中间纤维:修订间差异
删除的内容 添加的内容
无编辑摘要 |
无编辑摘要 |
||
| 第58行: | 第58行: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''中间纤维'''(英語:'''Intermediate filaments''','''IF''',又譯'''中間絲''')直径10[[纳米]](nm)左右,介于7 nm的[[肌动蛋白]][[微丝]]和25 nm的[[微管]]之间。<ref name="pmid5664223">{{cite journal | author = Ishikawa H, Bischoff R, Holtzer H | title = Mitosis and intermediate-sized filaments in developing skeletal muscle | journal = J. Cell Biol. | volume = 38 | issue = 3 | pages = 538–55 |date=September 1968 | pmid = 5664223 | pmc = 2108373 | doi = 10.1083/jcb.38.3.538 }}</ref><ref name="pmid17551517">{{cite journal | author = Herrmann H, Bär H, Kreplak L, Strelkov SV, Aebi U | title = Intermediate filaments: from cell architecture to nanomechanics | journal = Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. | volume = 8 | issue = 7 | pages = 562–73 |date=July 2007 | pmid = 17551517 | doi = 10.1038/nrm2197 }}</ref>与后两者不同的是中间纤维是最稳定的[[细胞骨架]]成分,它主要起支撑作用。中间纤维在细胞中围绕着[[细胞核]]分布,成束成网,并扩展到细胞质膜,与质膜相连结。中间纤维没有正负极性。它们是一个相关的蛋白质家族, 分享共同的结构和序列特征。大多数类型的中间纤维是[[细胞质]],但有一种类型[[核纤层蛋白]]是[[细胞核]]。 |
'''中间纤维'''(英語:'''Intermediate filaments''','''IF''',又譯'''中間絲''')直径10[[纳米]](nm)左右,介于7 nm的[[肌动蛋白]][[微丝]]和25 nm的[[微管]]之间。<ref name="pmid5664223">{{cite journal | author = Ishikawa H, Bischoff R, Holtzer H | title = Mitosis and intermediate-sized filaments in developing skeletal muscle | journal = J. Cell Biol. | volume = 38 | issue = 3 | pages = 538–55 |date=September 1968 | pmid = 5664223 | pmc = 2108373 | doi = 10.1083/jcb.38.3.538 }}</ref><ref name="pmid17551517">{{cite journal | author = Herrmann H, Bär H, Kreplak L, Strelkov SV, Aebi U | title = Intermediate filaments: from cell architecture to nanomechanics | journal = Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. | volume = 8 | issue = 7 | pages = 562–73 |date=July 2007 | pmid = 17551517 | doi = 10.1038/nrm2197 }}</ref>与后两者不同的是中间纤维是最稳定的[[细胞骨架]]成分,它主要起支撑作用。中间纤维在细胞中围绕着[[细胞核]]分布,成束成网,并扩展到细胞质膜,与质膜相连结。中间纤维没有正负极性。它们是一个相关的蛋白质家族, 分享共同的结构和序列特征。大多数类型的中间纤维是[[细胞质]],但有一种类型[[核纤层蛋白]]是[[细胞核]]。 |
||
== 生物力学特性 == |
|||
中间纤维(IF)是可以拉伸其初始长度数倍的,可变形的蛋白质。<ref>{{cite journal | author = Herrmann H, Bär H, Kreplak L, Strelkov SV, Aebi U | title = Intermediate filaments: from cell architecture to nanomechanics | journal = Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. | volume = 8 | issue = 7 | pages = 562–73 |date=July 2007 | pmid = 17551517 | doi = 10.1038/nrm2197 }}{{cite journal | author = Qin Z, Kreplak L, Buehler MJ | title = Hierarchical structure controls nanomechanical properties of vimentin intermediate filaments | journal = PLoS ONE | volume = 4 | issue = 10 | pages = e7294 | year = 2009 | pmid = 19806221 | pmc = 2752800 | doi = 10.1371/journal.pone.0007294 }}{{cite journal | author = Kreplak L, Fudge D | title = Biomechanical properties of intermediate filaments: from tissues to single filaments and back | journal = BioEssays | volume = 29 | issue = 1 | pages = 26–35 |date=January 2007 | pmid = 17187357 | doi = 10.1002/bies.20514 }}{{cite journal | author = Qin Z, Buehler MJ, Kreplak L | title = A multi-scale approach to understand the mechanobiology of intermediate filaments | journal = J Biomech | volume = 43 | issue = 1 | pages = 15–22 |date=January 2010 | pmid = 19811783 | doi = 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.09.004 }}{{cite journal | author = Qin Z, Kreplak L, Buehler MJ | title = Nanomechanical properties of vimentin intermediate filament dimers | journal = Nanotechnology | volume = 20 | issue = 42 | pages = 425101 |date=October 2009 | pmid = 19779230 | doi = 10.1088/0957-4484/20/42/425101 }}</ref> |
|||
== 种类 == |
== 种类 == |
||
2014年10月14日 (二) 06:22的版本

| Intermediate filament tail domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 structure of lamin a/c globular domain | |||||||||
| 鑑定 | |||||||||
| 標誌 | IF_tail | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00932(旧版) | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001322 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00198 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1ivt / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Intermediate filament protein | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 human vimentin coil 2b fragment (cys2) | |||||||||
| 鑑定 | |||||||||
| 標誌 | Filament | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00038(旧版) | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR016044 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00198 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1gk7 / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Intermediate filament head (DNA binding) region | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鑑定 | |||||||||
| 標誌 | Filament_head | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF04732(旧版) | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR006821 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1gk7 / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
中间纤维(英語:Intermediate filaments,IF,又譯中間絲)直径10纳米(nm)左右,介于7 nm的肌动蛋白微丝和25 nm的微管之间。[1][2]与后两者不同的是中间纤维是最稳定的细胞骨架成分,它主要起支撑作用。中间纤维在细胞中围绕着细胞核分布,成束成网,并扩展到细胞质膜,与质膜相连结。中间纤维没有正负极性。它们是一个相关的蛋白质家族, 分享共同的结构和序列特征。大多数类型的中间纤维是细胞质,但有一种类型核纤层蛋白是细胞核。
生物力学特性
中间纤维(IF)是可以拉伸其初始长度数倍的,可变形的蛋白质。[3]
种类
大约有70个不同的基因编码的各种中间纤维蛋白。但是,不同种类的中间纤维的共同的基本特征:一般情况下,在完全组装后,它们都是9-11纳米之间的测量直径的聚合物。
基于在氨基酸序列相似性和蛋白质结构的相似性,中间纤维被细分成6种类型。
I类和II类 - 酸性和碱性角蛋白
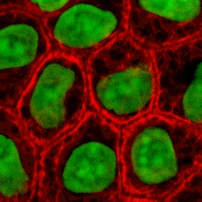
角蛋白是中间纤维中的一类,分子量约40~70KDa,出现在表皮细胞中,在人类上皮细胞中有20多种不同的角蛋白,分为α和β两类。角蛋白赋予细胞体一定的刚性。癌细胞需要对角蛋白进行重新分布,以使自身变得柔韧,可以通过基底膜或血管壁上的细小孔洞。
参考文献
- ^ Ishikawa H, Bischoff R, Holtzer H. Mitosis and intermediate-sized filaments in developing skeletal muscle. J. Cell Biol. September 1968, 38 (3): 538–55. PMC 2108373
 . PMID 5664223. doi:10.1083/jcb.38.3.538.
. PMID 5664223. doi:10.1083/jcb.38.3.538.
- ^ Herrmann H, Bär H, Kreplak L, Strelkov SV, Aebi U. Intermediate filaments: from cell architecture to nanomechanics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. July 2007, 8 (7): 562–73. PMID 17551517. doi:10.1038/nrm2197.
- ^ Herrmann H, Bär H, Kreplak L, Strelkov SV, Aebi U. Intermediate filaments: from cell architecture to nanomechanics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. July 2007, 8 (7): 562–73. PMID 17551517. doi:10.1038/nrm2197.Qin Z, Kreplak L, Buehler MJ. Hierarchical structure controls nanomechanical properties of vimentin intermediate filaments. PLoS ONE. 2009, 4 (10): e7294. PMC 2752800
 . PMID 19806221. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007294.Kreplak L, Fudge D. Biomechanical properties of intermediate filaments: from tissues to single filaments and back. BioEssays. January 2007, 29 (1): 26–35. PMID 17187357. doi:10.1002/bies.20514.Qin Z, Buehler MJ, Kreplak L. A multi-scale approach to understand the mechanobiology of intermediate filaments. J Biomech. January 2010, 43 (1): 15–22. PMID 19811783. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.09.004.Qin Z, Kreplak L, Buehler MJ. Nanomechanical properties of vimentin intermediate filament dimers. Nanotechnology. October 2009, 20 (42): 425101. PMID 19779230. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/20/42/425101.
. PMID 19806221. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007294.Kreplak L, Fudge D. Biomechanical properties of intermediate filaments: from tissues to single filaments and back. BioEssays. January 2007, 29 (1): 26–35. PMID 17187357. doi:10.1002/bies.20514.Qin Z, Buehler MJ, Kreplak L. A multi-scale approach to understand the mechanobiology of intermediate filaments. J Biomech. January 2010, 43 (1): 15–22. PMID 19811783. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.09.004.Qin Z, Kreplak L, Buehler MJ. Nanomechanical properties of vimentin intermediate filament dimers. Nanotechnology. October 2009, 20 (42): 425101. PMID 19779230. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/20/42/425101.
延伸阅读
- Herrmann H, Harris JR (编). Intermediate filaments. Springer. 1998. ISBN 978-0-306-45854-5.
- Omary MB, Coulombe PA (编). Intermediate filament cytoskeleton. Gulf Professional Publishing. 2004. ISBN 978-0-12-564173-9.
- Paramio JM (编). Intermediate filaments. Springer. 2006. ISBN 978-0-387-33780-7.
外部链接
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 这是一篇分子生物学小作品。你可以通过编辑或修订扩充其内容。 |
