劳伦氏壶腹:修订间差异
删除的内容 添加的内容
无编辑摘要 |
无编辑摘要 |
||
| 第6行: | 第6行: | ||
[[File:Lorenzini pores on snout of tiger shark.jpg|300px|right|thumb|[[鼬鯊]]壶腹的開口]] |
[[File:Lorenzini pores on snout of tiger shark.jpg|300px|right|thumb|[[鼬鯊]]壶腹的開口]] |
||
這些感覺器官讓魚類可以感知水中的電場。每個壶腹都有許多充滿糊狀物質的細管,透過[[体侧线]]在皮膚上有開口,另一端則會連結到一個充滿糊狀物質的囊中。壶腹會成群的分佈在體內,每一群會連接到不同部位的皮膚,不過會維持左右[[對稱]]。壶腹管的長度隨動物而不同,不過同一物種大致會有相同的特性。壶腹在皮膚表面的開孔會是明顯可見的黑點。壶腹讓魚類可以感知[[電場]]、[[磁場]]及溫度梯度等。 |
這些感覺器官讓魚類可以感知水中的電場。每個壶腹都有許多充滿糊狀物質的細管,透過[[体侧线]]在皮膚上有開口,另一端則會連結到一個充滿糊狀物質的囊中。壶腹會成群的分佈在體內,每一群會連接到不同部位的皮膚,不過會維持左右[[對稱]]。壶腹管的長度隨動物而不同,不過同一物種大致會有相同的特性。壶腹在皮膚表面的開孔會是明顯可見的黑點。壶腹讓魚類可以感知[[電場]]、[[磁場]]及溫度梯度等。 |
||
== 歷史 == |
|||
[[马尔切洛·马尔皮吉]]曾經描述過劳伦氏壶腹,後來具體的敘述是在1679年由義大利外科醫師及魚類學家{{link-en|斯特凡諾·勞倫齊尼|Stefano Lorenzini}}提出,不過還不知道其功能<ref name="Baranes Fishelson 1999">{{cite journal |last1=Baranes |first1=Avi |last2=Fishelson |first2=Lev |title=Distribution, morphology, and cytology of ampullae of Lorenzini in the Oman shark, Iago omanensis (Triakidae), from the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea |journal=The Anatomical Record |date=6 January 1999 |volume=251 |issue=251: 417–430 |pages=417–430 |doi=10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(199808)251:4<417::AID-AR1>3.0.CO;2-P |pmid=9713980 |s2cid=46064651 |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(199808)251:4%3C417::AID-AR1%3E3.0.CO;2-P |access-date=21 March 2022}}</ref>。20世紀初的[[电生理学]]實驗推測劳伦氏壶腹可以感測溫度、力學的壓力,也可能可以感測鹽度。1960年時才確認劳伦氏壶腹是可以感測[[電場]]的特殊感覺器官<ref name="Murray_1960">{{cite journal |vauthors=Murray RW |title=Electrical sensitivity of the ampullae of Lorenzini |journal=Nature |volume=187 |issue=4741 |pages=957 |date=September 1960 |pmid=13727039 |doi=10.1038/187957a0 |bibcode=1960Natur.187..957M |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref name="Murray_1962">{{cite journal |vauthors=Murray RW |title=The response of the ampullae of Lorenzini of elasmobranchs to electrical stimulation |journal=The Journal of Experimental Biology |volume=39 |pages=119–28 |date=March 1962 |pmid=14477490 |doi=10.1242/jeb.39.1.119 }}</ref>。最早有關{{le|鈣活化鉀離子通道|calcium-activated potassium channel}}的敘述中,有些就是以[[鳐科]]劳伦氏壶腹的研究為基礎的<ref name="Fields_2007b">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fields RD |title=The shark's electric sense. |journal=[[Scientific American]] |date=August 2007 |volume=297 |issue=2 |pages=74–81 |doi=10.1038/scientificamerican0807-74 |jstor=26069417 |pmid=17894175 |bibcode=2007SciAm.297b..74F }}</ref>。 |
|||
==參考資料== |
==參考資料== |
||
| 第17行: | 第20行: | ||
{{Ethology}} |
{{Ethology}} |
||
{{魚類多樣性}} |
{{魚類多樣性}} |
||
{{生物學小作品}} |
|||
[[Category:魚類解剖學]] |
[[Category:魚類解剖學]] |
||
[[Category:感覺器官]] |
[[Category:感覺器官]] |
||
2023年11月20日 (一) 15:52的版本
| 此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 |
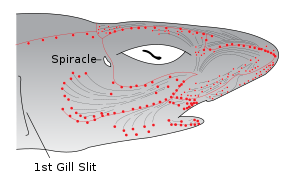

劳伦氏壶腹(ampullae of Lorenzini)是一種稱為電感受器的特殊器官,是內部填充糊狀物質的空隙。軟骨魚綱(鲨鱼、鳐总目、银鲛目)魚類體內有劳伦氏壶腹,而在软骨硬鳞附类中也有劳伦氏壶腹,例如蘆鰻[1]及鱘科[2]。在肺鱼亚纲內也曾找到此一器官[1],真骨类有演化出另一種電感受器[2]。劳伦氏壶腹最早是由斯特凡諾·勞倫齊尼在1678年發現。

這些感覺器官讓魚類可以感知水中的電場。每個壶腹都有許多充滿糊狀物質的細管,透過体侧线在皮膚上有開口,另一端則會連結到一個充滿糊狀物質的囊中。壶腹會成群的分佈在體內,每一群會連接到不同部位的皮膚,不過會維持左右對稱。壶腹管的長度隨動物而不同,不過同一物種大致會有相同的特性。壶腹在皮膚表面的開孔會是明顯可見的黑點。壶腹讓魚類可以感知電場、磁場及溫度梯度等。
歷史
马尔切洛·马尔皮吉曾經描述過劳伦氏壶腹,後來具體的敘述是在1679年由義大利外科醫師及魚類學家斯特凡諾·勞倫齊尼提出,不過還不知道其功能[3]。20世紀初的电生理学實驗推測劳伦氏壶腹可以感測溫度、力學的壓力,也可能可以感測鹽度。1960年時才確認劳伦氏壶腹是可以感測電場的特殊感覺器官[4][5]。最早有關鈣活化鉀離子通道的敘述中,有些就是以鳐科劳伦氏壶腹的研究為基礎的[6]。
參考資料
- ^ 1.0 1.1 Roth A, Tscharntke H. Ultrastructure of the ampullary electroreceptors in lungfish and Brachiopterygii. Cell Tissue Res. October 1976, 173 (1): 95–108. PMID 991235. doi:10.1007/bf00219268.
- ^ 2.0 2.1 Gibbs MA, Northcutt RG. Development of the lateral line system in the shovelnose sturgeon. Brain Behav Evol. 2004, 64 (2): 70–84. PMID 15205543. doi:10.1159/000079117.
- ^ Baranes, Avi; Fishelson, Lev. Distribution, morphology, and cytology of ampullae of Lorenzini in the Oman shark, Iago omanensis (Triakidae), from the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. The Anatomical Record. 6 January 1999, 251 (251: 417–430): 417–430 [21 March 2022]. PMID 9713980. S2CID 46064651. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(199808)251:4<417::AID-AR1>3.0.CO;2-P.
- ^ Murray RW. Electrical sensitivity of the ampullae of Lorenzini. Nature. September 1960, 187 (4741): 957. Bibcode:1960Natur.187..957M. PMID 13727039. doi:10.1038/187957a0
 .
.
- ^ Murray RW. The response of the ampullae of Lorenzini of elasmobranchs to electrical stimulation. The Journal of Experimental Biology. March 1962, 39: 119–28. PMID 14477490. doi:10.1242/jeb.39.1.119.
- ^ Fields RD. The shark's electric sense.. Scientific American. August 2007, 297 (2): 74–81. Bibcode:2007SciAm.297b..74F. JSTOR 26069417. PMID 17894175. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0807-74.
相關條目
| |||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

