血管收縮素
血管收縮素(Angiotensin),亦稱血管緊張素、血管緊縮素、血管張力素,是一種寡肽類激素,是腎素-血管收縮素系統(renin-angiotensin system)的重要組成部分。血管收縮素能引起血管收縮,升高血壓;促進腎上腺皮質釋放醛固酮。它也具有很強的致渴作用。血管收縮素的前體是由肝臟合成的一種血清球蛋白:血管收縮素原。血管收縮素最早於20世紀30年代末由美國印第安納和阿根廷的研究人員分別獨立分離,並被分別命名為Angiotonin和Hypertensin,後來被美國克利夫蘭診所和瑞士巴塞爾的汽巴實驗室(Ciba Laboratories)描述併合成。[1]
前體及種類
[編輯]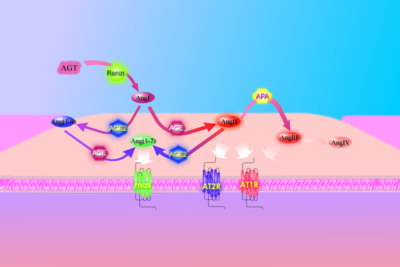
血管收縮素原
[編輯]血管收縮素原是一種主要由肝臟持續合成並釋放入血液循環的α-2球蛋白。它屬於絲胺酸蛋白酶抑制物超家族(serine protease inhibitors,serpin),雖然就目前所知它不能抑制任何酶的活性。皮質激素、雌激素、甲狀腺素和血管收縮素II可增高血漿血管收縮素原含量。
血管收縮素原是腎素的受質。
人血管收縮素原包含452個胺基酸殘基,而其他物種的血管收縮素原大小有所不同。它的N-端12個胺基酸殘基由於關係到其活性而最為重要。
Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe-His-Leu-Val-Ile
血管收縮素Ⅰ
[編輯]Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe-His-Leu
血管收縮素Ⅰ由腎素作用於血管收縮素原形成。腎素能催化血管收縮素原白胺酸(Leu)與纈胺酸(Val)間的肽鍵水解產生十肽血管收縮素I;
血管收縮素Ⅰ基本沒有生物學活性,而是作為血管收縮素Ⅱ的前體存在。
血管收縮素Ⅱ
[編輯]Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe | His-Leu
血管收縮素I經血管收縮素Ⅰ轉化酶剪切C-末端兩個胺基酸殘基而形成血管收縮素Ⅱ。血管收縮素II是一種可通過內分泌、自分泌/旁分泌以及胞內分泌發揮作用的激素。
血管收縮素Ⅱ通過血管收縮素酶降解為血管收縮素Ⅲ,其在循環系統的半衰期約為30秒,而在組織中最長可達15至30分鐘。
血管收縮素Ⅲ
[編輯]Asp | Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe
相比較血管收縮素Ⅱ而言,血管收縮素Ⅲ(七肽)仍具有40%的升壓活性和100%的促醛固酮分泌活性。
血管收縮素Ⅳ
[編輯]Arg | Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe
血管收縮素Ⅳ(六肽)與血管收縮素Ⅲ相似,而活性更低。
血管收縮素-(1-9)
[編輯]Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe-His |-Leu
血管收縮素-(1-7)
[編輯]Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro|-Phe
參考文獻
[編輯]- ^ Basso N, Terragno NA. History about the discovery of the renin-angiotensin system. Hypertension. 2001年12月, 38 (6): 1246–9 [2008-11-26]. PMID 11751697. (原始內容存檔於2012-07-12).
- ^ NCBI HomePage. [2021-05-15]. (原始內容存檔於2018-01-28).
延伸閲讀
[編輯]- de Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright JW, Unger T. International union of pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacological Reviews. September 2000, 52 (3): 415–72. PMID 10977869.
- Brenner & Rector's The Kidney, 7th ed., Saunders, 2004.
- Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 3rd Ed., CV Mosby Company, 1990.
- Review of Medical Physiology, 20th Ed., William F. Ganong, McGraw-Hill, 2001.
- Clinical Physiology of Acid-Base and Electrolyte Disorders, 5th ed., Burton David Rose & Theodore W. Post McGraw-Hill, 2001
- Lees KR, MacFadyen RJ, Doig JK, Reid JL. Role of angiotensin in the extravascular system. Journal of Human Hypertension. August 1993,. 7 Suppl 2: S7–12. PMID 8230088.
- Weir MR, Dzau VJ. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: a specific target for hypertension management. American Journal of Hypertension. December 1999, 12 (12 Pt 3): 205S–213S. PMID 10619573. doi:10.1016/S0895-7061(99)00103-X.
- Berry C, Touyz R, Dominiczak AF, Webb RC, Johns DG. Angiotensin receptors: signaling, vascular pathophysiology, and interactions with ceramide. American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology. December 2001, 281 (6): H2337–65. PMID 11709400. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.2001.281.6.H2337.
- Sernia C. A critical appraisal of the intrinsic pancreatic angiotensin-generating system. Journal of the Pancreas. January 2001, 2 (1): 50–5. PMID 11862023.
- Varagic J, Frohlich ED. Local cardiac renin-angiotensin system: hypertension and cardiac failure. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. November 2002, 34 (11): 1435–42. PMID 12431442. doi:10.1006/jmcc.2002.2075.
- Wolf G. Role of reactive oxygen species in angiotensin II-mediated renal growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 2006, 7 (9–10): 1337–45. PMID 16115039. doi:10.1089/ars.2005.7.1337.
- Cazaubon S, Deshayes F, Couraud PO, Nahmias C. [Endothelin-1, angiotensin II and cancer]. Médecine/Sciences. April 2006, 22 (4): 416–22. PMID 16597412. doi:10.1051/medsci/2006224416.
- Ariza AC, Bobadilla NA, Halhali A. [Endothelin 1 and angiotensin II in preeeclampsia]. Revista de Investigacion Clinica; Organo del Hospital de Enfermedades de la Nutricion. 2007, 59 (1): 48–56. PMID 17569300.
參見
[編輯]外部連結
[編輯]- The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: I04.953 (頁面存檔備份,存於網際網路檔案館)
- 醫學主題詞表(MeSH):Angiotensins
- Human AGT genome location and AGT gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- PDB中UniProt可用的所有結構資訊之概述:P01019 (Angiotensin) 在PDBe-KB。


