |
| 别名 | 氟化铜(II) |
| 识别 | |
| CAS号 | 7789-19-7 13454-88-1((dihydrate)) |
| PubChem | 82236 |
| ChemSpider | 74214 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
|
| InChIKey | GWFAVIIMQDUCRA-NUQVWONBAF |
| 性质 | |
| 化学式 | CuF2 |
| 摩尔质量 | 101.543 g·mol⁻¹ |
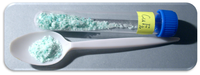
| 外观 | 白色晶体粉末 水合物为蓝色单斜结晶 |
| 密度 | 4.2 g/cm³ (固) |
| 熔点 | 836 °C (1109 ± 5 K) |
| 沸点 | 1676 °C |
| 溶解性(其他溶剂) | 能溶于醇和酸类,微溶于水,溶于丙酮和氨水[1] |
| 相关物质 | |
| 其他阴离子 | 溴化铜 氯化铜 |
| 其他阳离子 | 二氟化银 氟化钴 氟化亚铜 |
| 若非注明,所有数据均出自标准状态(25 ℃,100 kPa)下。 | |
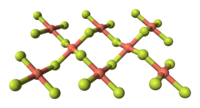
氟化铜、氟化铜(II),是化学式为CuF2的无机化合物。它是白色潮解晶体,为金红石结构,与其他通式为MF2的氟化物类似。
用途
[编辑]氧气存在下,芳香烃与氟化铜在450 °C以上反应可用于制取氟代芳烃,比桑德迈尔反应简单的多,但只适用于对热稳定的化合物。[2]
化学性质
[编辑]- Cu + F2 → CuF2
950 °C以上熔融态失氟:
- 2CuF2 → 2CuF + F2
- 2CuF → CuF2 + Cu
氟化铜可与氟离子(F−)配合生成CuF3−、CuF42−和CuF64−。
参考资料
[编辑]- ^ 《元素单质化学反应手册》P768
- ^ M. A. Subramanian, L. E. Manzer. A "Greener" Synthetic Route for Fluoroaromatics via Copper (II) Fluoride. Science. 2002, 297: 1665. doi:10.1126/science.1076397.
- C. Billy, H. M. Haendler. The Crystal Structure of Copper(II) Fluoride. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1957, 79: 1049–51. doi:10.1021/ja01562a011.
- P. C. de Mello, M. Hehenberg, S. Larson, M. Zerner. Studies of the electronic structure of copper fluorides and copper chlorides. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1980, 102: 1278–1288. doi:10.1021/ja00524a010.
- H. M. Haendler, L. H. Towle, E. F. Bennett, W. L. Patterson. The Reaction of Fluorine with Copper and Some of its Compounds. Some Properties of Copper(II) Fluoride. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1954, 76: 2178 – 2179. doi:10.1021/ja01637a039.
- T. C. Ehlert, J. S. Wang. Thermochemistry of the copper fluorides. Journal of Physical Chemistry. 1977, 81: 2069 – 2073. doi:10.1021/j100537a005.

