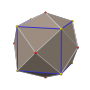
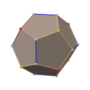
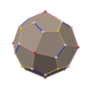
五角化十二面体
 (按这里观看旋转模型) | ||||
| 类别 | 卡塔兰立体 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
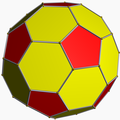
| 对偶多面体 | 截角二十面体 | |||
| 识别 | ||||
| 鲍尔斯缩写 | pakid | |||
| 数学表示法 | ||||
| 考克斯特符号 | ||||
| 康威表示法 | kD | |||
| 性质 | ||||
| 面 | 60 | |||
| 边 | 90 | |||
| 顶点 | 32 | |||
| 欧拉特征数 | F=60, E=90, V=32 (χ=2) | |||
| 二面角 | 153°43′6.79342″ arccos(−80 + 9√5/109) | |||
| 组成与布局 | ||||
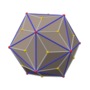
| 面的种类 | 等腰三角形 | |||
| 顶点的种类 | 20个6阶顶点 12个阶5顶点 20{6}+12{5} | |||
| 对称性 | ||||
| 对称群 | Ih, H3, [5,3], (*532) | |||
| 旋转对称群 | I, [5,3]+, (532) | |||
| 图像 | ||||
| ||||
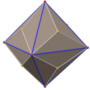
在几何学中,五角化十二面体(Pentakis dodecahedron)是一种六十面体[1],指经过五角化变换的正十二面体[2],换句话说,五角化十二面体是将正十二面体的每个正五边形面替换为五角锥后所形成的立体。当五角锥的锥高恰好使得所形成之立体的所有二面角等角时,则该几何形状是一种卡塔兰立体[3],为截角二十面体的对偶多面体。一般五角化二十面体一词用来称呼卡塔兰立体的版本,即凸多面体的版本,而更高的锥高会使得其成为非凸多面体,例如小星形十二面体[4]。
性质
[编辑]五角化十二面体由60个面、90条边和32个顶点组成[5],其中60个面皆为全等的等腰三角形组成;在其32个顶点中,其中20个顶点是6个面的公共顶点、12个顶点是5个面的公共顶点[6][7]。由于其具有32个顶点,因此对偶多面体是一个三十二面体,为截角二十面体[8]。五角化十二面体可透过在正十二面体的每个面上叠上锥体构成[9],当其锥高恰好使得所形成之立体的所有二面角等角时,则该几何形状是一种卡塔兰立体[3],在这个情况下,其对应的对偶多面体为一个半正三十二面体。
若将五角化十二面体,五角化变换的原像——正十二面体视为三维类五边形形[10],则五角化十二面体可以视为五边形五边各加一个等腰三角形拼成的正十边形在立体几何中的推广。
构造
[编辑]五角化十二面体可由正十二面体经过五角化变换来构造。五角化十二面体是将正十二面体的每个正五边形面替换为五角锥后所形成的立体[2]。根据锥高的不同,会使地所构成的立体有不同性质。要确保所构成的立体为严格凸多面体(即没有面两两共面的情况)其加入角锥的锥高不能超过[3]:
其中,为原像多面体的边长。
若锥高等于时,所形成的立体将会出现三角形两两共面的情况,若将每个两两共面的三角形是为菱形[9]:167,则所构成的立体为菱形三十面体。[3]更高的锥高将导致所形成的立体变为非凸多面体[9]:167,例如小星形十二面体为加入的锥高为时的情况[4]。
要成为塔卡兰立体,五角化十二面体在五角化的过程必须确保所加入的角锥后的结果所有二面角相等,要达成这个目标所要加入的角锥锥高须为:[3]
面的组成
[编辑]作为塔卡兰立体的五角化十二面体,其组成的面为等腰三角形,若腰长为1,则其底边长为[11],对应的底角约为55度41.5分[9]
对应的顶角约为68度37分[9]
应用
[编辑]在化学中
[编辑]部分分子的形状是五角化十二面体,例如Au20Si12[12]。
巴克明斯特富勒烯(C60)分子模型中会形成类似五角化十二面体的外型,其中五角化十二面体的每个面对应著一个碳原子,类似的现象也会出现在石狮子雕塑中的球状物中[13]。等效地,截角二十面体是富勒烯分子模型对应的多面体,每个顶点代表一个碳原子。[14]
在生物学中
[编辑]部分病毒的外壳模型为五角化十二面体,如腺相关病毒,其包含了60个二十面体对称的衣壳蛋白[15],结合起来构成了五角十二面体的60个对称面。[16]
文化引用
[编辑]华特迪士尼世界度假区未来世界的太空船地球号结构是五角化十二面体的细分结果[17]。
变体
[编辑]
当每面叠上的五角锥的高不能使是整个立体的二面角皆相等时,就会有如下情况:
| 图像 | 名称 | 加入锥体的方式 | 锥高 |
|---|---|---|---|

|
复合大三角六边形二十面体凹五角锥十二面体 | 加入倒五角锥并从另外一侧穿出 | |

|
凹五角锥十二面体 | 加入倒五角锥 | |

|
正十二面体 | 原始形状 | 0 |

|
五角化十二面体 | 加入到能使所有二面角等角的高度 | 0.251[3]
|

|
菱形三十面体 | 加入到面两两共面的高度 | 0.425[3]
|

|
小星形十二面体 | 1.37638 | |

|
大五角化十二面体 |
相关多面体
[编辑]五角化十二面体和三角化二十面体的多角化变换皆可形成菱形三十面体。
参见
[编辑]参考文献
[编辑]- ^ Pascual-Ahuir, JL and Silla, E and Tomasi, J and Bonaccorsi, R. Electrostatic interaction of a solute with a continuum. Improved description of the cavity and of the surface cavity bound charge distribution. Journal of Computational Chemistry (Wiley Online Library). 1987, 8 (6): 778–787.
- ^ 2.0 2.1 Çolak, Zeynep and Gelişgen, Özcan. New metrics for deltoidal hexacontahedron and pentakis dodecahedron. Sakarya Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü Dergisi. 2015, 19 (3): 353–360.
- ^ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Livio Zefiro; Maria Rosa Ardig. Description of the Forms Belonging to the 235 and m35 Icosahedral Point Groups Starting from the Pairs of Dual Polyhedra: Icosahedron-Dodecahedron and Archimedean Polyhedra-Catalan Polyhedra. mi.sanu.ac.rs. [2021-07-22]. (原始内容存档于2021-05-06).
- ^ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Weisstein, Eric W. (编). Small Stellated Dodecahedron. at MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. Wolfram Research, Inc. (英语).
- ^ Rene K. Mueller. Geodesic Pentakis Dodecahedron. simplydifferently.org. 2007 [2021-08-10]. (原始内容存档于2021-08-11).
- ^ Konstantinidis, NP. Discontinuous quantum and classical magnetic response of the pentakis dodecahedron. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.06739. 2021.
- ^ Robert Whittaker. The Pentakis Dodecahedron. polyhedra.mathmos.net. [2021-08-10]. (原始内容存档于2021-08-10).
- ^ De Witte, Erik and Marantis, Leonidas and Tong, Kin-Fai and Brennan, Paul and Griffiths, Hugh. Design and development of a spherical array antenna. 2006 First European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (IEEE). 2006: 1–5.
- ^ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Pearce, P. Structure in Nature Is a Strategy for Design. MIT Press. 1980: 160 [2021-08-10]. ISBN 9780262660457. LCCN 77026866. (原始内容存档于2021-08-10).
- ^ Coxeter, Harold Scott MacDonald, Regular Polytopes, New York: Dover Publications, 1973, ISBN 978-0-486-61480-9
- ^ Pentakis dodecahedron. Fillygons. [2021-08-10]. (原始内容存档于2021-08-10).
- ^ Guo, JJ and Zhao, HY and Wang, J and Ai, LY and Liu, Y. Au20Si12: a hollow catalan pentakis dodecahedron. The Journal of chemical physics (AIP Publishing LLC). 2017, 146 (6): 064310.
- ^ Katz, Eugene A and Jin, Bih-Yaw. Fullerenes, Polyhedra, and Chinese Guardian Lions. The Mathematical Intelligencer (Springer). 2016, 38 (3): 61–68.
- ^ Katz, E. A. Fullerene Thin Films as Photovoltaic Material. Sōga, Tetsuo (编). Nanostructured materials for solar energy conversion. Elsevier. 2006: 374 [2021-08-13]. ISBN 978-0-444-52844-5. (原始内容存档于2021-03-18).
- ^ Sonntag F, Schmidt K, Kleinschmidt JA. A viral assembly factor promotes AAV2 capsid formation in the nucleolus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. June 2010, 107 (22): 10220–5. Bibcode:2010PNAS..10710220S. PMC 2890453
 . PMID 20479244. doi:10.1073/pnas.1001673107.
. PMID 20479244. doi:10.1073/pnas.1001673107.
- ^ Raguram, Aditya and Sasisekharan, V and Sasisekharan, Ram. A chiral pentagonal polyhedral framework for characterizing virus capsid structures. Trends in microbiology (Elsevier). 2017, 25 (6): 438–446.
- ^ Rene K. Mueller. Geodesic Polyhedra. simplydifferently.org. 2007 [2021-08-10]. (原始内容存档于2021-08-11).